ε-Carotene
ε-Carotene (epsilon-carotene) is a carotene. It can be synthesized from 2,7-dimethyl-2,4,6-octatrienedial and 2-methyl-4-(2,6,6-trimethyl-2-cyclohexen-1-yl)-3-butenal.[2]
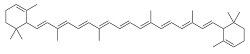 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
ε,ε-carotene | |
| Other names
4,4'-Didehydro-6,6'-dihydro-β,β-carotene | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C40H56 | |
| Molar mass | 536.888 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Crystal |
| Melting point | 190 °C[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Karrer, P.; Eugster, C. H.; Tobler, E. "Synthesis of carotenoids. III. Total synthesis of lycopene". Helvetica Chimica Acta (in German). 33: 1349–1352. doi:10.1002/hlca.19500330534. ISSN 0018-019X..
- Wu, Xin-Yan; Guo, Xing-Tao; Sha, Feng (Sep 26, 2016). "Highly Enantioselective Michael Addition of Aromatic Ketones to Nitrodienes and the Application to the Synthesis of Chiral γ-Aminobutyric Acid". Synthesis. Georg Thieme Verlag KG. 49 (3): 647–656. doi:10.1055/s-0036-1588604. ISSN 0039-7881.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.