Árva County
Árva County (Hungarian: Árva vármegye, Latin: Comitatus Arvensis, Slovak: Oravská stolica/župa,[1] German: Komitat Arwa, Polish: Komitat Orawa) was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary since the 14th century until 1920. Its territory is now in northern Slovakia and southern Poland. Today, the Slovak name is only used as an informal designation of the corresponding territory (see Orava region).
| Árva County | |
|---|---|
| County of the Kingdom of Hungary (14th century-1854, 1860-1920) | |
.svg.png.webp) Coat of arms
| |
 | |
| Capital | Árvavárallya; Alsókubin (1683-1854, 1860-1920) |
| Area | |
| • Coordinates | 49°13′N 19°18′E |
• 1910 | 2,019 km2 (780 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 1910 | 78700 |
| History | |
| History | |
• Established | 14th century |
• Merged to Árva-Turóc County | 1854 |
• County recreated | 20 October 1860 |
| 4 June 1920 | |
| Today part of | Slovakia Poland |
| Oravský Podzámok; Dolný Kubín are the current name of the capital. | |
Geography
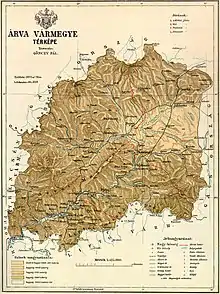
Between 1804-1854 and 1860-1920, Árva County shared borders with Austrian Galicia and the Hungarian counties of Trencsén, Turóc and Liptó County. The county's territory was situated along the Árva (Orava) river between Zázriva (Zázrivá) and the Tatra mountains. Its area was 2,019 km² around 1910. Now the territory is divided between Poland and Slovakia. The main Polish town of Orava is Jabłonka.
Capitals
The county seat was at the Orava Castle (Hungarian: Árva vára). After the destruction of the town by the Lithuanian troops in 1683, the seat was moved to Alsókubin (also Kolbin, Kublen, Kubin, Also Helben, Clbin, Culbyn, Cublyn, present-day Dolný Kubín).[2]
History
Emerging from the Zólyom royal land (Hungarian: zólyomi erdőispánság), the first written mention about Árva County is from 1349.[3] However, the territory had been still referenced as a district in 1351-1368 and it finally became a county with its own self-administration in 1370.[3]
In the aftermath of World War I, the territory of the whole county became part of newly formed Czechoslovakia. After a border dispute (treated in detail under Polish–Czechoslovak border conflicts) several villages in the north-east territory were exchanged between Poland and Czechoslovakia. The former county's Czechoslovak part was abolished with effective date 1 January 1923[4] and its territory became a part of Váh County.
Demographics

| Census | Total | Slovak | Hungarian | German | Other or unknown |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1880[5] | 81,643 | 75,901 (96.26%) | 355 (0.45%) | 2,213 (2.81%) | 378 (0.48%) |
| 1890[6] | 84,820 | 81,600 (96.20%) | 773 (0.91%) | 1,918 (2.26%) | 529 (0.62%) |
| 1900[7] | 85,009 | 80,487 (94.68%) | 1,494 (1.76%) | 2,127 (2.50%) | 901 (1.06%) |
| 1910[8] | 78,745 | 59,096 (75.05%) | 2,000 (2.54%) | 1,518 (1.93%) | 16,131 (20.49%)[lower-alpha 2] |
| Census | Total | Roman Catholic | Lutheran | Jewish | Other or unknown |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1880 | 81,643 | 71,407 (87.46%) | 7,272 (8.91%) | 2,934 (3.59%) | 30 (0.04%) |
| 1890 | 84,820 | 74,892 (88.30%) | 7,153 (8.43%) | 2,742 (3.23%) | 33 (0.04%) |
| 1900 | 85,009 | 75,337 (88.62%) | 6,936 (8.16%) | 2,648 (3.11%) | 88 (0.10%) |
| 1910 | 78,745 | 69,788 (88.63%) | 6,674 (8.48%) | 2,205 (2.80%) | 78 (0.10%) |
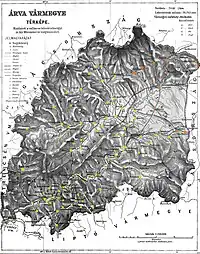
Districts
.jpg.webp)
In the early 20th century, the districts and their capitals were:
| Districts (járás) | |
|---|---|
| District | Capital |
| Alsókubin | Alsókubin (now Dolný Kubín) |
| Námesztó | Námesztó (now Námestovo) |
| Trsztena | Trsztena (now Trstená) |
| Vár | Turdossin (now Tvrdošín) |
Notes
- Only linguistic communities > 1% are displayed.
- most of them Polish
- Only religious communities > 1% are displayed.
References
- Viliam, Volko; Kiš, Miloslav (2007). Stručný vývoj územného a administratívneho členenia Slovenska [A Brief History of the Territorial and Administrative Division of Slovakia]. Bratislava: Ministry of Interior of the Slovak Republic. pp. 21, 23.
- Maslíková, Ľudmila (2010). "Hospodárske pomery vo Veličnej na základe urbárov z 17. a prvej polovice 18. storočia". Historia nova (in Slovak). Bratislava: Filozofická fakulta Univerzity Komenského (1): 46. ISBN 978-80-8127-160-1.
- Maslíková 2010, p. 41.
- Volko-Kiš 2007, p. 38.
- "Az 1881. év elején végrehajtott népszámlálás főbb eredményei megyék és községek szerint rendezve, II. kötet (1882)". library.hungaricana.hu. Retrieved 2021-09-28.
- "A Magyar Korona országainak helységnévtára (1892)". library.hungaricana.hu. Retrieved 2021-09-29.
- "A MAGYAR KORONA ORSZÁGAINAK 1900". library.hungaricana.hu. Retrieved 2021-09-29.
- "KlimoTheca :: Könyvtár". Kt.lib.pte.hu. Retrieved 2021-09-29.
External links
- (in Slovak) http://www.orava.sk
- (in Polish) http://skansen.nowotarski.pl Orawa Ethnographic Park
- http://www.oravafoto.com
- (in Slovak) http://www.namestovo-orava.webnode.sk
