(523622) 2007 TG422
(523622) 2007 TG422, provisional designation 2007 TG422, is a trans-Neptunian object on a highly eccentric orbit in the scattered disc region at the edge of Solar System. Approximately 260 kilometers (160 miles) in diameter, it was discovered on 3 October 2007 by astronomers Andrew Becker, Andrew Puckett and Jeremy Kubica during the Sloan Digital Sky Survey at Apache Point Observatory in New Mexico, United States.[1] According to American astronomer Michael Brown, the bluish object is "possibly" a dwarf planet.[7] It belongs to a group of objects studied in 2014, which lead to the proposition of the hypothetical Planet Nine.[10]
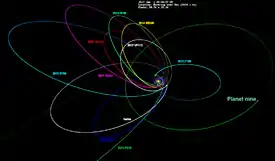 Orbital diagram of extreme Trans-neptune objects, including 2007 TG422 together with the hypothetical Planet Nine | |
| Discovery[1][2] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | |
| Discovery site | APO |
| Discovery date | 3 October 2007 |
| Designations | |
| (523622) 2007 TG422 | |
| 2007 TG422 | |
| Orbital characteristics[3] | |
| Epoch 27 April 2019 (JD 2458600.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 1 | |
| Observation arc | 13.14 yr (4,800 d) |
| Aphelion | 910.01 AU |
| Perihelion | 35.532 AU |
| 472.77 AU | |
| Eccentricity | 0.9248 |
| 10279.78 yr (3,754,688 d) | |
| 0.4774° | |
| 0° 0m 0.36s / day | |
| Inclination | 18.620° |
| 112.84° | |
| 285.54° | |
| Physical characteristics | |
Mean diameter | |
| 0.04 (est.)[7] | |
| 22.4[9] | |
| 6.5[1][3][7] | |
Orbit and classification
2007 TG422 orbits the Sun at a distance of 35.5–910 AU once every 10279 years and 9 months (3,754,688 days; semi-major axis of 473 AU). Its orbit has an exceptionally high eccentricity of 0.92 and an inclination of 19° with respect to the ecliptic.[3]
2007 TG422 is an extended scattered disc object,[6] as its large aphelion distance is similar to that of the detached objects such as the sednoids (e.g. 90377 Sedna), its perihelion distance, however, is much lower and still just inside the gravitational influence of Neptune.[4] The object came to perihelion in 2005 at a heliocentric distance of 35.5 AU,[3] and is currently 37.9 AU from the Sun.[9] It was in the constellation of Taurus until 2018, and came to opposition 29 November 2017. The body's observation arc begins at Apache Point in September 2007, one month prior to its official discovery observation.[1] It has since been observed over a hundred times and has an orbital uncertainty of 1.[3]
Unstable heliocentric solutions
| Year[lower-alpha 1] (epoch) | Aphelion (AU) | Orbital period years |
|---|---|---|
| 28 August 2007[4] | 932 | 10652 |
| 30 September 2012[11] | 1099 | 13512 |
| 16 February 2017[3] | 917 | 10399 |
| 26 June 2018 | 901 | 10143 |
| Stable Barycentric 2017[12] | 970 | 11300 |
Given the orbital eccentricity of this object, different epochs can generate quite different heliocentric unperturbed two-body best-fit solutions to the aphelion (maximum distance from the Sun) of this object.[lower-alpha 2] With a 2007 epoch the object had an approximate period of about 10,611 years with aphelion at 930 AU.[4] But using a 2012 epoch shows a period of about 13,512 years with aphelion at 1099 AU.[11] For objects at such high eccentricity, the Sun's barycentric coordinates are more stable than heliocentric coordinates.[13] Using JPL Horizons with an observed orbital arc of 5 years, the barycentric orbital elements for epoch 2008-May-14 generate a semi-major axis of 503 AU and a period of 11,300 years.[12] For comparison, Sedna has a barycentric semi-major axis of 506 AU and a period of 11,400 years.[12] Both (308933) 2006 SQ372 and (87269) 2000 OO67 take longer than Sedna and 2007 TG422 to orbit the Sun using barycentric coordinates.
Numbering and naming
This minor planet was numbered by the Minor Planet Center on 25 September 2018 (M.P.C. 111778).[14] As of 2018, it has not been named.[1]
Physical characteristics
2007 TG422 is expected to have a low albedo (see below) due to its blue (neutral) color.[7]
Diameter and albedo
According to the Johnston's archive and to Michael Brown, 2007 TG422 measures 222 and 331 kilometers in diameter, based on an absolute magnitude of 6.5 and an assumed standard albedo of 0.09 and 0.04 for the body's surface, respectively.[6][7] As of 2018, no rotational lightcurve has been obtained from photometric observations. The body's rotation period, pole and shape remain unknown.[3][8] Michael Brown's website lists it as a possible dwarf planet.[7]
Comparison
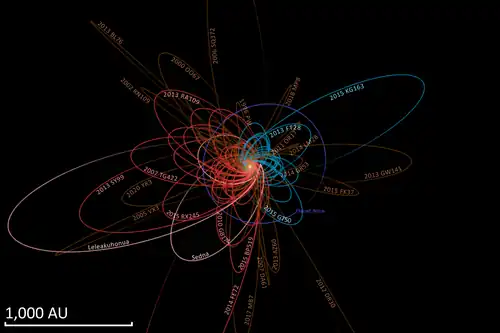
Notes
- Heliocentric solution unstable due to the changing position of Jupiter over Jupiter's 12 year orbit which perturbs the eccentricity of the two-body solution of the Sun+asteroid. Barycentric solutions are more stable for objects that take thousands of years to orbit the Sun.
- Read osculating orbit for more details about heliocentric unperturbed two-body solutions
References
- "523622 (2007 TG422)". Minor Planet Center. Retrieved 10 October 2018.
- "MPEC 2008-D39: 2007 TG422, 2007 TH422, 2007 TJ422, 2007 UL126, 2007 VH305". IAU Minor Planet Center. 26 February 2008. Retrieved 30 January 2011. (K07Tg2G)
- "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 523622 (2007 TG422)" (2018-01-13 last obs.). Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Retrieved 10 October 2018.
- Marc W. Buie. "Orbit Fit and Astrometric record for 07TG422" (2009-09-28 using 32 of 32 observations). SwRI (Space Science Department). Archived from the original on 30 May 2015. Retrieved 30 January 2011.
- "List Of Centaurs and Scattered-Disk Objects". Minor Planet Center. Retrieved 10 October 2018.
- Johnston, Wm. Robert (30 December 2017). "List of Known Trans-Neptunian Objects". Johnston's Archive. Retrieved 10 October 2018.
- Brown, Michael E. "How many dwarf planets are there in the outer solar system?". California Institute of Technology. Retrieved 10 October 2018.
- "Asteroid (523622) 2007 TG422". Small Bodies Data Ferret. Retrieved 10 October 2018.
- "Asteroid (523622) 2007 TG422". AstDyS-2, Asteroids – Dynamic Site – Department of Mathematics, University of Pisa, Italy. Archived from the original on 2 September 2016. Retrieved 10 October 2018.
- Trujillo, Chadwick A.; Sheppard, Scott S. (March 2014). "A Sedna-like body with a perihelion of 80 astronomical units". Nature. 507 (7493): 471–474. Bibcode:2014Natur.507..471T. doi:10.1038/nature13156. PMID 24670765. S2CID 4393431.
- JPL Epoch 2012-Sep-30 solution
- Horizons output (30 January 2011). "Barycentric Osculating Orbital Elements for 2007 TG422". Archived from the original on 28 March 2014. Retrieved 30 January 2011. (Horizons)
- Kaib, Nathan A.; Becker, Andrew C.; Jones, R. Lynne; Puckett, Andrew W.; Bizyaev, Dmitry; Dilday, Benjamin; et al. (April 2009). "2006 SQ372: A Likely Long-Period Comet from the Inner Oort Cloud". The Astrophysical Journal. 695 (1): 268–275. arXiv:0901.1690. Bibcode:2009ApJ...695..268K. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/695/1/268. S2CID 16987581.
- "MPC/MPO/MPS Archive". Minor Planet Center. Retrieved 10 October 2018.
External links
- Discovery Circumstances: Numbered Minor Planets (520001)–(525000) – Minor Planet Center
- (523622) 2007 TG422 at AstDyS-2, Asteroids—Dynamic Site
- (523622) 2007 TG422 at the JPL Small-Body Database