AAZ-A-154
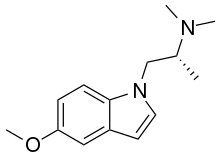
AAZ-A-154 is a novel isotryptamine derivative which acts as a 5-HT2A receptor agonist discovered and synthesized by the lab of Professor David E. Olson at UCDavis. Animal studies suggest that it produces antidepressant effects without the psychedelic action typical of drugs from this class.[1][2] In tests, AAZ-A-154 had antidepressant effects in mice without causing the head-twitch response linked to hallucinogenic effects.[3] Due to the rapidly-induced and enduring neuroplasticity, AAZ-A-154 is a member of the class of compounds known as non-hallucinogenic psychoplastogens.[4] This compound, as well as related compounds, are licensed by Delix Therapeutics and are being developed as potential medicines for neuropsychiatric disorders.[4]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| PubChem CID | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H20N2O |
| Molar mass | 232.327 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
See also
References
- Dong C, Ly C, Dunlap LE, Vargas MV, Sun J, Hwang IW, Azinfar A, Oh WC, Wetsel WC, Olson DE, Tian L (May 2021). "Psychedelic-inspired drug discovery using an engineered biosensor". Cell. 184 (10): 2779–2792.e18. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.03.043. PMC 8122087. PMID 33915107.
- WO 2020176597, Olson DE, Dunlap L, Wagner FF, "N-substituted indoles and other heterocycles for treating brain disorders", published 3 September 2020, assigned to The Regents of the University of California
- Cross, Ryan (2021-09-27). "Delix raises $70 million to synthesize psychedelic-inspired drugs". cen.acs.org. Archived from the original on 2021-09-27. Retrieved 2022-01-14.
- "Can we take the high out of psychedelics?". Wired UK. ISSN 1357-0978. Retrieved 2022-07-07.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.