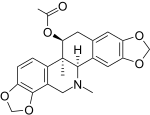
Acetylcorynoline
Acetylcorynoline is a bio-active isolate of Corydalis ambigua. It inhibits the maturing of bone marrow-derived dendritic cells in mice. However, it is only cytotoxic in amounts of greater than 20 μM.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
(5bR,6S,12bR)-5b,13-Dimethyl-5b,6,7,12b,13,14-hexahydro-2H,10H-[1,3]benzodioxolo[5,6-c][1,3]dioxolo[4,5-i]phenanthridin-6-yl acetate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.208.690 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C23H23NO6 | |
| Molar mass | 409.438 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Fu, RH; Wang, YC; Liu, SP; Chu, CL; Tsai, RT; Ho, YC; Chang, WL; Chiu, SC; Harn, HJ; Shyu, WC; Lin, SZ (2013). Caldwell, Charles C (ed.). "Acetylcorynoline impairs the maturation of mouse bone marrow-derived dendritic cells via suppression of IκB kinase and mitogen-activated protein kinase activities". PLOS ONE. 8 (3): e58398. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...858398F. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0058398. PMC 3589392. PMID 23472193.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.