Avascular necrosis
| Avascular necrosis | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Osteonecrosis,[1] bone infarction,[2] aseptic necrosis,[1] ischemic bone necrosis[1] | |
 | |
| Head of the femur showing a flap of cartilage due to avascular necrosis (osteochondritis dissecans). Specimen removed during total hip replacement surgery. | |
| Specialty | Orthopedics |
| Symptoms | Joint pain, decreased ability to move[1] |
| Complications | Osteoarthritis[1] |
| Usual onset | Gradual[1] |
| Risk factors | Bone fractures, joint dislocations, alcoholism, high dose steroids[1] |
| Diagnostic method | Medical imaging, biopsy[1] |
| Differential diagnosis | Osteopetrosis, rheumatoid arthritis, Legg–Calvé–Perthes syndrome, sickle cell disease[3] |
| Treatment | Medication, not walking on the affected leg, stretching, surgery[1] |
| Frequency | ~15,000 per year (US)[4] |
Avascular necrosis (AVN), also called osteonecrosis or bone infarction, is death of bone tissue due to interruption of the blood supply.[1] Early on, there may be no symptoms.[1] Gradually joint pain may develop which may limit the ability to move.[1] Complications may include collapse of the bone or nearby joint surface.[1]
The most common risk factors are excess alcohol and use of high-dose steroids.[5] Other risks factors include sickle cell disease, lupus, deep sea diving, [5] bone fractures and joint dislocations.[1] The condition may also occur without any clear reason.[1] The most commonly affected bone is the femur.[1] Other relatively common sites include the upper arm bone, knee, shoulder, and ankle.[1] Diagnosis is typically by medical imaging such as X-ray, CT scan, or MRI.[1] Rarely biopsy may be used.[1]
Treatments may include medication, not walking on the affected leg, stretching, and surgery.[1] Most of the time surgery is eventually required and may include core decompression, osteotomy, bone grafts, or joint replacement.[1] About 15,000 cases occur per year in the United States.[4] People 30 to 50 years old are most commonly affected.[3] Males are more commonly affected than females.[4]
Signs and symptoms
In many cases, there is pain and discomfort in a joint which increases over time. While it can affect any bone, about half of cases show multiple sites of damage.[6]
Avascular necrosis most commonly affects the ends of long bones such as the femur (the bone extending from the knee joint to the hip joint). Other common sites include the humerus (the bone of the upper arm),[7][8] knees,[7] shoulders,[8] ankles and the jaw.[7]
Causes
The main risk factors are bone fractures, joint dislocations, alcoholism, and the use of high-dose steroids.[1] Other risk factors include radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and organ transplantation.[1] Osteonecrosis is also associated with cancer, lupus, sickle cell disease, HIV infection, Gaucher's disease, and Caisson disease.[1] The condition may also occur without any clear reason.[1]
Bisphosphonates are associated with osteonecrosis of the mandible[9]. Prolonged, repeated exposure to high pressures (as experienced by commercial and military divers) has been linked to AVN, though the relationship is not well understood.[10]
Pathophysiology
The hematopoietic cells are most sensitive to low oxygen and are the first to die after reduction or removal of the blood supply, usually within 12 hours.[2] Experimental evidence suggests that bone cells (osteocytes, osteoclasts, osteoblasts etc.) die within 12–48 hours, and that bone marrow fat cells die within 5 days.[2]
Upon reperfusion, repair of bone occurs in 2 phases. First, there is angiogenesis and movement of undifferentiated mesenchymal cells from adjacent living bone tissue grow into the dead marrow spaces, as well as entry of macrophages that degrade dead cellular and fat debris.[2] Second, there is cellular differentiation of mesenchymal cells into osteoblasts or fibroblasts.[2] Under favorable conditions, the remaining inorganic mineral volume forms a framework for establishment of new, fully functional bone tissue.[2]
Diagnosis

In the early stages, bone scintigraphy and MRI are the preferred diagnostic tools.[11]
X-ray images of avascular necrosis in the early stages usually appear normal. In later stages it appears relatively more radio-opaque due to the nearby living bone becoming resorbed secondary to reactive hyperemia.[2] The necrotic bone itself does not show increased radiographic opacity, as dead bone cannot undergo bone resorption which is carried out by living osteoclasts.[2]
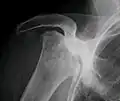 Radiography of total avascular necrosis of right humeral head. Woman of 81 years with diabetes of long evolution.
Radiography of total avascular necrosis of right humeral head. Woman of 81 years with diabetes of long evolution.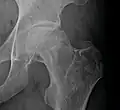 Radiography of avascular necrosis of left femoral head. Man of 45 years with AIDS.
Radiography of avascular necrosis of left femoral head. Man of 45 years with AIDS.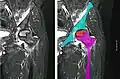 Nuclear magnetic resonance of avascular necrosis of left femoral head. Man of 45 years with AIDS.
Nuclear magnetic resonance of avascular necrosis of left femoral head. Man of 45 years with AIDS.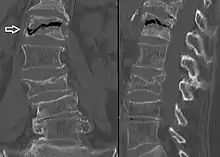 The intravertebral vacuum cleft sign (white arrow) is a sign of avascular necrosis. (Avascular necrosis of a vertebral body after a vertebral compression fracture is called Kümmel's disease.[12])
The intravertebral vacuum cleft sign (white arrow) is a sign of avascular necrosis. (Avascular necrosis of a vertebral body after a vertebral compression fracture is called Kümmel's disease.[12])
Types
When AVN affects the scaphoid bone, it is known as Preiser disease[13]. Another named form of AVN is Köhler disease, which affects the navicular bone of the foot, primarily in children.[14]
Treatment
A variety of methods may be used to treat[6] the most common being the total hip replacement (THR). However, THRs have a number of downsides including long recovery times and short life spans (of the hip joints). THRs are an effective means of treatment in the older population; however, in younger people they may wear out before the end of a person's life.[15]
Other techniques such as metal on metal resurfacing may not be suitable in all cases of avascular necrosis; its suitability depends on how much damage has occurred to the femoral head.[16] Bisphosphonates which reduce the rate of bone breakdown may prevent collapse (specifically of the hip) due to AVN.[17]
Core decompression
Other treatments include core decompression, where internal bone pressure is relieved by drilling a hole into the bone, and a living bone chip and an electrical device to stimulate new vascular growth are implanted; and the free vascular fibular graft (FVFG), in which a portion of the fibula, along with its blood supply, is removed and transplanted into the femoral head.[18] A 2016 Cochrane review found no clear improvement between people who have had hip core decompression and participate in physical therapy, versus physical therapy alone. There is additionally no strong research on the effectiveness of hip core decompression for people with sickle cell disease.[19]
Progression of the disease could possibly be halted by transplanting nucleated cells from bone marrow into avascular necrosis lesions after core decompression, although much further research is needed to establish this technique.[20][21]
Prognosis
The amount of disability that results from avascular necrosis depends on what part of the bone is affected, how large an area is involved, and how effectively the bone rebuilds itself. The process of bone rebuilding takes place after an injury as well as during normal growth.[16] Normally, bone continuously breaks down and rebuilds—old bone is resorbed and replaced with new bone. The process keeps the skeleton strong and helps it to maintain a balance of minerals.[16] In the course of avascular necrosis, however, the healing process is usually ineffective and the bone tissues break down faster than the body can repair them. If left untreated, the disease progresses, the bone collapses,[22] and the joint surface breaks down, leading to pain and arthritis.[1]
Epidemiology
Avascular necrosis usually affects people between 30 and 50 years of age; about 10,000 to 20,000 people develop avascular necrosis in the US each year[3]. When it occurs in children at the femoral head, it is known as Legg–Calvé–Perthes syndrome[23]
Society and culture
Cases of avascular necrosis have been identified in a few high-profile athletes. It abruptly ended the career of American football running-back Bo Jackson in 1991. Doctors discovered Jackson to have lost all of the cartilage supporting his hip while he was undergoing tests following a hip-injury he had on the field during a 1991 NFL Playoff game.[24] Avascular necrosis of the hip was also identified in a routine medical check-up on quarterback Brett Favre following his trade to the Green Bay Packers in 1991,[25] however, Favre would go on to have a long career at the Packers.Another high-profile athlete was American road racing cyclist Floyd Landis,[26] winner of the 2006 Tour de France, the title being subsequently stripped from his record by cycling's governing bodies after his blood samples tested positive for banned substances.[27] During that tour, Landis was allowed cortisone shots to help manage his ailment, despite cortisone also being a banned substance in professional cycling at the time.[28]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 "Questions and Answers about Osteonecrosis (Avascular Necrosis)". NIAMS. October 2015. Archived from the original on 9 August 2017.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Khan, Ali Nawaz; Al-Salman, Mohammed Jassim; Chandramohan, Muthusamy; MacDonald, Sumaira; Hutchinson, Charles Edward. "Bone Infarct". eMedicine Specialties. Archived from the original on 4 March 2010.
- 1 2 3 "Osteonecrosis". NORD (National Organization for Rare Disorders). 2009. Archived from the original on 19 February 2017. Retrieved 8 August 2017.
- 1 2 3 Ferri, Fred F. (2017). Ferri's Clinical Advisor 2018 E-Book: 5 Books in 1. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 166. ISBN 9780323529570. Archived from the original on 9 August 2017.
- 1 2 Conway, Richard (2020). "19. Bone disease". In Feather, Adam; Randall, David; Waterhouse, Mona (eds.). Kumar and Clark's Clinical Medicine (10th ed.). Elsevier. p. 482. ISBN 978-0-7020-7870-5. Archived from the original on 15 December 2021. Retrieved 13 December 2021.
- 1 2 National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (March 2006). "Osteonecrosis". Food and Drug Administration. Archived from the original on 23 May 2009. Retrieved 25 May 2009.
- 1 2 3 Matthews, Alexander H.; Davis, Donald D.; Fish, Michael J.; Stitson, David (2020). "Avascular Necrosis". StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Archived from the original on 8 February 2021. Retrieved 4 November 2020.
- 1 2 Mansat P, Huser L, Mansat M, Bellumore Y, Rongières M, Bonnevialle P (March 2005). "Shoulder arthroplasty for atraumatic avascular necrosis of the humeral head: nineteen shoulders followed up for a mean of seven years". Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery. 14 (2): 114–20. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2004.06.019. PMID 15789002.
- ↑ Khan, Aliya. "Bisphosphonate-associated osteonecrosis of the jaw". Canadian Family Physician. 54 (7): 1019–1021. ISSN 0008-350X. Archived from the original on 27 August 2021. Retrieved 4 November 2020.
- ↑ White, Tyler C.; Davis, Donald D.; Cooper, Jeffrey S. (2020). "Dysbaric Osteonecrosis". StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Archived from the original on 27 August 2021. Retrieved 16 November 2020.
- ↑ Weissman, Barbara N. W. Imaging of Arthritis and Metabolic Bone Disease. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 29. ISBN 978-0-323-04177-5. Archived from the original on 27 August 2021. Retrieved 4 November 2020.
- ↑ Freedman BA, Heller JG (2009). "Kummel disease: a not-so-rare complication of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures". Journal of the American Board of Family Medicine. 22 (1): 75–8. doi:10.3122/jabfm.2009.01.080100. PMID 19124637.
- ↑ Claessen, Femke M.A.P; Schol, Ilse; Kolovich, Gregory P.; Ring, David (2020). "Avascular Necrosis of the Scaphoid Preiser Disease". Archives of Bone and Joint Surgery. 8 (1): 94–98. doi:10.22038/abjs.2019.39187.2047. ISSN 2345-4644. Archived from the original on 27 August 2021. Retrieved 20 November 2020.
- ↑ Trammell, Amy P.; Davis, Donald D.; Scott, Aaron T. (2020). "Kohler Disease". StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Archived from the original on 27 August 2021. Retrieved 20 November 2020.
- ↑ Scaglione, Michelangelo; Fabbri, Luca; Celli, Fabio; Casella, Francesco; Guido, Giulio (2015). "Hip replacement in femoral head osteonecrosis: current concepts". Clinical Cases in Mineral and Bone Metabolism. 12 (Suppl 1): 51–54. doi:10.11138/ccmbm/2015.12.3s.051. ISSN 1724-8914. Archived from the original on 27 August 2021. Retrieved 16 November 2020.
- 1 2 3 de Bernard, Benedetto (15 November 1989). "Calcium Metabolism and Bone Mineralization". In Hall, Brian K. (ed.). Bone. CRC Press. pp. 74–. ISBN 978-0-936923-24-6. Archived from the original on 26 July 2020. Retrieved 6 November 2016.
- ↑ Agarwala S, Jain D, Joshi VR, Sule A (March 2005). "Efficacy of alendronate, a bisphosphonate, in the treatment of AVN of the hip. A prospective open-label study". Rheumatology. 44 (3): 352–9. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keh481. PMID 15572396.
- ↑ Judet H, Gilbert A (May 2001). "Long-term results of free vascularized fibular grafting for femoral head necrosis". Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 386 (386): 114–9. doi:10.1097/00003086-200105000-00015. PMID 11347824.
- ↑ Martí-Carvajal, Arturo J.; Solà, Ivan; Agreda-Pérez, Luis H. (10 July 2014). "Treatment for avascular necrosis of bone in people with sickle cell disease". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (7): CD004344. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004344.pub5. ISSN 1469-493X. PMID 25009086.
- ↑ Gangji V, Hauzeur JP (March 2005). "Treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head with implantation of autologous bone-marrow cells. Surgical technique". The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume. 87 Suppl 1 (Pt 1): 106–12. doi:10.2106/JBJS.D.02662. PMID 15743852. Archived from the original on 14 February 2009. Retrieved 27 April 2010.
- ↑ Lieberman JR, Conduah A, Urist MR (December 2004). "Treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head with core decompression and human bone morphogenetic protein". Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 429 (429): 139–45. doi:10.1097/01.blo.0000150312.53937.6f. PMID 15577478.
- ↑ DiGiovanni CW, Patel A, Calfee R, Nickisch F (April 2007). "Osteonecrosis in the foot" (PDF). The Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. 15 (4): 208–217. doi:10.5435/00124635-200704000-00004. PMID 17426292.
- ↑ Karkenny, Alexa J.; Tauberg, Brandon M.; Otsuka, Norman Y. (September 2018). "Pediatric Hip Disorders: Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis and Legg-Calvé-Perthes Disease". Pediatrics in Review. 39 (9): 454–463. doi:10.1542/pir.2017-0197. ISSN 1526-3347. Archived from the original on 27 August 2021. Retrieved 9 November 2020.
- ↑ Altman, Lawrence K. "Jackson's Case Is Dividing The Doctors". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 26 May 2018. Retrieved 26 May 2018.
- ↑ "What, his hip? Favre reveals he has avascular necrosis". JS Online. 27 September 2006. Archived from the original on 27 September 2006.
- ↑ "What He's Been Pedaling". The New York Times. 16 July 2006. Archived from the original on 11 January 2016. Retrieved 26 May 2018.
- ↑ "Landis Tests Positive; Title is a total complete loss". Chicago Tribune. 5 August 2006.
- ↑ Fotheringham, Alasdair (24 July 2006). "Cycling: Landis the Tour king celebrates a triumph of survival". The Independent. London. Archived from the original on 6 August 2006. Retrieved 28 July 2006. (subscription required)
Further reading
- Cooper, C.; Steinbuch, M.; Stevenson, R.; Miday, R.; Watts, N. B. (2010). "The epidemiology of osteonecrosis: findings from the GPRD and THIN databases in the UK". Osteoporosis International. 21 (4): 569–577. doi:10.1007/s00198-009-1003-1. ISSN 0937-941X. Archived from the original on 27 August 2021. Retrieved 9 November 2020.
External links
- Osteonecrosis / Avascular Necrosis Archived 13 May 2008 at the Wayback Machine at the National Institute of Health
- Osteonecrosis / Avascular necrosis Archived 16 March 2006 at the Wayback Machine at Merck Manual for patients
- Osteonecrosis / Avascular necrosis Archived 12 May 2009 at the Wayback Machine at Merck Manual for medical professionals
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
|