Allantoic acid
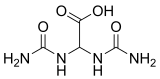
Allantoic acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula C4H8N4O4. It is a crystalline acid obtained by hydrolysis of allantoin.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Bis(carbamoylamino)acetic acid[1] | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 3DMet | |
| 1790227 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.487 |
| EC Number |
|
| 240954 | |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | allantoic+acid |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H8N4O4 | |
| Molar mass | 176.132 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.618 g mL−1 |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 219.4 °C (426.9 °F; 492.5 K) |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
In nature, allantoic acid is produced from allantoin by the enzyme allantoinase (encoded by the gene AllB (Uniprot: P77671) in Escherichia coli and other bacteria).
References
- "allantoic acid - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 16 September 2004. Identification. Retrieved 27 June 2012.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.