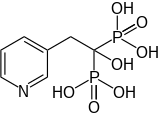
Risedronic acid
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Actonel, Atelvia, Benet, others |
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Bisphosphonate[1] |
| Main uses | Osteoporosis, Paget's disease of bone[1] |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | By mouth |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| US NLM | Risedronic acid |
| Legal | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Bioavailability | 0.63% |
| Protein binding | ~24% |
| Metabolism | None |
| Elimination half-life | 1.5 h |
| Excretion | Kidney and fecal |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C7H11NO7P2 |
| Molar mass | 283.112 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Risedronic acid, often used as its salt risedronate sodium, is a bisphosphonate used to treat and prevent osteoporosis or to treat Paget's disease of bone.[1] It is taken by mouth.[1]
Common side effects include constipation, nausea, headache, and rash.[1] Other side effects may include esophageal inflammation, esophageal perforation, osteonecrosis of the jaw, low calcium, and muscle pain.[1] Use is not recommended in those with significant kidney problems.[2] It works by inhibiting the cells which break down bone.[1]
Risedronic acid was patented in 1984 and approved for medical use in 1998.[3] It is available as a generic medication.[4] In the United States it costs about 30 USD per month as of 2021.[4] In the United Kingdom it costs the NHS about £10 per month.[2]
Medical uses
Dosage
It may be taken as 5 mg a day, 35 mg a week, or 150 mg a month.[1]
Side effects
In common with other bisphosphonate drugs, risedronate appears to be associated with the rare side effect osteonecrosis of the jaw, often preceded by dental procedures inducing trauma to the bone.
Pharmacology
| Bisphosphonate | Relative potency |
|---|---|
| Etidronate | 1 |
| Tiludronate | 10 |
| Pamidronate | 100 |
| Alendronate | 100-500 |
| Ibandronate | 500-1000 |
| Risedronate | 1000 |
| Zoledronate | 5000 |
Society and culture
Brand names
It is produced and marketed by Warner Chilcott, Sanofi-Aventis, and in Japan by Takeda under the trade names Actonel, Atelvia, and Benet. It is also available in a preparation that includes a calcium carbonate supplement, as Actonel with Calcium.
Controversies
In January 2006 P&G and its marketing partner Sanofi-Aventis filed a Lanham Act false claims lawsuit against rival drugmakers Roche and GlaxoSmithKline claiming false advertising about Boniva.[6] The manufacturers of Boniva, a rival bisphosphonate, were accused in the suit of causing a "serious public health risk" through misrepresentation of scientific findings. In a ruling on September 7, 2006 U.S. District Judge Paul A. Crotty rejected P&G's attempted injunction. P&G was criticized for attempting to "preserve its market share by denigrating Boniva". Judge Crotty wrote that "Roche was clearly entitled to respond with its own data, provided that the data was truthfully and accurately presented".[7]
In 2006, P&G faced controversy over its handling of clinical research involving risedronate (News Reports[8] and discussion).[9]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 "Risedronate Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 25 January 2021. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- 1 2 BNF (80 ed.). BMJ Group and the Pharmaceutical Press. September 2020 – March 2021. p. 770. ISBN 978-0-85711-369-6.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: date format (link) - ↑ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 523. ISBN 9783527607495. Archived from the original on 2021-03-18. Retrieved 2020-08-27.
- 1 2 "Risedronate Prices, Coupons & Savings Tips - GoodRx". GoodRx. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ↑ Tripathi KD (30 September 2013). Essentials of medical pharmacology (Seventh ed.). New Delhi. ISBN 9789350259375. OCLC 868299888.
- ↑ "P&G Press statement". Uk.pg.com. Archived from the original on 2011-09-29. Retrieved 2013-03-01.
- ↑ "Boniva advertising 'not misleading' says US judge". Pharma Times. 8 September 2006. Archived from the original on 29 August 2021. Retrieved 27 August 2020.
- ↑ "Actonel Case Media Reports". Scientific Misconduct Wiki. Archived from the original on 2 February 2009.
- ↑ "Scientific Misconduct Blog". Scientific-misconduct.blogspot.com. Archived from the original on 2013-02-24. Retrieved 2013-03-01.
External links
| Identifiers: |
|---|
- "Risedronic acid". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Archived from the original on 2020-06-10. Retrieved 2020-06-10.
- "Risedronate sodium". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Archived from the original on 2020-06-10. Retrieved 2020-06-10.