Prostatic utricle
| Prostatic utricle | |
|---|---|
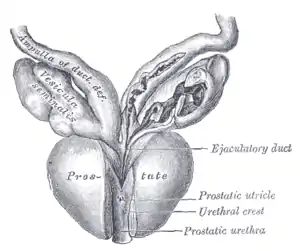 Vesiculae seminales and ampullæ of ductus deferentes, seen from the front. | |
 The male urethra laid open on its anterior (upper) surface. | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | remnant of paramesonephric duct |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Utriculus prostaticus, utriculus masculinus, vagina masculina, sinus pocularis |
| TA98 | A09.4.02.009 |
| TA2 | 3449 |
| FMA | 19702 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The prostatic utricle (Latin for "pouch of the prostate") is a small indentation in the prostatic urethra, at the apex of the urethral crest, on the seminal colliculus (verumontanum), laterally flanked by openings of the ejaculatory ducts. It is also known as the vagina masculina or uterus masculinus or (in older literature) vesicula prostatica.[1]
Structure
It is often described as "blind", meaning that it is a duct that does not lead to any other structures.[2] It tends to be about one cm in length.[3] It can sometimes be enlarged.[4][5] The utricle is deemed enlarged if it allows insertion of a cystoscope at least 2 cm deep.[6] This is often associated with Hypospadias.[7]
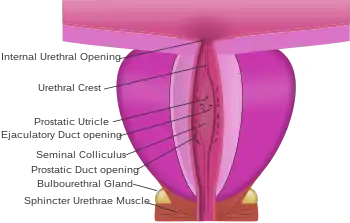
Function
The prostatic utricle is the homologue of the uterus and vagina, usually described as derived from the paramesonephric duct,[8] although this is occasionally disputed.[9]
In 1905 Robert William Taylor described the function of the utricle: "In coitus it so contracts that it draws upon the openings of the ejaculatory ducts, and thus renders them so patulous that the semen readily passes through."[10]
See also
References
- ↑ Henry Thompson (1883). "vesicula+prostatica"+utricle&pg=PA13 The diseases of the prostate. J&A Churchill.
- ↑ Butler, Paul; Mitchell, Adam W. M.; Ellis, Harold (1999). Applied Radiological Anatomy (illustrated ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 286. ISBN 9780521481106.
- ↑ Cunningham, Daniel John (1968). Manual of Practical Anatomy: Thorax and abdomen. Manual of Practical Anatomy. Vol. 2 (13th ed.). University of Michigan: Oxford University Press. p. 238.
- ↑ Meisheri IV, Motiwale SS, Sawant VV (2000). "Surgical management of enlarged prostatic utricle". Pediatr. Surg. Int. 16 (3): 199–203. doi:10.1007/s003830050722. PMID 10786981.
- ↑ Lopatina OA, Berry TT, Spottswood SE (2004). "Giant prostatic utricle (utriculus masculinis): diagnostic imaging and surgical implications". Pediatr Radiol. 34 (2): 156–9. doi:10.1007/s00247-003-1048-9. PMID 12961046.
- ↑ Kogan, S.J.; Hafez, E.S. (2012). Pediatric Andrology. Clinics in Andrology. Vol. 7 (illustrated ed.). Springer Science & Business Media. p. 188. ISBN 9789401037198.
- ↑ Al-Salem, Ahmed H. (2016). An Illustrated Guide to Pediatric Urology. Springer. p. 446. ISBN 9783319441825.
- ↑ Kawashima, A.; Sandler, C. M.; Wasserman, N. F.; LeRoy, A. J.; King, B. F.; Goldman, S. M. (1 October 2004). "Imaging of Urethral Disease: A Pictorial Review". Radiographics. 24 (suppl_1): S195–S216. doi:10.1148/rg.24si045504. PMID 15486241.
- ↑ Shapiro E, Huang H, McFadden DE, et al. (2004). "The prostatic utricle is not a Müllerian duct remnant: immunohistochemical evidence for a distinct urogenital sinus origin". J. Urol. 172 (4 Pt 2): 1753–6, discussion 1756. doi:10.1097/01.ju.0000140267.46772.7d. PMID 15371806.
- ↑ R. W. Taylor. "A practical treatise on sexual disorders of the male and female". New York and Philadelphia, 1897; 3rd edition, 1905. P. 48
External links
- Anatomy photo:44:05-0204 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center—"The Male Pelvis: The Prostate Gland"
- pelvis at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (malebladder)
- figures/chapter_34/34-3.HTM: Basic Human Anatomy at Dartmouth Medical School