Allylescaline
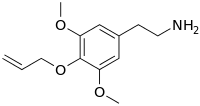
Allylescaline (4-allyloxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine) is a lesser-known psychedelic drug. It is closely related in structure to mescaline. Allylescaline was first synthesized by Otakar Leminger in 1972.[1] The compound was later synthesized by Alexander Shulgin and further described in his book PiHKAL.[2] The dosage range is listed as 20–35 mg, and the duration 8–12 hours.[2] Allylescaline produces an entactogenic warmth, an entheogenic effect, and a feeling of flowing energy. Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of allylescaline.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-{3,5-Dimethoxy-4-[(prop-2-en-1-yl)oxy]phenyl}ethan-1-amine | |
| Other names
2-[4-(Allyloxy)-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl]ethan-1-amine 2-[4-(Allyloxy)-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl]ethanamine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H19NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 237.299 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Legal status
Allylescaline is illegal in Sweden as of January 2016.[3]
See also
References
- Leminger, Otakar (1972). "The Chemistry of Alkoxylated Phenethylamines – Part 2". Chemický Průmysl. 22: 553.
- AL Entry in PiHKAL
- "31 nya ämnen kan klassas som narkotika eller hälsofarlig vara" (in Swedish). Folkhälsomyndigheten. November 2015.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.