Alaska Conservation Society
The Alaska Conservation Society was the first grassroots environmental conservation group in the U.S. state of Alaska.[2] It was founded in 1960 to coordinate opposition to Project Chariot, a plan to blast a harbor at Point Hope, Alaska, using nuclear explosions. The group subscribed to environmental preservation and the principles of conservation. After the defeat of Project Chariot, the group decided to fight the proposed Rampart Dam project on the Yukon River. After succeeding, the society took a stance on the development of the Trans-Alaska Pipeline System, encouraging environmental mitigation during and after its construction. This led to the society becoming a major factor in environmental policy within the state.[3] The group operated between 1960 and 1993 and was superseded by the Alaska Conservation Foundation, which was founded in 1980 and still operates today.
| Formation | 1960 |
|---|---|
| Founder | Ginny Wood[1] Morton Wood[1] |
| Purpose | Conservation |
| Headquarters | College, Alaska; United States |
Founding and History
In 1960, the Alaska Conservation Society was founded by Alaskan environmentalist Ginny Wood and her then husband, Morton "Woody" Wood,[1] at the University of Alaska Fairbanks in College, Alaska to bring together like-minded people in order to better organize opposition to two major projects in Alaska: Project Chariot and the Rampart Dam.[4] The group hoped that its status as an organization "by Alaskans and for Alaskans" would allow its arguments to gain traction in places where speakers from the Continental United States had not.[4] According to Ginny Wood, one of their main reasons for establishing their own organization was that they didn't want "outside people" controlling the newly minted state.[5] Celia M. Hunter, one of the group's founding members, became its first president.[2] Early on, the society operated out of living rooms and utilized a small printing press to distribute their bulletin. Many of the early members were scientists, although this was not true for either the Woods or Hunter.[5]
The Conservation Society was organized into two groups: Alaskan members, who had voting authority, and "associate," or non-Alaskan members, who did not. It was very important to the Woods that Alaskans maintain control over the organization. By 1961, one year after its founding, the Alaska Conservation Society had about 300 members, 50 percent of whom were associate members.[6] Thanks to widening coverage granted it during its opposition to Chariot and Rampart development projects, the group expanded to more than 600 members by 1965.[7] While early on the group focused on things like the negative effects hunting wolves had on ecosystems or the importance of large carnivore conservation, they eventually scrutinized government projects.[5] The group's influence grew after Project Chariot and the Rampart Dam were successfully canceled, a fact illustrated by the selection of Alaska Conservation Society president Ernst W. Muller as commissioner of the Alaska State Department of Environmental Conservation in 1975.[8]
Main Accomplishments
Project Chariot
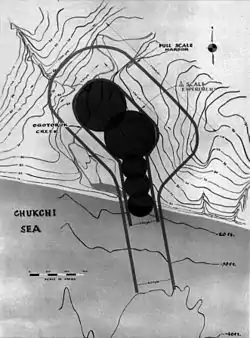
During the conflict with Russia called the Cold War, the US proposed Project Chariot: a plan to detonate atomic bombs at Cape Thompson, near Point Hope, Alaska, to make an artificial bay.[9] It was a part of Operation Plowshare. There was significant local resistance to the project by the Iñupiaq groups who live nearby, but the government conducted some tests in secrecy,[9] although, according to Gerald Johnson, none of the people involved in the project had ever visited the site.[10] Although these documents were declassified in 2014, the full extent of the damage to the local area is not known.[9] The Alaska Conservation Society, in conjunction with local groups, opposed the project.
Despite the ostensible win for ACS and the local Iñupiaq groups, people living in Point Hope continue to suffer elevated levels of certain cancers, indicating radiation, chemical contaminants, and other pollutants.[9] This historical episode contributes to high levels of mistrust among the locals towards government, especially the federal government.[9] Since the experiments were done secretly and the documents involved are difficult to understand, local people have accepted that they may never know exactly what happened. This has been difficult for many Indigenous people of the area to come to terms with.
The Rampart Dam
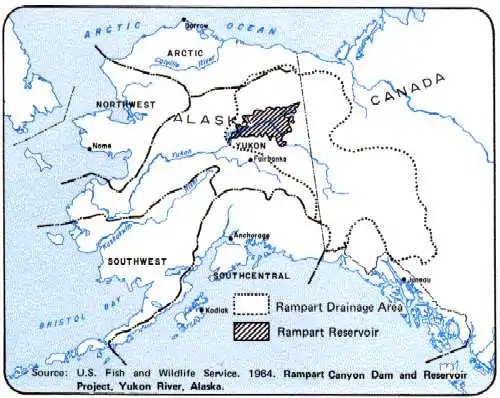
The Rampart Dam was a project suggested to build a large hydroelectric dam on the Yukon River, stopping its flow and creating a large floodplain.[11] Such a dam would have caused significant loss to both Indigenous villages as well as to animal habitat, as the Yukon Flats, when flooded, take up a space greater than that of the current Lake Erie.[11] The Alaska Conservation Society opposed the project. After a long fight, including surveys done by scientists to examine the environmental impact of flooding the Yukon Flats, the project was halted.[11] Ginny Wood cites the Rampart Dam fight as a significant one for the ACS.[5] They brought in outside economists and other people to specifically counter claims made by the government about the benefits the dam would have for the state, including the idea of cheap electricity.[5]
Designation of the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge
The Arctic National Wildlife Refuge, also known as ANWR, lies in Northeastern Alaska and covers 19.3 million acres. It was established in 1980 by President Carter, and cannot be opened up to oil exploration without congressional action.[12] This designation occurred after a number of smaller tracts of land in the same area, with the same name, were protected; the ACS was first involved in 1959, then in 1960 helped protect 8.9 million acres of the refuge.[5] People who contributed significantly to this effort included Olaus and Margaret Murie, as well as George Collins.
Although the ACS contributed to the establishment of the refuge in its early days, debate over ANWR, oil drilling, and conservation continues to this day.
Legacy
Ginny Wood, the founder of ACS, and Celia Hunter, its first president, are considered the matriarchs of Alaskan conservation.[5] In 1993, the Society disbanded. It was replaced by the Alaska Conservation Foundation, which credits Wood and Denny Wilcher, who helped found the Sierra Club, on its website.[13] It also has influenced the state by being an early proponent of wildlife refuges and other large wildernesses that are not considered parks, which continue to this day.[5] Debates over pipelines also continue, such as the Dakota Access Pipeline and others; the ACS was an early example of counter-pipeline debates and voices.[3]
Notes
- "Ginny Wood dies at 95; pioneering Alaska environmentalist". Los Angeles Times. 2013-03-14. Retrieved 2013-03-14.
- State University of New York College of Environmental Science and Forestry. "1988 Feinstone Environmental Awards", ESF.edu. Accessed February 18, 2009.
- Haycox, pp. 267-268
- Coates, p. 101.
- Brewster, Karen (2012). Boots, Bikes, and Bombers. Fairbanks, Alaska: University of Alaska Press. pp. Ch. 17.
- Coates, p. 144
- Coates, p. 150
- Coates, p. 224
- Hughes, Zachariah; Media, Alaska Public (2014-08-09). "As Project Chariot Clean-Up Ends, Legacy Lingers for Point Hope". Alaska Public Media. Retrieved 2020-11-23.
- O'Neill, Dan. (2015). The Firecracker Boys : H-Bombs, Inupiat Eskimos, and the Roots of the Environmental Movement. New York: Basic Books. ISBN 978-0-465-09752-4. OCLC 913696151.
- "Area History - Yukon Flats - U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service". www.fws.gov. Retrieved 2020-11-29.
- July 13; Palmer, 2016 Brian. "The Long, Long Battle for the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge". NRDC. Retrieved 2020-11-30.
- "Founders | Alaska Conservation Foundation". Retrieved 2020-11-23.
References
- Coates, Peter A. The Trans-Alaska Pipeline Controversy. University of Alaska Press, 1991.
- Haycox, Stephen. Alaska: An American Colony. University of Washington Press, 2006.
- Layne, Elizabeth N. "Nominees for the American Heritage Society Awards", American Heritage Magazine. February 1970. Volume 21, Issue 2. p. 3.
- The Associated Press. "Two pioneering conservationists honored", The Peninsula Clarion. August 16, 2001. Accessed February 18, 2009.
- Woodford, Riley. "Tales of pioneer conservationists", The Juneau Empire. Accessed February 18, 2009.