10 Artillery Brigade (South Africa)
10 Artillery Brigade was a South African Defence Force formation designed for mass artillery barrages, mainly for the 7 South African Infantry Division or 8 South African Armoured Division, as well as an ad hoc formation during Operation Prone, when needed and detached and reattached where required. Smaller components would then be used at the battlegroup level.
| 10 Artillery Brigade | |
|---|---|
 10 Artillery Brigade | |
| Active | 1983–1992 |
| Country | |
| Allegiance | |
| Branch | |
| Type | Artillery Brigade |
| Part of | South African Artillery Corps |
| Garrison | Potchefstroom |
| Nickname(s) | 10 Art |
| Equipment |
|
| Engagements | South African Border War |
| Commanders | |
| OC Operation Excite/Hilti | Commandant George Swanepoel |
| Insignia | |
| SADF 10 Artillery Brigade laurel |  |
| 10 Artillery Brigade beret badge |  |
History
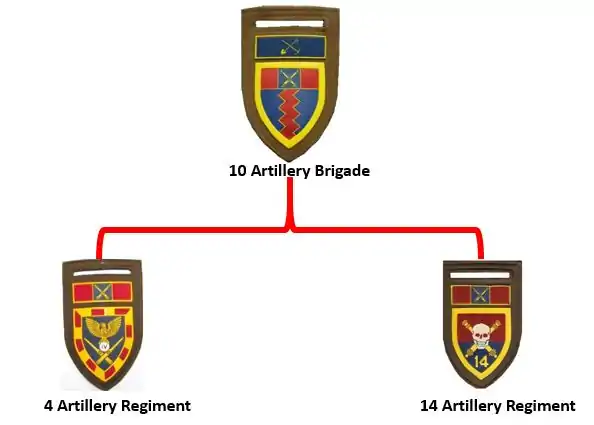
10 Artillery Brigade[1][2][3] was formed in Potchefstroom in 1983, when 4 Field Regiment[4] and 14 Field Regiment[5] were both incorporated as 4 Artillery Regiment and 14 Field Artillery Regiment. 4 Artillery Regiment was located to the old 14 Field Regiment base where the Brigade was established. It provided the base and training facilities as well as National Servicemen gunner training between each regiment on an annual basis.
Equipment
The Brigade utilized the following equipment:
- G5 155mm long range howitzer
- G6 155mm long range howitzer
- G2 140mm medium range howitzer
- Bateleur 127mm multiple rocket launcher
- M5 120mm heavy mortars
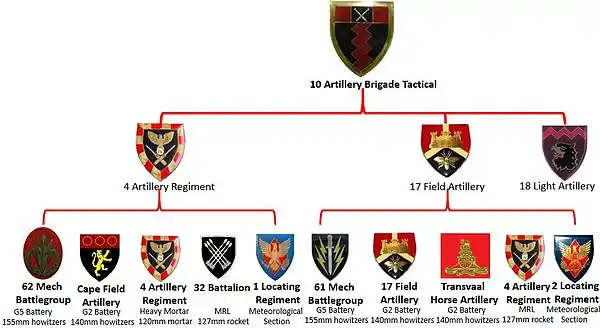
Tactical Headquarters
10 Artillery Brigade[6] Tactical headquarters was an artillery formation created in 1988 to support the ad hoc formation of 10 SA Division which had been formed to counter the Cuban threat in south-western Angola in June 1988. It was composed of:
- a tactical headquarters,
- 14 Field Artillery Regiment comprising:
- 14 Field Artillery Regiment HQ,
- 155mm G5 battery from 62 Mechanised Battalion Group,
- a 140mm G2 battery from Cape Field Artillery,
- a 127 mm MRL battery from 32 Battalion,
- a 120mm mortar battery from 4 Artillery Regiment,
- a meteorological section from 1 Locating Regiment,
- a light workshop troop and
- a signals troop
- 17 Field Regiment comprising:
- 17 Field Regiment HQ,
- a 155mm G5 Battery from 61 Mechanised Battalion Group,
- a 140mm G2 Battery from 17 Field Regiment,
- another 140mm G2 Battery from Transvaal Horse Artillery,
- a 127mm MRL battery from 4 Artillery Regiment,
- a meteorological section from 2 Locating Regiment,
- a light workshop troop and
- a signals troop
- 181 battery from 18 Light Regiment
Engagements
- Battles fought around Cuito Cuanavale
- Operation Excite/Hilti
- Operation Prone
Disbandment
10 Artillery Brigade became the basis for the South African Army Artillery Formation.
See also
Notes
- Velthuizen, Andreas (2009). "The significance of the battle for Cuito Cuanavale: Long term foresight of the current strategic landscape". Scientia Militaria: South African Journal of Military Studies. 37 (2). doi:10.5787/37-2-71. ISSN 2224-0020.
References
- Crook, Lionel, Col (RTD). "The South African Gunner" (PDF). p. 18. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-06-13. Retrieved 2014-04-21.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - "South African Gunners Association - SANDF Reserve Force - SA Reserves' Achievements in 2016 Netherlands International Shooting Competition (2016NISC) - News". Archived from the original on 2016-10-16. Retrieved 2018-12-11.
- "Fact file: The SA Artillery". defenceWeb. 2010-02-09. Retrieved 2021-09-04.
- "Gunners Association in Potchefstroom". www.potchefstroom.co.za. Retrieved 2021-09-04.
- "APRIL 2011 newsletter - Cape Town - South African Military History Society - Title page".
- Roberts, Sean. "44 Battery, 4 Artillery Brigade at 10 Artillery HQ in Potchefstroom 1990". Sentinel Projects. Sentinel Projects. Retrieved 12 September 2016.