Actaea rubifolia
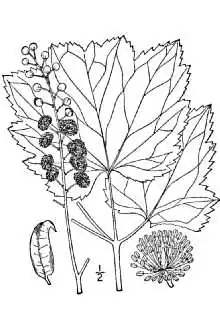
Actaea rubifolia, commonly known as Appalachian black cohosh or Appalachian bugbane, is a species of flowering plant in the buttercup family. The plant does well in alkaline soils[2] and mature forests.[3] The "bugbane" in the name refers to the unpleasantness of its flowers' smell repelling insects. It is poisonous if consumed by humans.[4]
| Actaea rubifolia | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Order: | Ranunculales |
| Family: | Ranunculaceae |
| Genus: | Actaea |
| Species: | A. rubifolia |
| Binomial name | |
| Actaea rubifolia (Kearney) Kartesz | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The plant produces flowers in the early fall from August to October,[3] and is distinctly identifiable by its large stamens and reduced white petals.[5]
The species is vulnerable to extinction; small populations exist in Tennessee, Virginia, Alabama, and the lower Ohio River Valley.[4]
Both Actaea rubifolia and Actaea podocarpa bear resemblance to black cohosh, which, due to its vasodilation properties, is valuable for the treatment of menopause symptoms; harvesters of black cohosh sometimes mistake A. podocarpa for black cohosh, accidentally harvesting it.[6]
References
- "NatureServe Explorer 2.0". explorer.natureserve.org. Retrieved 2023-10-18.
- "Actaea rubifolia". Native Plant Trust.
- "NatureServe Explorer 2.0". explorer.natureserve.org. Retrieved 2023-10-18.
- "Actaea rubifolia (Appalachian bugbane)". florafinder.org. Retrieved 2023-10-18.
- "Cimicifuga rubifolia". illinoisbotanizer.com. Retrieved 2023-10-18.
- Churchill, John B.; Brosi, Sunshine; Howell, James. "Risk Assessment to State Rare Mountain Bugbane in Western Maryland" (PDF).
