Alexidine
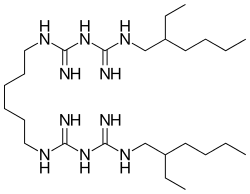
Alexidine is an antimicrobial of the biguanide class.[1] More specifically, it is a bisbiguanide.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
N1,N1′-(Hexane-1,6-diyl)bis[N3-(2-ethylhexyl)imidodicarbonic diamide] | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.040.981 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C26H56N10 | |
| Molar mass | 508.804 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Barrios, Rocío; Ferrer-Luque, Carmen María; Arias-Moliz, María Teresa; Ruiz-Linares, Matilde; Bravo, Manuel; Baca, Pilar (November 2013). "Antimicrobial substantivity of alexidine and chlorhexidine in dentin". J Endod. 39 (11): 1413–5. doi:10.1016/j.joen.2013.07.038. PMID 24139264.
- Tanzer JM, Slee AM, Kamay BA (1977). "Structural requirements of guanide, biguanide, and bisbiguanide agents for antiplaque activity". Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 12 (6): 721–9. doi:10.1128/aac.12.6.721. PMC 430011. PMID 931371.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.