Venule
| Venule | |
|---|---|
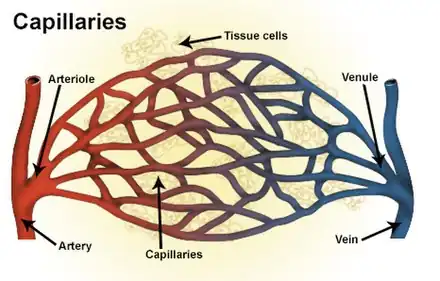 Types of blood vessels, including a venule, vein, and capillaries | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | venula |
| MeSH | D014699 |
| TA98 | A12.0.00.037 |
| TA2 | 3903 |
| TH | H3.09.02.0.03002 |
| FMA | 63130 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
A venule is a very small blood vessel in the microcirculation that allows blood to return from the capillary beds to drain into the larger blood vessels, the veins. Venules range from 7μm to 1mm in diameter. Veins contain approximately 70% of total blood volume, 25% of which is contained in the venules.[1] Many venules unite to form a vein.
Structure
Venule walls have three layers: An inner endothelium composed of squamous endothelial cells that act as a membrane, a middle layer of muscle and elastic tissue and an outer layer of fibrous connective tissue. The middle layer is poorly developed so that venules have thinner walls than arterioles. They are porous so that fluid and blood cells can move easily from the bloodstream through their walls.
Short portal venules between the neural and anterior pituitary lobes provide an avenue for rapid hormonal exchange via the blood.[2] Specifically within and between the pituitary lobes is anatomical evidence for confluent interlobe venules providing blood from the anterior to the neural lobe that would facilitate moment-to-moment sharing of information between lobes of the pituitary gland.[2]
In contrast to regular venules, high endothelial venules are a special type of venule where the endothelium is made up of simple cuboidal cells. Lymphocytes exit the blood stream and enter the lymph nodes via these specialized venules when an infection is detected. Compared with arterioles, the venules are larger with much weaker muscular coat. They are the smallest united common branch in the human body.
See also
References
- ↑ Woods, Susan (2010). Cardiac Nursing. New York: Lippincotts. p. 955. ISBN 9780781792806.
- 1 2 Gross, PM; Joneja, MG; Pang, JJ; Polischuk, TM; Shaver, SW; Wainman, DS (1993). "Topography of short portal vessels in the rat pituitary gland: A scanning electron-microscopic and morphometric study of corrosion cast replicas". Cell and Tissue Research. 272 (1): 79–88. doi:10.1007/bf00323573. PMID 8481959. S2CID 23657199.