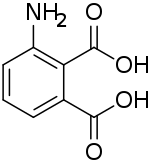
3-Aminophthalic acid
3-Aminophthalic acid is a product of the oxidation of luminol. The reaction requires the presence of a catalyst. A mixture of luminol and hydrogen peroxide is used in forensics. When the mixture is sprayed on an area that contains blood, the iron in the hemoglobin in the blood catalyzes a reaction between the mixture, resulting in 3-aminophthalate which gives out light by chemiluminescence.[1]
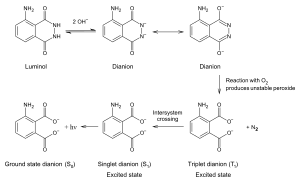 Luminol reaction
Luminol reaction
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-Aminobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid | |
| Other names
3-Aminophthalic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.024.178 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H7NO4 | |
| Molar mass | 181.147 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Harris, Tom. "How Luminol Works". HowStuffWorks. Discovery Communications. Retrieved 5 August 2013.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.