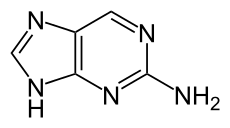
2-Aminopurine
2-Aminopurine, a purine analog of guanine and adenine, is a fluorescent molecular marker used in nucleic acid research.[1] It most commonly pairs with thymine as an adenine-analogue, but can also pair with cytosine as a guanine-analogue.[2] For this reason it is sometimes used in the laboratory for mutagenesis.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
9H-Purin-2-amine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.545 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H5N5 | |
| Molar mass | 135.130 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
See also
References
- Jean JM, Hall KB (2001). "2-Aminopurine fluorescence quenching and lifetimes: role of base stacking". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98 (1): 37–41. doi:10.1073/pnas.011442198. PMC 14540. PMID 11120885.
- Sowers LC, Fazakerley GV, Eritja R, Kaplan BE, Goodman MF (1986). "Base pairing and mutagenesis: observation of a protonated base pair between 2-aminopurine and cytosine in an oligonucleotide by proton NMR". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83 (15): 5434–5438. Bibcode:1986PNAS...83.5434S. doi:10.1073/pnas.83.15.5434. PMC 386301. PMID 3461441.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.