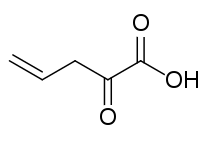
2-Oxopent-4-enoic acid
2-Oxopent-4-enoic acid (2-oxopent-4-enoate) is formed by the dehydration of 4-hydroxy-2-oxopentanoate by 2-oxopent-4-enoate hydratase or by the hydrolysis of 2-hydroxymuconate semialdehyde by 2-hydroxymuconate-semialdehyde hydrolase.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Oxopent-4-enoic acid | |
| Other names
2-Keto-4-pentenoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 1851398 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H6O3 | |
| Molar mass | 114.100 g·mol−1 |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
Pentenoic acid; 4-Hydroxy-3-pentenoic acid; 2-Amino-5-chloro-4-pentenoic acid; (2R)-2-Methylpent-4-enoic acid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Sala-Trepat JM, Evans WC (1971). "The meta cleavage of catechol by Azotobacter species 4-Oxalocrotonate pathway". Eur. J. Biochem. 20 (3): 400–13. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01406.x. PMID 4325686.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.