2-Chloropropionic acid
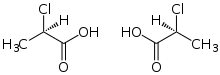
2-Chloropropionic acid (2-chloropropanoic acid) is the chemical compound with the formula CH3CHClCO2H. This colorless liquid is the simplest chiral chlorocarboxylic acid, and it is noteworthy for being readily available as a single enantiomer. The conjugate base of 2-chloropropionic acid (CH3CHClCO2−), as well as its salts and esters, are known as 2-chloropropionates or 2-chloropropanoates.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Chloropropanoic acid | |
| Other names
α-Chloropropanoic acid α-Chloropropionic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.049 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2511 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H5ClO2 | |
| Molar mass | 108.52 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.18 g/mL |
| Melting point | −13 °C (9 °F; 260 K) |
| Boiling point | 78 °C (172 °F; 351 K) at 10 mmHg |
| Miscible | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards |
Toxic, corrosive |
| GHS labelling: | |
    | |
| Danger | |
| H301, H302, H310, H314, H331, H371, H373 | |
| P260, P261, P262, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P312, P301+P330+P331, P302+P350, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P309+P311, P310, P311, P314, P321, P322, P330, P361, P363, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | 101 °C (214 °F; 374 K) |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
Propionic acid Chloroacetic acid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Preparation
Racemic 2-chloropropionic acid is produced by chlorination of propionyl chloride followed by hydrolysis of the 2-chloropropionyl chloride.[1] Enantiomerically pure (S)-2-chloropropionic acid can be prepared from L-alanine via diazotization in hydrochloric acid.[2] Other α-amino acids undergo this reaction.
Reactions
Reduction of (S)-2-chloropropionic acid with lithium aluminium hydride affords (S)-2-chloropropanol, the simplest chiral chloro-alcohol. This alcohol undergoes cyclization upon treatment with potassium hydroxide, which causes dehydrohalogenation to give the epoxide, (R)-propylene oxide (methyloxirane).[3]
2-Chloropropionyl chloride reacts with isobutylbenzene to give, after hydrolysis, ibuprofen.[1]
Safety
In general, α-halocarboxylic acids and their esters are good alkylating agents and should be handled with care. 2-Chloropropionic acid is a neurotoxin.[4]
See also
References
- Samel, Ulf-Rainer; Kohler, Walter; Gamer, Armin Otto; Keuser, Ullrich (2005). "Propionic Acid and Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a22_223.
- Koppenhoefer, Bernhardt; Schurig, Volker (1988). "(S)-2-Chloroalkanoic Acids of High Enantiomeric Purity from (S)-2-Amino Acids: (S)-2-Chloropropanoic Acid". Organic Syntheses. 66: 151. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.066.0151.
- Bernhard Koppenhoefer; Volker Schurig (1988). "(R)-Alkyloxiranes of High Enantiomeric Purity from (S)-2-Chloroalkanoic Acids Via (S)-2-Chloro-1-Alkanols: (R)-Methyloxirane". Organic Syntheses. 66: 160. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.066.0160.
- Simpson MG, Wyatt I, Jones HB, Gyte AJ, Widdowson PS, Lock EA (1996). "Neuropathological changes in rat brain following oral administration of 2-chloropropionic acid". Neurotoxicology. 17 (2): 471–480. PMID 8856742.
