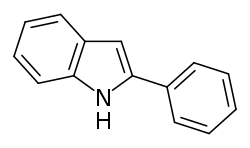
2-Phenylindole
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Phenyl-1H-indole | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.215 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C14H11N |
| Molar mass | 193.249 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
2-Phenylindole is an organic compound. It is the parent structure of a group of nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) that includes zindoxifene, bazedoxifene, and pipendoxifene, as well as the nonsteroidal estrogen D-15414 (the major metabolite of zindoxifene).[1][2][3]
References
- ↑ Michael Oettel; Ekkehard Schillinger (6 December 2012). Estrogens and Antiestrogens I: Physiology and Mechanisms of Action of Estrogens and Antiestrogens. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 68–69. ISBN 978-3-642-58616-3.
- ↑ International position paper on women's health and menopause : a comprehensive approach. DIANE Publishing. pp. 111–. ISBN 978-1-4289-0521-4.
- ↑ Gordon W. Gribble (9 October 2010). Heterocyclic Scaffolds II:: Reactions and Applications of Indoles. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 14–. ISBN 978-3-642-15732-5.
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.