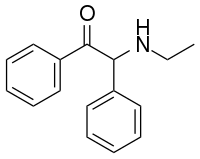
2-(Ethylamino)-1,2-diphenylethanone
2-(Ethylamino)-1,2-diphenylethanone (also known as α-ethylamino-deoxybenzoin, [α-(Ethylamino)benzyl]-(phenyl)-ketone and βk-Ephenidine) is a chemical compound which was first invented in 1955,[1] researched by ICI in 1969 as an antidepressant,[2] and subsequently claimed by AstraZeneca as an inhibitor of the enzyme 11β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1.[3] No other pharmacological data has been disclosed, though its chemical structure closely resembles that of certain designer drug compounds such as ephenidine and N-ethylhexedrone.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H17NO |
| Molar mass | 239.318 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
References
- Hinderling R, Prijs B, Erlenmeyer H (1955). "Über α‐Alkylamino‐ketone". Helvetica Chimica Acta. 38 (6): 1415–1420. doi:10.1002/hlca.19550380613.
- GB 1143263, Gilman DJ, "Desyl amines and compositions thereof. gdate = 19 February 1969", assigned to ICI Ltd.
- US Abandoned 2005272036, Barton P, Clarke D, Davies C, Hargreaves R, Pease J, Rankine M, "Ketones", published 8 December 2005, assigned to AstraZeneca AB
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.