Aconiazide
Aconiazide is an anti-tuberculosis medication. It is a prodrug of isoniazide that was developed and studied for its lower toxicity,[1][2] but it does not appear to be marketed anywhere in the world in 2021.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
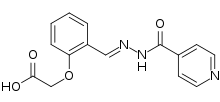
| IUPAC name
2-[2-[(E)-(Pyridine-4-carbonylhydrazinylidene)methyl]phenoxy]acetic acid | |
| Other names
Isonicophen; Phenoxalid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H13N3O4 | |
| Molar mass | 299.286 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Hansen Jr, EB; Dooley, KL; Thompson Jr, HC (1995). "High-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of the antituberculosis drugs aconiazide and isoniazid". Journal of Chromatography B. 670 (2): 259–66. doi:10.1016/0378-4347(95)00176-x. PMID 8548016.
- Peloquin, C. A.; James, G. T.; Craig, L. D.; Kim, M; McCarthy, E. A.; Iklé, D; Iseman, M. D. (1994). "Pharmacokinetic evaluation of aconiazide, a potentially less toxic isoniazid prodrug". Pharmacotherapy. 14 (4): 415–23. doi:10.1002/j.1875-9114.1994.tb02831.x. PMID 7937278. S2CID 6134967.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.