Alangium salviifolium
Alangium salviifolium, commonly known as sage-leaved alangium, is a flowering plant in the Cornaceae family. It is also commonly known as Ankolam in Malayalam, Ankola in Kannada, Akola or Ankol in Hindi and Alanji in Tamil. In India, Its mostly found in dry regions in plains and low hills and also found on roadsides.[2][3]
| Alangium salviifolium | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Cornales |
| Family: | Cornaceae |
| Genus: | Alangium |
| Species: | A. salviifolium |
| Binomial name | |
| Alangium salviifolium | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
| |
Etymology
The name Alangium is Latinized from the Malayalam name Alangi, which, in Kerala, refers to Alangium salviifolium.[4] It was named in 1783 by Jean-Baptiste Lamarck in his Encyclopédie Méthodique [5][6]

Description
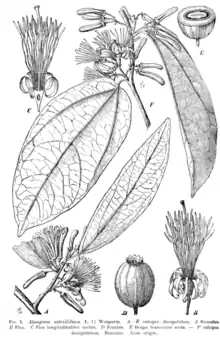
Sage-leaved alangium is a small, bushy tree offering a dense canopy with a short trunk. It bears fragrant white flowers which have green buds. The petals of the flower typically curl backwards exposing the multiple stamens and a linear stigma distinctly sticking out. The fruits are spherical berry like and red in color. The prominent remains of the calyx can be seen distinctly with a white color. The leaves are simple, alternate, oblong-lanceolate.[2][3] The stunted branches end up with sharp ends making it look like thorns.[7]
In India, this tree is mostly found near sandy riverine tracts and road cuttings.[2] This tree flowers between February and April and Fruits between March and May just in time before the rainy season starts. It sheds it leaves completely when it flowers and leaves start coming when it begins to fruit.[7] It is considered as a holy tree and temples have been built near it.[8]



Distribution
It is native to the Indian subcontinent, the Comoro Islands and eastern tropical Africa.[1] In the Indian sub-continent, it is found in Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Goa, Gujarat, Karnataka, Kerala, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Odisha, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, Tripura, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand and West Bengal.[9] Other countries and regions which it occurs in are: Bangladesh; Sri Lanka; Nepal; West Himalya; Comoro Islands; Kenya; and Tanzania.[1]
Biodiversity and ecology
The flowers are bird and bee pollinated. It is mainly pollinated by pale-billed flowerpecker (Dicaeum erythrorhynchos), purple-rumped sunbird (Leptocoma zeylonica), purple sunbird (Cinnyris asiaticus) and two large carpenter bee species, Xylocopa latipes and Xylocopa pubescens.[10][11]
The birds that feed on the fruits are common myna (Acridotheres tristis), babblers (Turdoides sp) and rose-ringed parakeets (Psittacula krameri).[12]
This is the host plant of the larvae of a rare Western Ghat hawkmoth Daphnis minima[13]
Uses
In Ayurveda the roots and the fruits are used for the treatment of rheumatism and haemorrhoid. Externally, it is used for the treatment of bites by rabbits, rats, and dogs.[14] The root-bark is also used in traditional medicine skin problems and as an antidote for snake bite.[2] The root-bark is also used to expel parasitic worms (Platyhelminthes) and other internal parasites from the body. It is used as an emetic and purgative as well.[9]
The wood is said to be hard and close-grained because of which good finishing is possible. It is used to make ornamental work, pestles and rollers and also is good as a fuel wood.[2][3] The stems because of its sharp ends are used as a spear in Kenya. The twigs are also used as toothbrush in India. It is considered to be good for making musical instruments and for making furniture as well.
Gallery
References
- "Alangium salviifolium (L.f.) Wangerin". Plants of the World Online. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Retrieved 23 March 2021.
- Krishen, Pradip (2013). Jungle Trees of Central India. Penguin group. p. 164. ISBN 9780143420743.
- Neginhal, S.G (2011). Forest trees of the western ghats. S.G Neginhal IFS (Retd). p. 176. ISBN 9789350671733.
- Umberto Quattrocchi. 2000. CRC World Dictionary of Plant Names volume I. CRC Press: Boca Raton; New York; Washington, DC;, USA. London, UK. ISBN 978-0-8493-2675-2 (vol. I). (see External links below).
- Alangium At: International Plant Names Index. (See External links below).
- Jean-Baptiste Lamarck. 1783. Encyclopédie Méthodique: botanique. 1(1):174 (See External links below).
- A, Kavitha; N, Deepthi; R, Ganesan; S C, Gladwin Joseph (2012). Common dryland trees of Karnataka. Bangalore: ATREE. p. 42. ISBN 978-81-902338-4-2.
- "Holy Ankola or Alinjal Tree". January 2013. Retrieved 24 April 2023.
- K. N, Ganeshaiah; R, Ganesan; R, Vasudeva; C G, Kushalappa; A R R, Menon; Patwardhan, Ankur; S R, Yadav; Shanker, Uma (2012). Plants of Western Ghats (Vol.1). Bangalore: School of Ecology and Conservation GKVS Bangalore. p. 57.
- Raju, A. J. Solomon; Rao, S. Purnachandra (2006). "Nesting habits, floral resources and foraging ecology of large carpenter bees (Xylocopa latipes and Xylocopa pubescens) in India". Current Science. 90: 1211.
- Aluri Raju, Jacob Solomon; Rao, S Purnachandra; K, Rangaiah (2005). "Bird-mediated pollination and seed dispersal in a deciduous tree species, Alangium salviifolium (L.f.) Wangerin (Alangiaceae) in the Subtropical Eastern Ghats Forests of India". Journal of the National Taiwan Museum: 69.
- J, Patrick DAvid; Manakadan, Ranjit; T, Ganesh (2015). "Frugivory and seed dispersal by birds and mammals in the coastal tropical dry evergreen forests of southern India: A review" (PDF). International Society for Tropical Ecology: 45.
- KUMAR GHORPADÉ; R.R. PATIL; MALLAPPA K. CHANDARAGI (2013). "Notes on Hawk Moths (Lepidoptera—Sphingidae) in the Karwar-Dharwar transect, peninsular India: a tribute to T.R.D. Bell (1863-1948)1" (PDF). Colemania: 9.
- "Alangium salviifolium. Sage Leaved Alangium". Retrieved 24 April 2023.
External links
- [https://web.archive.org/web/20140824082644/http://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/Lobed-leaf%20Alangium.html Alangium platanifolium
- Lobed-leaf Alangium]










_fruits_in_Visakhapatnam.jpg.webp)