8-Oxogeranial
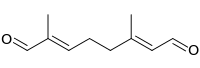
8-Oxogeranial is a chemical substance (also incorrectly called 10-oxogeranial), that is a monoterpene.[1] The terpenoid is produced by 8-hydroxygeraniol dehydrogenase which uses 8-hydroxygeraniol as its substrate. 8-Oxogeranial is itself a substrate for iridoid synthase which synthesizes cis–trans-iridodial and cis–trans-nepetalactol.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2E,6E)-2,6-Dimethylocta-2,6-dienedial | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H14O2 | |
| Molar mass | 166.220 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Dewick (2009) Medicinal Natural Products: A Biosynthetic Approach.
- Miettinen, Karel; Dong, Lemeng; Navrot, Nicolas; Schneider, Thomas; Burlat, Vincent; Pollier, Jacob; Woittiez, Lotte; Van Der Krol, Sander; Lugan, Raphaël; Ilc, Tina; Verpoorte, Robert; Oksman-Caldentey, Kirsi-Marja; Martinoia, Enrico; Bouwmeester, Harro; Goossens, Alain; Memelink, Johan; Werck-Reichhart, Danièle (2014). "The seco-iridoid pathway from Catharanthus roseus". Nature Communications. 5: 3606. Bibcode:2014NatCo...5.....M. doi:10.1038/ncomms4606. PMC 3992524. PMID 24710322.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.