Hereditary neuropathy with liability to pressure palsy
| Hereditary neuropathy with liability to pressure palsy | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Tomaculous neuropathy | |
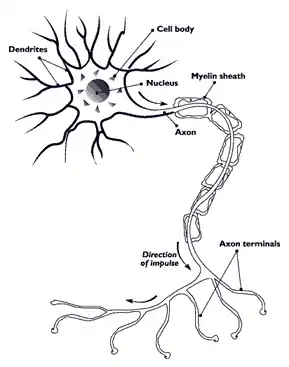 | |
| Nerve with myelin sheath | |
| Causes | Genetic (autosomal dominant mutation in the PMP22 gene)[1] |
| Diagnostic method | Family history, Electrophysiologic testing[2] |
| Treatment | Occupational therapist, ankle/wrist supports[3] |
Hereditary neuropathy with liability to pressure palsy (HNPP) is a peripheral neuropathy, a condition that affects the nerves.[4] Pressure on the nerves can cause tingling sensations, numbness, pain, weakness, muscle atrophy and even paralysis of the affected area. In normal individuals, these symptoms disappear quickly, but in sufferers of HNPP even a short period of pressure can cause the symptoms to occur. Palsies can last from minutes or days to weeks or even months.[4][1]
HNPP is caused by a mutation in the gene PMP22, which makes peripheral myelin protein 22. This protein has a role in the maintenance of the myelin sheath that insulates nerves, resulting in insufficient conductivity in the nerves. HNPP is part of the group of hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy (HMSN) disorders and is linked to Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease (CMT).[5]
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms and symptom onset vary; some individuals are diagnosed in childhood, others in adulthood, some report minor problems, whilst others experience severe discomfort and disability. In many cases, symptoms are mild enough to go unnoticed. The time period between episodes is known to vary between individuals. HNPP has not been found to alter the lifespan, although in some cases a decline in quality of life is noticed. Some sufferers (10–15%) report various pains growing in severity with progression of the disease.[1] The nerves most commonly affected are the peroneal nerve at the fibular head (leg and feet), the ulnar nerve at the elbow (arm) and the median nerve at the wrist (palm, thumbs and fingers), but any peripheral nerve can be affected. Among the signs/symptoms are the following (different symptoms are caused by different nerves, such as the foot drop caused by the peroneal nerve[4]):
Causes
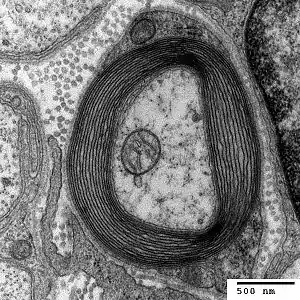
The condition is caused by a mutation in one copy of the gene PMP22 (peripheral myelin protein 22, located at locus 17p11.2). This makes it autosomal dominant.[7] PMP22 is involved in maintaining the myelin sheath that surrounds nerves to facilitate conductivity.[5] The mutation causes haploinsufficiency, where the activity of the normal gene is insufficient to compensate for the loss of function of the other gene.[8]
Genetics
The peripheral myelin protein 22 gene encodes a 22-kD protein that comprises 2 to 5% of peripheral nervous system myelin.[9]
Overlap with Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease type 1A has been found in Gly94fsX222 (c.281_282insG), due to point mutations in PMP22 that occur in a minority of cases of HNPP. The point mutations missense, nonsense and splice-site have each been alluded to in HNPP.[10]
Diagnosis

Measuring nerve conduction velocity may give an indication of the presence of the disease. Other methods via which to ascertain the diagnosis of HNPP are:[4][3]
- Family history
- Genetic test
- Proband
- Multi-gene panel
- Physical exam (lack of ankle reflex)
Treatment

There is no current treatment, however management of HNPP can be done via:[3][10]
- Physical therapist
- Occupational therapist
- Ankle/foot orthosis
- Wrist splint
- Avoid repetitive movements
Epidemiology
HNPP is a rare disorder. Partly because it is so rare and partly because many people who have it only experience mild symptoms, it is difficult to tell what percentage of people have it. One range of estimates is from one in 50,000 up to about one in 33,333.[1] Another is from one in 119,049 up to one in 6,250.[11] In a study of newborns in Korea who all got a genetic test for the disorder, around one in 1,698 of the newborns had it.[11]
History
Inherited peripheral nervous system disorders were first described by Charcot, Marie and Tooth (1886). De Jong (1947) first described HNPP in a Dutch family. Dyck and Lambert (1968) showed nerve conduction studies, and Chance et al. (1993) detected the chromosome deletion in most of the individuals with the HNPP condition.[2][10][12]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 Genetics Home Reference (April 2007). "Hereditary neuropathy with liability to pressure palsies". NIH.gov. Archived from the original on 2020-09-26. Retrieved 2020-02-09.
- 1 2 3 4 RESERVED, INSERM US14 -- ALL RIGHTS. "Orphanet: Hereditary neuropathy with liability to pressure palsies". www.orpha.net. Archived from the original on 28 June 2021. Retrieved 18 August 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Hereditary neuropathy with pressure palsies (HNPP)". NHS. NHS.uk. Archived from the original on 11 September 2017. Retrieved 18 August 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 Bird, Thomas D. (1 January 1993). "Hereditary Neuropathy with Liability to Pressure Palsies". GeneReviews. Archived from the original on 6 May 2021. Retrieved 6 August 2016.update 2014
- 1 2 Watila MM, Balarabe SA (2015). "Molecular and clinical features of inherited neuropathies due to PMP22 duplication". Journal of the Neurological Sciences. 355 (1–2): 18–24. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2015.05.037. PMID 26076881. S2CID 40080925.
- ↑ "OMIM Entry - # 162500 - NEUROPATHY, HEREDITARY, WITH LIABILITY TO PRESSURE PALSIES; HNPP". www.omim.org. Archived from the original on 25 March 2021. Retrieved 18 August 2016.
- ↑ Kuhlenbäumer, G.; Stögbauer, F.; Ringelstein, E. B.; Young, P. (2006-01-16). Hereditary Peripheral Neuropathies. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 96, 126. ISBN 9783798515864. Archived from the original on 2021-07-05. Retrieved 2022-01-30.
- ↑ Vallat, Jean-Michel; Weis, Joachim; Neuropathology, International Society of (2014-10-20). Peripheral Nerve Disorders: Pathology and Genetics. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 9781118618431. Archived from the original on 2021-07-06. Retrieved 2022-01-30.
- ↑ "OMIM Entry - * 601097 - PERIPHERAL MYELIN PROTEIN 22; PMP22". omim.org. Archived from the original on 2017-03-10. Retrieved 2016-08-18.
- 1 2 3 van Paassen, Barbara W; Kooi, Anneke J van der; Spaendonck-Zwarts, Karin Y van; Verhamme, Camiel; Baas, Frank; Visser, Marianne de (19 March 2014). "PMP22 related neuropathies: Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A and Hereditary Neuropathy with liability to Pressure Palsies". Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases. 9 (1): 38. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-9-38. ISSN 1750-1172. PMC 3994927. PMID 24646194.
- 1 2 Park, Jong Eun; Noh, Seung-Jae; Oh, Mijin; Cho, Dae-Yeon; Kim, So Young; Ki, Chang-Seok (2018-03-15). "Frequency of hereditary neuropathy with liability to pressure palsies (HNPP) due to 17p11.2 deletion in a Korean newborn population". Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases. 13 (1): 40. doi:10.1186/s13023-018-0779-5. ISSN 1750-1172. PMC 5856277. PMID 29544507.
- ↑ Sango, Kazunori; Yamauchi, Junji (2014-02-13). Schwann Cell Development and Pathology. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 83. ISBN 9784431547648. Archived from the original on 2022-04-07. Retrieved 18 August 2016.
Further reading
- Horowitz, S. H.; Spollen, L. E.; Yu, W. (1 November 2004). "Hereditary neuropathy with liability to pressure palsy: fulminant development with axonal loss during military training". Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry. 75 (11): 1629–1631. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2003.029314. ISSN 1468-330X. PMC 1738805. PMID 15489403.
- Lorenzoni, Paulo J.; Scola, Rosana H.; Cardoso, Juliana; Kay, Cláudia S.K.; Fugmann, Elmar A.; Marques Jr, Wilson; Silvado, Carlos E.; Werneck, Lineu C. (December 2008). "Swallowing dysfunction in hereditary neuropathy with liability to pressure palsies". Arquivos de Neuro-Psiquiatria. 66 (4): 898–900. doi:10.1590/S0004-282X2008000600027. PMID 19099137.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
|