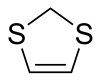
1,3-Dithiole
In organosulfur chemistry, 1,3-dithioles are a class of heterocycles based on the parent compound 1,3-dithiacyclopentene (also known as 1,3-dithiole). The ligand dmit2- is a 1,3-dithiole.[1] Heating solutions of Na2dmit gives the isomeric disulfide, a 1,2-dithiole.
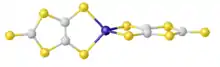
Structure of the anion [Zn(dmit)2]2-, featuring two 1,3-dithiole-4,5-dithiolate ligands complexed to zinc.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2H-1,3-Dithiole | |
| Other names
1,3-Dithiacyclopentene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H4S2 | |
| Molar mass | 104.19 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Niels Svenstrup; Jan Becher (1995). "The Organic Chemistry of 1,3-Dithiole-2-thione-4,5-dithiolate (DMIT)". Synthesis: 215–235. doi:10.1055/s-1995-3910.
- W.T.A. Harrison; R.A. Howie; J.L. Wardell; S.M.S.V. Wardell; N.M. Comerlato; L.A.S. Costa; A.C. Silvino; A.I. de Oliveira; R.M. Silva. "Crystal structures of three [bis(1,3-dithiole-2-thione-4,5-dithiolato)zincate]2− salts: [Q]2[Zn(dmit)2] (Q = 1,4-Me2-pyridinium or NEt4) and [PPh4]2[Zn(dmit)2]·DMSO. Comparison of the dianion packing arrangements in [Q]2[Zn(dmit)2]". Polyhedron. 19: 821–827. doi:10.1016/S0277-5387(00)00322-3.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.