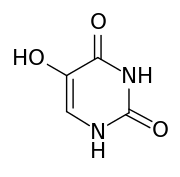
5-Hydroxyuracil
5-Hydroxyuracil is an oxidized form of cytosine that is produced by the oxidative deamination of cytosines by reactive oxygen species.[1] It does not distort the DNA molecule and is bypassed by replicative DNA polymerases. It can miscode for adenine and is potentially mutagenic.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,4,5-Pyrimidinetriol | |
| Other names
5-Hydroxy-2,4(1H,3H)-pyrimidinedione | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.119 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H4N2O3 | |
| Molar mass | 128.087 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Varatharasa Thiviyanathan; Anoma Somasunderam; David E. Volka & David G. Gorenstein (2005). "5-Hydroxyuracil can form stable base pairs with all four bases in a DNA duplex". Chem. Commun. (3): 400–402. doi:10.1039/B414474K. PMID 15645051.
- Helmut Greim; Richard J. Albertini (2012). The Cellular Response to the Genotoxic Insult: The Question of Threshold for Genotoxic Carcinogens. Royal Society of Chemistry. ISBN 9781849731775. Retrieved July 20, 2015.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.