Alfio Giuffrida
Alfio Giuffrida, also known as Alfio Giuffrida AG Sinnwerke (born 28 January 1953 in Zafferana Etnea) is a contemporary Italian sculptor, installation artist, set designer and painter.
Alfio Giuffrida | |
|---|---|
 Alfio Giuffrida (2008) | |
| Born | 28 January 1953 Zafferana Etnea, Italy |
| Nationality | Italian |
| Education | Accademia di Belle Arti di Roma |
| Known for | Painting, sculpture, scenography |
| Website | AG Sinnwerke |
Biography
Giuffrida's affinity for art emerged during his formative years. His passion was evident as he meticulously crafted a scaled replica of his hometown's church, dedicating years to perfecting it through multiple iterations. This unwavering pursuit of excellence, seeking to translate his creative visions into their finest form, remained a constant throughout his artistic journey.
During his youth, Giuffrida delved into painting and experimented with various painting and collage techniques. His artworks often exude tranquility, featuring serene and azure spaces. Notably, he incorporated blister packaging into his pieces, creating a visual reminiscent of a computer keyboard. This unique addition invokes imagery of both technological interfaces and lunar-filtered aerial snapshots, offering viewers an alternative perspective on urban landscapes and city structures.
A period of intense nature studies followed these works, though he did not formulate them as naturalistic reproductions but instead took them in an abstract direction. With scientific precision, he examined plant structures in particular, dissecting organic material and making cross sections in natural tissue in order to study the essence of things and figure out the basic nature of form. Giuffrida understood the minutiae at the heart of the elements he analysed as fundamental forms of nature, which are combined in natural creation in myriad, endlessly varied formations. He reduces these basic shapes to geometric patterns which he captures in small square pictures in equally diverse variations. These mainly take the form of black-and-white dabbed paintings, some of which are on transparent paper that seems to correspond to the materiality of the diaphanous floral tissue. It is at this point that he begins to be captivated by the technical quality and effect of transparency, another guiding principle running consistently through Giuffrida's art and his constant search for the best forms of expression for the wide range of materials suited to him.
Works
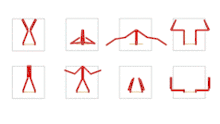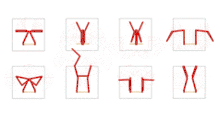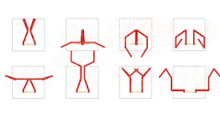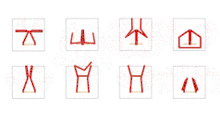
There was a concentrated series of works in the early 1970s influenced by Minimalism (Minimal Art). Among other things, he created transparent, folded canvases that incorporated superimposed folded shapes, form elements – cut out and therefore definitively liberated from their original context: floating particles in a solidified fluid, like scattered inlays in radiant amber. The colour only becomes apparent in the light and iridescence, further differentiated by the surface. As in other still haptic works, the first configurations are not created through construction but through attachments that allow forms to emerge through a mechanical process, almost by chance and in a semi-experimental way. Impression, abrasion, reprinting, reduction are pseudo-objective processes that resemble scientific production methods in the infusion of chance and methodology, subjectivity and objectivity. Pastel colours are dabbed on paper then gently lifted off, their image detached onto gauze impregnated with glue, the colour particles sticking to it like delicate pollen. In the milky-white of the semi-transparent base mass, the detached pigments float like preciously preserved spolia and spores, sprinkled like stars over the universe of the paper. Imperceptibly yet inexorably their blaze expands the sfumato-white background into an all-encompassing space which attains cosmic dimensions and spans light years.
In 1975 he returned to non-figurative representation. This period saw him participating at the X Rome Quadriennale that year.
Between 1977 and 1985 he worked as a freelance painter and set designer in Rome. At this point he began to develop a substantial body of painted work, a stringent transitional route in which the reduction of form revealed his early proximity to Minimalist Art and at the same time took on mythical, fantastic features. His pictorial language incorporates traces of Italian Futurism (Giacomo Balla, Carlo Carrà), of painters such as Lucio Fontana, Mario Nigro, Gustav Klimt, Sonia and Robert Delaunay, Pablo Picasso and Wassily Kandinsky. Added to which, it can also be traced back to Pre-Columbian Mayan art. Experience of post-Impressionism (Pointillism) combines with computer graphics techniques (raster graphics), which in turn have links to the visual effects of his current high-tech constructions (microwave towers).
He moved to Cologne in 1986, deliberately setting his sights on one of the most active centres in contemporary art at that time. The colours appear in characteristic dapple style on large-format canvasses, under which shapes are silhouetted, apparently moving as if behind textured glass. The horizontally layered colours are broken up in irregular though rhythmic sequences, and in this way suggest the movement of an undetected being that is captured in a distortion akin to a wipe effect in photography. Something similar happens in the human images group of works in which figurative representation becomes an experimental sphere. The human images develop their suggestive power through serial sequencing and dynamic distortion. In their mask-like reproduction of almost identical forms, they run counter to any expression of unique personality, which differs from the classical portrait which emphasizes one person's individuality. The human being mutates into a prototype, appearing in diverse variations within the serial arrangement and disappearing in the masses.
From 1990 to 2004 he worked in his studio in Bonn. Still committed to varied sequences and rhythmic movement, Giuffrida ended up in his new group of works at the picture puzzle using abstract elements and shapes. Canvasses were now inspired by architectural and ornamental structures captured in mysterious light and shadow arrangements, in shades of grey-blue and white. With the wooden reliefs and sculptures that followed in 1995, Giuffrida transposed the notion of picture puzzles into the third dimension. He made assemblages from dismantled individual items and furniture freed from their functional context, combining them with worked wood panels. The relief-like wooden sculptures look like magnified details of the painted puzzles. Symmetrical arrangements, repetitions and sequences crop up here as well.
Following his principle of systematically carrying on the experiments he had begun with these expressive tools, Giuffrida used the static wooden reliefs to develop symmetrical yet mobile iron sculptures in similar dimensions, the so-called Elements or Adjustable Sculptures. Giuffrida linked iron strips with multiple joints together in such a way that they could pivot on the joints; the observer consciously becomes a participant in art by being encouraged to alter the sculptures.

From this point the road led to new materials and dimensions. Sculptures made of iron and Perspex represented a new group of works. Initially they were made life-size. Everyday found objects were put on Perspex plinths and became assemblages associated with new meaning. Later they took up so much room that the Perspex bases grew into navigable spaces with corridors and transparent walls, while antenna-like watchmen or signals loomed high above the viewers. Giuffrida increasingly brought his creative drive to the public space. The project The whole world as a sculpture park was conceived and presented in public for the first time in September 1997. A tower made of steel struts about 21 metres high forms the end point of a series of steel sculptures, each of which denotes one of the steps linking the graphic design and the end result of the monument. The structures of the steel sculptures are reminiscent of electricity pylons, bearers and conductors of energy that belong to the absolutely essential nature of the living world, just like art. The ultimate aim of the project is to gradually replace all pylons with new large-scale sculptures designed by artists that are both art works and functional objects.

2003 saw the founding of the fictitious factory A.G. Sinnwerke®. The first products to appear under the A.G. Sinnwerke label were the CDs, CD-Sets, and Selbstbau-Sets. More concentrated object cycles followed: CD-Roms, Samples, Ovali, Kugeln, Irrigatoren, Mona Lisa, and Sample-Sets, all offered in blister packs. Adjustable, space-consuming sculptures were made in parallel, their models presented in the form of corsets. Many ideas were captured in painting. He followed the same principle when he continued the richly varied idea of the objects in painting : Irrigatoren, Irrigatoren-Sätze, CD-Homes, Figuren, Enthüllungen, Bezüge, Seitenblicke, Antennen, Töpfe, Tempel, Angebote, CD-Stapel, Kathedralen etc. Eventually the artist provided only the material, that is, the Do-it-yourself-Baukästen, allowing the buyer to come to a personal decision about what form to use for his or her individual picture.
Exhibitions
Selected exhibitions
March/April 1989 Bahnwärterhaus Villa Merkel – Galerie der Stadt Esslingen. February/April 2001 Suermondt-Ludwig-Museum Aachen. April/June 2001 Stadtmuseum Siegburg. July/August 2004 Mannheimer Kunstverein. September/December 2006 Märkisches Museum Witten. March/June 2007 Stadtmuseum Bergkamen.
Stage design
Alongside his creative work Giuffrida has devoted himself to set design for dance theatre ever since his days in Rome. The stage images he has created are characterized by light, transparency, movement and a lightness of touch. Typical features are large-scale objects without a fixed installation, like steel struts and frames that the dancers can move around in the space: the rhythm and variation of stage set and dance are mutually complementary. This allows the creation of ever-new spatial definitions and flexible images, in which the notion of the relativity of viewer and object through the movement in space or the movement of space itself in turn becomes the theme itself. From 1995 he has been set designer for, among others, Tanzforum Köln, Euregio Tanzforum, and Jochen Ulrich.
Notebook, Premiere, 2 May 1995, Oper der Stadt Köln. Die Verlobung in St. Domingo, 17 June 1995, Schlosserei Schauspiel Köln. Goya-Danzas negras, 20 December 1995, Oper der Stadt Köln. Get up Early, 22 February 1996, Internationales Tanzfestival Wien. Citizen Kane, 4 April 1997, Oper der Stadt Köln. Diaghilew - Die Offenbarung, 10 January 1999, Tiroler Landestheater Innsbruck. Lorca y Dalí-Perros de Luna, 19 February 1999, Stadsschouwburg Heerlen (NL). Mon Orphée, 1 April 2000, Ludwig Forum für Internationale Kunst, Aachen. Phädra, 30 November 2000, Deutsche Oper am Rhein, Düsseldorf. Romeo und Julia, 20 January 2001, Tiroler Landestheater Innsbruck. Casanova, 10 November 2001, Tiroler Landestheater Innsbruck. Diaghilew - Die Favoriten, 8 November 2003, Aalto Theater Essen. Caravaggio, 22 November 2003, Tiroler Landestheater Innsbruck. Sissi - Kaiserliche Hoheit, 22 October 2005, Tiroler Landestheater Innsbruck.
Bibliography
- Künstler in Köln 1990, Köln 1989. M. Haas, A. Tolnay (Bearb.)
- Grafische Sammlung der Stadt Esslingen am Neckar, Bestands-Kat. II, Esslingen 1991
- B. Colarossi (Ed.), Quadriennale D′arte di Roma, Inv. Dell′arch., Rome 2000, ISBN 8876211276
- Ulrich Schneider, Gert Fischer: Suermondt Ludwig Museum Aachen
- Stadtmuseum Siegburg (Hrsg.): Giuffrida, Aachen/Siegburg 2001, ISBN 3-00-007525-9.
- Martin Stather: A.G. Sinnwerke
- Mannheimer Kunstverein (Hrsg.): A.G. Sinnwerke Giuffrida CDs, Bonn 2004, ISBN 3-00-014058-1.
- Nele Lipp, Uwe Rüth: Skulpturenmuseum Glaskasten Marl (Hrsg.): Körper – Leib – Raum: Der Raum im zeitgenössischen Tanz und in der zeitgenössischen Plastik, Marl 2006, ISBN 3-924790-73-6.
Gallery
 Spiegel-exp9, 2009
Spiegel-exp9, 2009 Irrigatoren-exp8, 2006
Irrigatoren-exp8, 2006 Figuren-exp5, 2009
Figuren-exp5, 2009 Figuren-exp34, 2009
Figuren-exp34, 2009
 Bezüge-exp4, 2008
Bezüge-exp4, 2008 Bezüge-exp7, 2008
Bezüge-exp7, 2008 Kathedralen-Do it yourself-Baukaesten-Set1, 2009
Kathedralen-Do it yourself-Baukaesten-Set1, 2009 Kathedralen-exp1, 2009
Kathedralen-exp1, 2009
 Angebote-exp15, 2008
Angebote-exp15, 2008 Kathedralen-schwerelos-exp7, 2009
Kathedralen-schwerelos-exp7, 2009 Antennen-exp2, 2009
Antennen-exp2, 2009 CD-HOMES-exp19, 2008
CD-HOMES-exp19, 2008
See also
References
External links
- a-g-sinnwerke.com Archived 2021-11-24 at the Wayback Machine
- a-g-sinnwerke.de Archived 2012-04-02 at the Wayback Machine
- a-g-sinnwerke.eu Archived 2016-04-22 at the Wayback Machine
- a-g-sinnwerke.net Archived 2013-07-13 at the Wayback Machine
- Alfio Giuffrida Landestheater Linz Person Details