Stress management
Stress management consists of a wide spectrum of techniques and psychotherapies aimed at controlling a person's level of stress, especially chronic stress, usually for the purpose of improving everyday functioning. Stress produces numerous physical and mental symptoms which vary according to each individual's situational factors. These can include a decline in physical health, such as headaches, chest pain, fatigue, and sleep problems,[1] as well as depression. The process of stress management is named as one of the keys to a happy and successful life in modern society. Life often delivers numerous demands that can be difficult to handle, but stress management provides a number of ways to manage anxiety and maintain overall well-being.
There are several models of stress management, each with distinctive explanations of mechanisms for controlling stress. Much more research is necessary to provide a better understanding of which mechanisms actually operate and are effective in practice.
Historical foundations
Walter Cannon and Hans Selye used animal studies to establish the earliest scientific basis for the study of stress. They measured the physiological responses of animals to external pressures, such as heat and cold, prolonged restraint, and surgical procedures then extrapolated from these studies to human beings.[2][3]
Subsequent studies of stress in humans by Richard Rahe and others established the view that stress is caused by distinct, measurable life stressors, and further, that these life stressors can be ranked by the median degree of stress they produce (leading to the Holmes and Rahe stress scale). It is important to note that the done by Holmes and Rahe is focused on how life's stressors can influence ones health and wellness. The scale was developed to measure the effects of stress on health using life change units, in an attempt to quantify stress and its correlation to illness.Thus, stress was traditionally conceptualized to be a result of external insults beyond the control of those experiencing the stress. More recently, however, it has been argued that external circumstances do not have any intrinsic capacity to produce stress, but instead, their effect is mediated by the individual's perceptions, capacities, and understanding.
Models
The generalized models are:
- The emergency response/fight-or-flight response by Walter Cannon (1914, 1932)
- General Adaptation Syndrome by Hans Selye (1936)
- Stress Model of Henry and Stephens (1977)
- Transactional (or cognitive) Stress Model / stress model of Lazarus after Lazarus (1974)
- Theory of resource conservation by Stevan Hobfoll (1988, 1998; Hobfoll & Buchwald, 2004)
Transactional model
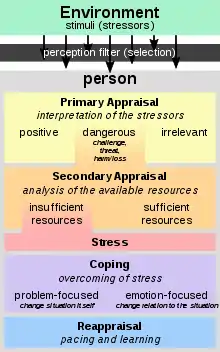
In 1981, Richard Lazarus and Susan Folkman suggested that stress can be thought of as resulting from an "imbalance between demands and resources" or as occurring when "pressure exceeds one's perceived ability to cope". Stress management was developed and premised on the idea that stress is not a direct response to a stressor but rather an individual's resources and abilities to cope and mediate the stress response which are amenable to change, thus allowing stress to be controllable.[4][5]
Among the many stressors mentioned by employees, these are the most common:
- Conflicts in company
- The way employees are treated by their bosses/supervisors or company
- Lack of job security
- Company policies
- Co-workers who do not do their fair share
- Unclear expectations
- Poor communication
- Not enough control over assignments
- Inadequate pay or benefits
- Urgent deadlines
- Too much work
- Long hours
- Time consumption
- Uncomfortable physical conditions
- Relationship conflicts
- Co-workers making careless mistakes
- Dealing with rude customers
- Lack of co-operation
- How the company treats co-workers[6]
In order to develop an effective stress management program, it is first necessary to identify the factors that are central to a person controlling his/her stress and to identify the intervention methods which effectively target these factors. Lazarus and Folkman's interpretation of stress focuses on the transaction between people and their external environment (known as the Transactional Model). The model contends that stress may not be a stressors if the person does not perceive the stressors as a threat but rather as positive or even challenging. Also, if the person possesses or can use adequate coping skills, then stress may not actually be a result or develop because of the stressors. The model proposes that people can be taught to manage their stress and cope with their stressors. They may learn to change their perspective of the stressors and provide them with the ability and confidence to improve their lives and handle all of the types of stressors.
Health realization/innate health model
The health realization/innate health model of stress is also founded on the idea that stress does not necessarily follow the presence of a potential stressor. Instead of focusing on the individual's appraisal of so-called stressors in relation to his or her own coping skills (as the transactional model does), the health realization model focuses on the nature of thought, stating that it is ultimately a person's thought processes that determine the response to potentially stressful external circumstances. In this model, stress results from appraising oneself and one's circumstances through a mental filter of insecurity and negativity, whereas a feeling of well-being results from approaching the world with a "quiet mind".[7][8] This theory deposits that moods fluctuate and cannot be changed by a specific pattern of thinking. Mental discomfort is only deepened by focus on how to change one's mood, so moods should be "waited out" and dwelling avoided based on this framework.[9] This model proposes that helping stressed individuals understand the nature of thought—especially providing them with the ability to recognize when they are in the grip of insecure thinking, disengage from it, and access natural positive feelings—will reduce their stress.
Techniques
Many stress management techniques cope with stresses one may find themselves withholding. Some of the following ways reduce a lower than usual stress level temporarily, to compensate the biological issues involved; others face the stressors at a higher level of abstraction:
- Autogenic training
- Social activity
- Cognitive therapy
- Conflict resolution
- Cranial release technique
- Getting a hobby
- Meditation
- Mindfulness
- Music as a coping strategy
- Deep breathing
- Yoga Nidra
- Nootropics
- Reading novels
- Prayer
- Relaxation techniques
- Artistic expression
- Fractional relaxation
- Humour
- Physical exercise
- Progressive relaxation
- Spas
- Somatics training
- Spending time in nature
- Stress balls
- Natural medicine
- Clinically validated alternative treatments
- Time management
- Planning and decision making
- Listening to certain types of relaxing music[10][11]
- Spending quality time with pets
Some stresses are caused by high demand levels that load the person with extra effort and work. in this case, a new time schedule can be worked up, limiting the normal frequency and duration of former schedules until the period of abnormally high personal demand has passed.
Techniques of stress management will vary according to the philosophical paradigm.[12]
Stress prevention and resilience
Although many techniques have traditionally been developed to deal with the consequences of stress, considerable research has also been conducted on the prevention of stress, a subject closely related to psychological resilience-building. A number of self-help approaches to stress-prevention and resilience-building have been developed, drawing mainly on the theory and practice of cognitive-behavioral therapy.[13]
Measuring stress
There are different ways to measure stress levels. One way is through psychological testing. The Holmes and Rahe Stress Scale is used to rate stressful life events and how life stressors influence illness. The DASS (Depression Anxiety Stress Scales) contains a scale for stress based on self-report items. Changes in blood pressure and galvanic skin response can also be measured to test stress levels. A digital thermometer can be used to evaluate changes in skin temperature, which can indicate activation of the fight-or-flight response drawing blood away from the extremities. Cortisol is the main hormone released during a stress response and measuring cortisol from hair will give a 60- to 90-day baseline stress level of an individual. This method of measuring stress is currently the most popular method in the clinic .
Despite stress often being thought of as a subjective experience, levels of stress are readily measurable; using various physiological tests, similar to those used in polygraphs. An example of stress being measured is using nano EEG sensors in detecting stress.[14]
Effectiveness
Stress management has physiological and immune benefits.[15]
Positive outcomes are observed using a combination of non-drug interventions:[16]
- treatment of anger or hostility,
- autogenic training which is a relaxation technique used to reduce stress and bring the mind and the body into balance through repeated exercises, such as deep breathing, to promote mental relaxation. Research done by L. Varvogli and C. Darviri shows that this technique has several therapeutic health benefits aiding in those that experienced tension headaches, heart disease, anxiety, and many others.
- talking therapy (around relationship or existential issues)
- biofeedback allows people to monitor their bodies internal function such as, heart rate, muscle tension, temperature, and use this information to learn how to control the bodies response which can lead to better physical, mental, and emotional health. Some consider it to be effective however critics have compared its efficacy[17] to that of conventional therapies as well as the cost effectiveness of biofeedback is uncertain.
- cognitive therapy for anxiety or clinical depression
Types of stress
Acute stress
Acute stress is the most common form of stress among humans worldwide.[18] It deals with the pressures of the near future or the very recent past. While acute stress is often interpreted as being a negative experience, it can actually be beneficial and even necessary for one's wellbeing because of its protective effects against potentially dangerous threats.[19] Slamming on the brakes while driving in order to avoid a car accident could be considered a moment of beneficial acute stress.[20] Running or any other form of exercise would also be considered an acute stressor. Some exciting or exhilarating experiences such as riding a roller coaster is an acute stress but is usually very enjoyable. Acute stress is a short term stress and as a result, does not have enough time to do the damage that long term stress causes.[21]
Chronic stress
Unlike acute stress, which only lasts for a moment, chronic stress lasts for longer time spans. It has a wearing effect on people that can become a very serious health risk if it continues over a long period of time.
Chronic stress can lead to memory loss, damage spatial recognition and produce a decreased drive of eating. Additional symptoms of chronic stress include aches and pains, insomnia or other sleep disturbances, changes in social behaviors, low energy, emotional withdrawal or other changes in emotional responses, and unfocused thinking.[22] Chronic stress has also been associated with other medical conditions such as hypertension, heart disease, diabetes, obesity, and arthritis.[23]
The severity varies from person to person. Gender difference can also be an underlying factor. Women are able to take longer durations of stress than men without showing the same maladaptive changes. Men can deal with shorter stress duration better than women can but once males hit a certain threshold, the chances of them developing mental issues increase drastically.[24]
Chronic stress is a major health issue that affects people of all ages and can have profound effects on physical and mental health. It is a long-standing, unrelieved, and unavoidable stress, such as busy work and school schedules, and complex relationships. Over time, chronic stress can alter the body's systems, leading to a variety of illnesses and conditions.[25]
Workplace
All of us have some position in society, in the workplace, within the family, economic status and so on. Unfortunately, most of us are unwilling to accept where we are. Instead, we wish we were somewhere else, usually at a higher position. Managing that stress becomes vital in order to keep up job performance as well as relationship with co-workers and employers.[26] For some workers, changing the work environment relieves work stress. Making the environment less competitive between employees decreases some amounts of stress.
Author J, Carr [27] highlighted three areas of the workplace that affects the levels of stress experienced which are: Job demands, individual differences, and social demands. These areas that heighten stress are addressed in Rahe's scale suggesting that some of the greatest stressors in life are connected to the workplace
That said, stress in the workplace does not always have to be negatively viewed. When managed well, stress can increase employees' focus and productivity.
According to the Yerkes–Dodson law, stress is beneficial to human functioning, but only up to a point. People who experience too low levels of stress might feel understimulated and passive; people experiencing stress that are at excessively high levels would feel overwhelmed, anxious, and irritable. Thus, establishing an optimum level of stress is key.[28]
Organizational stress levels that an individual faces is dependent not just on external factors such as job characteristics or environment, but also on intrapersonal factors such as personality, temperament, and individual coping and thinking styles. Both aspects need to be managed well.
Also, stress at workplace is not limited to employees. Entrepreneurs also undergo stress[29] This stress can vary from team management, business management or unfavorable policy from the government.
Some examples of stressors in the workplace can be their perception of Organization Commitment, which is the way an employee conceptualizes his/her reasons for staying in the organizations for either Affective, Continuance, or Normative reasons.[30]
Affective commitment to the organization is ideal, as it is the situation where an employee strongly identifies with the values and culture of the organization. While this is not directly telling of an employee's stress levels, genuine interest and enjoyment in the employee's work and work relations places the employee in a good position to manage stress well.
Employees who stay in an organization for continuance reasons stay as a result of weighing the pros and cons, and then decides that the opportunity cost of leaving the organization is too high.
Employees under this category might experience moderate levels of stress, as their reasons for staying is driven more by external rather than internal motivation.
Employees who stay for normative reasons, however, are most likely to experience the highest levels of stress, as these are the employees who stay out of obligation and duty.[31]
Salary can also be an important concern of employees. Salary can affect the way people work because they can aim for promotion and in result, a higher salary. This can lead to chronic stress.
Cultural differences have also shown to have some major effects on stress coping problems. Eastern Asian employees may deal with certain work situations differently from how a Western North American employee would.[32] In a study conducted in Malaysia, it was found that while the classification of workplace stress is similar between Malaysians and Western employees, the perception of workplace stress as well as the approaches to coping with stress were different.[32]
In order to manage stress in the workplace, employers can provide stress managing programs[33] such as therapy, communication programs, and a more flexible work schedule.[34] There have been many studies conducted demonstrating the benefits of mindfulness practices on subjective well-being and work outcomes.[35] Productivity, organization, and performance increase, while burnout rates decrease.
Medical environment
A study was done on the stress levels in general practitioners and hospital consultants in 1999. Over 500 medical employees participated in this study done by R.P Caplan. These results showed that 47% of the workers scored high on their questionnaire for high levels of stress. 27% of the general practitioners even scored to be very depressed. These numbers came to a surprise to Dr. Caplan and it showed how alarming the large number of medical workers become stressed out because of their jobs. Managers stress levels were not as high as the actual practitioners themselves. An eye opening statistic showed that nearly 54% of workers suffered from anxiety while being in the hospital. Although this was a small sample size for hospitals around the world, Caplan feels this trend is probably fairly accurate across the majority of hospitals.[36]
In addition, there is a study that the objective of this study was to investigate the relationship between work performance and self-reported symptoms of depression, stress, and anxiety among nurses working in tuberculosis (TB)/HIV and COVID-19 units on Timor Island, Indonesia. The study used a comparative, cross-sectional design and collected data between October 2020 and January 2021. The study group comprised 236 nurses working in TB/HIV isolation rooms and 423 nurses in COVID-19 isolation rooms. The Depression, Anxiety, and Stress scale (DASS-42) and a work performance questionnaire were used to collect data, which were analyzed using independent t-testing and Pearson correlation coefficient. The results showed that the mean DASS-42 scores of nurses in TB/HIV isolation units were low, indicating minimal effects, while those in COVID-19 isolation units demonstrated moderate levels of depression, stress, and anxiety. Additionally, the work performance results indicated that the nurses in the TB/HIV isolation rooms had sufficient work performance, while those in the COVID-19 isolation rooms had weaker work performance. There was a significant difference in work performance between nurses in the two units. The study concluded that there was a correlation between nurses' depression, stress, and anxiety levels and their work performance in TB/HIV and COVID-19 isolation units.[37]
Stress management programs
Many businesses today have begun to use stress management programs for employees who are having trouble adapting to stress at the workplace or at home. Some companies provide special equipments adapting to stress at the workplace to their employees, like coloring diaries[38] and stress relieving gadgets.[39] Many people have spill over stress from home into their working environment. There are a couple of ways businesses today try to reduce the stress levels of their employees. One way is through individual intervention. This starts off by monitoring the stressors in the individual. After monitoring what causes the stress, next is attacking that stressor and trying to figure out ways to alleviate them in any way. Developing social support is vital in individual intervention, being with others to help you cope has proven to be a very effective way to avoid stress. Avoiding the stressors altogether is the best possible way to get rid of stress but that is very difficult to do in the workplace. Changing behavioral patterns, may in turn, help reduce some of the stress that is put on at work as well.
Employee assistance programs can include in-house counseling programs on managing stress. Evaluative research has been conducted on EAPs that teach individuals stress control and inoculation techniques such as relaxation, biofeedback, and cognitive restructuring. Studies show that these programs can reduce the level of physiological arousal associated with high stress. Participants who master behavioral and cognitive stress-relief techniques report less tension, fewer sleep disturbances, and an improved ability to cope with workplace stressors.[40]
Another way of reducing stress at work is by simply changing the workload for an employee, or even giving them more control as to when or where they work.[41] Some may be too overwhelmed that they have so much work to get done, or some also may have such little work that they are not sure what to do with themselves at work.
Improving communications between employees also sounds like a simple approach, but it is very effective for helping reduce stress. Sometimes making the employee feel like they are a bigger part of the company, such as giving them a voice in bigger situations shows that you trust them and value their opinion. Having all the employees mesh well together is a very underlying factor which can take away much of workplace stress. If employees fit well together and feed off of each other, the chances of much stress are minimal. Lastly, changing the physical qualities of the workplace may reduce stress. Changing things such as the lighting, air temperature, odor, and up to date technology.
Intervention is broken down into three steps: primary, secondary, tertiary. Primary deals with eliminating the stressors altogether. Secondary deals with detecting stress and figuring out ways to cope with it and improving stress management skills. Finally, tertiary deals with recovery and rehabbing the stress altogether. These three steps are usually the most effective way to deal with stress not just in the workplace, but overall.[42]
Aviation industry
Aviation is a high-stress industry, given that it requires a high level of precision at all times. Chronically high stress levels can ultimately decrease the performance and compromise safety.[43] To be effective, stress measurement tools must be specific to the aviation industry, given its unique working environment and other stressors.[44] Stress measurement in aviation seeks to quantify the psychological stress experienced by aviators, with the goal of making needed improvements to aviators' coping and stress management skills.[44]
To more precisely measure stress, aviators' many responsibilities are broken down into "workloads." This helps to categorise the broad concept of "stress" by specific stressors.[45] Additionally, since different workloads may pose unique stressors, this method may be more effective than measuring stress levels as a whole. Stress measurement tools can then help aviators identify which stressors are most problematic for them, and help them improve on managing workloads, planning tasks, and coping with stress more effectively.
To evaluate workload, a number of tools can be used. The major types of measurement tools are:
- Performance-based measures;
- Subjective measures, like questionnaires which aviators answer themselves; and
- Physiological measures, like measurement of heart rate.[44]
Implementation of evaluation tools requires time, instruments for measurement, and software for collecting data.[44]
Measurement systems
The most commonly used stress measurement systems are primarily rating scale-based. These systems tend to be complex, containing multiple levels with a variety of sections, to attempt to capture the many stressors present in the aviation industry. Different systems may be utilised in different operational specialties.
- The Perceived Stress Scale (PSS) – The PSS is a widely used subjective tool for measuring stress levels.[46] It consists of 10 questions, and asks participants to rate, on a five-point scale, how stressed they felt after a certain event. All 10 questions are summed to obtain a total score from 0 to 40.[47] In the aviation industry, for example, it has been used with flight training students to measure how stressed they felt after flight training exercises.[47]
- The Coping Skills Inventory – This inventory measures aviators' skills for coping with stress. This is another subjective measure, asking participants to rate, on a five-point scale, the extent to which they use eight common coping skills:[47] Substance abuse, Emotional support, Instrumental support (help with tangible things, like child care, finances, or task sharing), Positive reframing (changing one's thinking about a negative event, and thinking of it as a positive instead), Self-blame, Planning, Humour and Religion. An individual's total score indicates the extent to which he or she is using effective, positive coping skills (like humor and emotional support); ineffective, negative coping skills (like substance abuse and self-blame); and where the individual could improve.
- The Subjective Workload Assessment Technique (SWAT) – SWAT is a rating system used to measure individuals' perceived mental workload while performing a task, like developing instruments in a lab, multitasking aircraft duties, or conducting air defense.[48] SWAT combines measurements and scaling techniques to develop a global rating scale.
Pilot stress report systems
Early pilot stress report systems were adapted and modified from existing psychological questionnaires and surveys.[49] The data from these pilot-specific surveys is then processed and analyzed through an aviation-focused system or scale. Pilot-oriented questionnaires are generally designed to study work stress or home stress.[49] Self-report can also be used to measure a combination of home stress, work stress, and perceived performance. A study conducted by Fiedler, Della Rocco, Schroeder and Nguyen (2000) used Sloan and Cooper's modification of the Alkov questionnaire to explore aviators' perceptions of the relationship between different types of stress. The results indicated that pilots believed performance was impaired when home stress carried over to the work environment. The degree of home stress that carried over to work environment was significantly and negatively related to flying performance items, such as planning, control, and accuracy of landings. The questionnaire was able to reflect pilots' retroactive perceptions and the accuracy of these perceptions.[50]
Alkov, Borowsky, and Gaynor started a 22-item questionnaire for U.S. Naval aviators in 1982 to test the hypothesis that inadequate stress coping strategies contributed to flight mishaps.[49] The questionnaire consists of items related to lifestyle changes and personality characteristics. After completing the questionnaire, the test group is divided into two groups: "at-fault" with mishap, and "not-at-fault" in a mishap. Then, questionnaires from these two groups were analyzed to examine differences.[51] A study of British commercial airline pilots, conducted by Sloan and Cooper (1986), surveyed 1,000 pilot members from the British Airline Pilots' Association (BALPA). They used a modified version of Alkov, Borowsky, and Gaynor's questionnaire to collect data on pilots' perceptions of the relationship between stress and performance. Being a subjective measure, this study's data was based on pilots' perceptions, and thus rely on how accurately they recall past experiences their relationships to stress. Despite relying on subjective perceptions and memories, the study showed that pilot reports are noteworthy.[49]
Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) is another scale used in many industries, including the mental health professions, to screen for depressive symptoms.[52]
Parsa and Kapadia (1997) used the BDI to survey a group of 57 U.S. Air Force fighter pilots who had flown combat operations.[49] The adaptation of the BDI to the aviation field was problematic. However, the study revealed some unexpected findings. The results indicated that 89% of the pilots reported insomnia; 86% reported irritability; 63%, dissatisfaction; 38%, guilt; and 35%, loss of libido. 50% of two squadrons and 33% of another squadron scored above 9 on the BDI, suggesting at least low levels of depression. Such measurement may be difficult to interpret accurately.
College
College can be a stressful time for many students, as they adjust to a new and unfamiliar environment while transitioning from adolescence to adulthood. Nearly 80% of college students report frequently dealing with daily stress.[53] Sources of stress that influence college students’ stress levels include family and friends who are often physically further away, as well as changes in communication patterns with these individuals. Long-held beliefs (i.e. religious beliefs) as well as new opportunities for various behavior (i.e. alcohol and drug use) are also significant influential factors. In addition to these potential sources of stress, college students are also faced with often rigorous academic demands.[54] In order to manage this stress, students rely on many strategies including problem-focused and emotion-focused coping.[55]
Problem-focused strategies employ action-oriented behavioral activities like planning, for example. Emotion-focused strategies involve the expression of emotion and often include the altering of expectations. Although problem-focused strategies have often been found to be more effective than emotion-focused strategies, both categories include coping mechanisms that effectively reduce the negative impacts of stress.[56][57]
There are several practical examples of problem-focused or approach-based coping strategies. Notably, developing time management skills, avoiding procrastination, and goal-setting are associated with stress reduction. These skills allow students to better prioritize new responsibilities, leaving them more time for sleep and leisure activities, which have been shown to reduce stress. Additionally, working towards or maintaining healthy sleep habits helps individuals better cope with high levels of stress.[58][59]
Several emotion-focused strategies have also been found to be effective in combating stress. Accommodation strategies that do not directly change the stressor, but rather change one's emotions surrounding the stressors, such as positive re framing, are widely associated with stress reduction.[60] Strategies like finding humor and journaling—especially gratitude journaling—are also effective.[61][59]
Without effective coping skills, students tend to engage in unsafe behaviors as a means of trying to reduce the stress they feel. Ineffective coping strategies popular among college students include drinking excessively, drug use, excessive caffeine consumption, withdrawal from social activities, self-harm, and eating disorders.[53] These ineffective strategies can be dangerous because they often become habitual, addictive, and sometimes fatal. For example, when college students turn to drinking as a way of coping with stress, they begin to drink larger quantities and more frequently, instead of just occasionally with friends.[62] This can lead to alcohol poisoning, addiction, and other dangerous behaviors. The problems these coping methods create can cause more harm than good and often lead to more stress for the student.[63]
Researchers have not found significant gender differences in regard to how men and women use problem-focused coping strategies. However, there is gender variation in regard to emotion-focused coping. Women tend to use emotion-focused coping strategies more often than men on average. However, men do report using one emotion-focused coping strategy more often than women—mental disengagement in the form of alcohol use.[57] Mental disengagement refers to when individuals refocus their negative emotions to an alternative resource, such as alcohol, instead of addressing the original stressor.[64] Overall, women report higher stress levels than men, specifically for social relationships, daily hassles, finances, self-imposed stress, frustration, and academics.[57] This could be because women are often more in-tune to their emotions and are more comfortable expressing their feelings.[65]
While stress for college students is part of the transitional experience, there are many strategies that students can use to reduce stress in their lives and manage the impacts of stress. Time management skills which encompass goal setting, scheduling, and pacing are effective approaches to reducing stress. Additionally, students should keep up their physical and mental health with regular exercise, healthy eating, good sleep habits, and mindfulness practices.[59] There are several services, such as counseling and therapy, available to students that can be accessed both on and off campus to support stress management and overall student wellbeing.
See also
References
- "How stress affects your body and behavior". Mayo Clinic. Retrieved 2022-06-29.
- Cannon W (1939). The Wisdom of the Body (2nd ed.). New York: Norton Publications.
- Selye H (June 1950). "Stress and the general adaptation syndrome". British Medical Journal. 1 (4667): 1383–1392. doi:10.1136/bmj.1.4667.1383. PMC 2038162. PMID 15426759.
- Lazarus, R.S., & Folkman, S. (1984). Stress, Appraisal, and Coping. New York: Springer.
- Biggs A, Brough P, Drummond S (2017-02-18). "Lazarus and Folkman's Psychological Stress and Coping Theory". In Cooper CL, Quick JC (eds.). The Handbook of Stress and Health. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. pp. 349–364. doi:10.1002/9781118993811.ch21. ISBN 978-1-118-99381-1.
- Somaz WH, Tulgan B (2003). Performance Under Pressure: Managing Stress in the Workplace. Canada: HRD Press Inc. pp. 7–8. ISBN 0-87425-741-7.
- Mills RC (1995). Realizing Mental Health: Toward a new Psychology of Resiliency. Sulzberger & Graham Publishing, Ltd. ISBN 0-945819-78-1.
- Sedgeman JA (December 2005). "Health Realization/Innate Health: can a quiet mind and a positive feeling state be accessible over the lifespan without stress-relief techniques?". Medical Science Monitor. 11 (12): HY47–HY52. PMID 16319796.
- Wartel SG (April 2003). "A Strengths-Based Practice Model: Psychology of Mind and Health Realization". Families in Society: The Journal of Contemporary Social Services. 84 (2): 185–191. doi:10.1606/1044-3894.104. ISSN 1044-3894. S2CID 144256238.
- Lehrer PM, Woolfolk RL, Sime WE (2007). Principles and Practice of Stress Management (Third ed.). New York: Guilford Press. pp. 46–47. ISBN 978-1-59385-000-5.
- Leubner D, Hinterberger T (2017). "Reviewing the Effectiveness of Music Interventions in Treating Depression". Frontiers in Psychology. 8: 1109. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2017.01109. PMC 5500733. PMID 28736539.
- Spence JD, Barnett PA, Linden W, Ramsden V, Taenzer P (May 1999). "Lifestyle modifications to prevent and control hypertension. 7. Recommendations on stress management. Canadian Hypertension Society, Canadian Coalition for High Blood Pressure Prevention and Control, Laboratory Centre for Disease Control at Health Canada, Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada". CMAJ. 160 (9 Suppl): S46–S50. PMC 1230339. PMID 10333853.
Dubbed "Destressitizers"
- Robertson D (2012). Build your Resilience. London: Hodder. ISBN 978-1444168716.
- Praveena G, Mathana JM (April 2022). Review on Stress Detection and Management Techniques using Nano EEG Sensors. 2022 IEEE International Conference on Nanoelectronics, Nanophotonics, Nanomaterials, Nanobioscience & Nanotechnology (5NANO). pp. 1–7. doi:10.1109/5NANO53044.2022.9828889. ISBN 978-1-6654-3728-8. S2CID 250662211.
- Bower JE, Segerstrom SC (January 2004). "Stress management, finding benefit, and immune function: positive mechanisms for intervention effects on physiology". Journal of Psychosomatic Research. 56 (1): 9–11. doi:10.1016/S0022-3999(03)00120-X. PMID 14987958.
- Linden W, Lenz JW, Con AH (April 2001). "Individualized stress management for primary hypertension: a randomized trial". Archives of Internal Medicine. 161 (8): 1071–1080. doi:10.1001/archinte.161.8.1071. PMID 11322841.
- Frank DL, Khorshid L, Kiffer JF, Moravec CS, McKee MG (June 2010). "Biofeedback in medicine: who, when, why and how?". Mental Health in Family Medicine. 7 (2): 85–91. PMC 2939454. PMID 22477926.
- LaMorte WW. "What is Stress?". Boston University School of Public Health. Retrieved 2022-06-29.
- Dhabhar FS (May 2014). "Effects of stress on immune function: the good, the bad, and the beautiful". Immunologic Research. 58 (2–3): 193–210. doi:10.1007/s12026-014-8517-0. PMID 24798553. S2CID 255495219.
- Aschbacher K, O'Donovan A, Wolkowitz OM, Dhabhar FS, Su Y, Epel E (September 2013). "Good stress, bad stress and oxidative stress: insights from anticipatory cortisol reactivity". Psychoneuroendocrinology. 38 (9): 1698–1708. doi:10.1016/j.psyneuen.2013.02.004. PMC 4028159. PMID 23490070.
- McGonagle KA, Kessler RC (October 1990). "Chronic stress, acute stress, and depressive symptoms". American Journal of Community Psychology. 18 (5): 681–706. doi:10.1007/BF00931237. hdl:2027.42/117092. PMID 2075897. S2CID 38713589.
- McEwen BS (February 2017). "Neurobiological and Systemic Effects of Chronic Stress". Chronic Stress. 1: 247054701769232. doi:10.1177/2470547017692328. PMC 5573220. PMID 28856337.
- "Good stress, bad stress". News Center (in Samoan). Retrieved 2022-07-15.
- Bowman RE, Beck KD, Luine VN (January 2003). "Chronic stress effects on memory: sex differences in performance and monoaminergic activity". Hormones and Behavior. 43 (1): 48–59. doi:10.1016/S0018-506X(02)00022-3. PMID 12614634. S2CID 23133767.
- Kang JS, Shin DH, Baek JW, Chung K (2019-10-12). "Activity Recommendation Model Using Rank Correlation for Chronic Stress Management". Applied Sciences. 9 (20): 4284. doi:10.3390/app9204284. ISSN 2076-3417.
- "7 tips to prevent and reduce work stress". Archived from the original on 2016-03-10. Retrieved 2016-03-09.
- Carr J, Kelley B, Keaton R, Albrecht C (2011-01-01). "Getting to grips with stress in the workplace: Strategies for promoting a healthier, more productive environment". Human Resource Management International Digest. 19 (4): 32–38. doi:10.1108/09670731111140748. ISSN 0967-0734.
- Yerkes RM, Dodson JD (November 1908). "The relation of strength of stimulus to rapidity of habit-formation". Journal of Comparative Neurology and Psychology. 18 (5): 459–482. doi:10.1002/cne.920180503. ISSN 0092-7015.
- "Simple Hacks to Stress Management for Nigerian Entrepreneurs - Insight.ng". 2021-10-28. Retrieved 2022-08-10.
- Michael L (1998). "Commitment in the workplace: Theory, research and application, by Meyer JP, Allen NJ. (1997). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage. 150 pp., $34.00 cloth, $15.95 paper". Human Resource Development Quarterly. 9 (3): 309–312. doi:10.1002/hrdq.3920090309. ISSN 1044-8004.
- Ates ÖT, Ihtiyaroglu N (2019-01-06). "Analysis of the Relationship between Stress and Organizational Commitment in Employees: A Meta-Analysis Study" (PDF). Journal of Education and Training Studies. 7 (1): 94–106. doi:10.11114/jets.v7i1.3702. ISSN 2324-805X. S2CID 149692383. ERIC EJ1202105.
- Awang Idris M, Dollard MF, Winefield AH (2010-01-01). "Lay theory explanations of occupational stress: the Malaysian context". Cross Cultural Management. 17 (2): 135–153. doi:10.1108/13527601011038714. ISSN 1352-7606.
- "Workplace Stress Management Resource - OFAI". www.ofai.co.uk. Archived from the original on 2016-03-27.
- Preisler M. "Avoiding change-induced stress in the workplace". Nordic Labour Journal. Archived from the original on 2013-08-24.
- Bhojani Z, Kurucz EC (2020). "Sustainable Happiness, Well-Being, and Mindfulness in the Workplace". The Palgrave Handbook of Workplace Well-Being. Springer International Publishing. pp. 1–25. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-02470-3_52-1. ISBN 978-3-030-02470-3. S2CID 216344603.
- Caplan RP (November 1994). "Stress, anxiety, and depression in hospital consultants, general practitioners, and senior health service managers". BMJ. 309 (6964): 1261–1263. doi:10.1136/bmj.309.6964.1261. PMC 2541798. PMID 7888846.
- Merlin NM (2022). "Influence of depression, stress and anxiety on work performance among timor island nurses in tuberculosis/HIV unit and covid-19 unit". Journal of Psychiatric Nursing. doi:10.14744/phd.2022.79027. S2CID 248906141.
- "Anti stress diary with adult coloring pages". Archived from the original on 2017-05-15.
- "20 Gadgets to Help You Fight Stress". Hongkiat Magazine. 2016-07-14. Archived from the original on 2017-02-17.
- Schultz DP, Schultz SE (2010). Psychology and Work Today. New York: Prentice Hall. p. 374.
- Kröll C, Doebler P, Nüesch S (2017-09-03). "Meta-analytic evidence of the effectiveness of stress management at work". European Journal of Work and Organizational Psychology. 26 (5): 677–693. doi:10.1080/1359432X.2017.1347157. ISSN 1359-432X. S2CID 149409419.
- Hardy S (1998). Occupational Stress: Personal & Professional Approaches. United Kingdom: Stanley Thornes ltd. pp. 18–43.
- Woldring M (1996-03-15). "Human Factors Module: Stress" (PDF). European Organisation for the Safety of Air Navigation. 1: 3–16. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2015-12-22.
- Lehrer P, Karavidas M, Lu SE, Vaschillo E, Vaschillo B, Cheng A (May 2010). "Cardiac data increase association between self-report and both expert ratings of task load and task performance in flight simulator tasks: An exploratory study". International Journal of Psychophysiology. 76 (2): 80–87. doi:10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2010.02.006. PMID 20172000.
- Biondi M, Picardi A (1999). "Psychological stress and neuroendocrine function in humans: the last two decades of research". Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics. 68 (3): 114–150. doi:10.1159/000012323. PMID 10224513. S2CID 41340845.
- Langan-Fox J, Sankey MJ, Canty JM (October 2009). "Human factors measurement for future air traffic control systems". Human Factors. 51 (5): 595–637. doi:10.1177/0018720809355278. PMID 20196289. S2CID 206409588.
- Kirschner J, Young J, Fanjoy R (2014). "Stress and coping as a function of experience level in collegiate flight students". Journal of Aviation Technology and Engineering. 3 (2): 14–19. doi:10.7771/2159-6670.1092.
- Corwin WH (1992-04-01). "In-flight and post flight assessment of pilot workload in commercial transport aircraft using the subjective workload assessment technique". The International Journal of Aviation Psychology. 2 (2): 77–93. doi:10.1207/s15327108ijap0202_1.
- Young J (December 2008). The Effects of Life-Stress on Pilot Performance (PDF) (Report). NASA Ames Research Center. pp. 1–7. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2016-03-05.
- Muller R, Wittmer A, Drax C, eds. (2014). Aviation Risk and Safety Management: Methods and Applications In Aviation Organizations. Springer International. ISBN 978-3-319-02779-1.
- O'Connor PE, Cohn JV, eds. (2010). Human Performance Enhancement in High-Risk Environments: Insights, Developments, and Future Directions from Military Research. ABC-CLIO. ISBN 978-0-313-35983-5.
- Barral C, Rodríguez-Cintas L, Martínez-Luna N, Bachiller D, Pérez-Pazos J, Alvarós J, Casas M, Roncero C (March 2016). "Reliability of the Beck Depression Inventory in opiate-dependent patients". Journal of Substance Abuse. 21 (2): 128–132. doi:10.3109/14659891.2014.980859. S2CID 71642211.
- "The Student's Guide To Managing Stress". AffordableCollegesOnline.org. Red Ventures Company. 11 April 2023.
- Zaleski EH, Levey-Thors C, Schiaffino KM (1998). "Coping Mechanisms, Stress, Social Support, and Health Problems in College Students". Applied Developmental Science. 2 (3): 127–137. doi:10.1207/s1532480xads0203_2.
- Dyson R, Renk K (October 2006). "Freshmen adaptation to university life: depressive symptoms, stress, and coping". Journal of Clinical Psychology. 62 (10): 1231–1244. doi:10.1002/jclp.20295. PMID 16810671. S2CID 20374373.
- Penley JA, Tomaka J, Wiebe JS (December 2002). "The association of coping to physical and psychological health outcomes: a meta-analytic review". Journal of Behavioral Medicine. 25 (6): 551–603. doi:10.1023/a:1020641400589. PMID 12462958. S2CID 27649585.
- Brougham RR, Zail CM, Mendoza CM, Miller JR (2009). "Stress, sex differences, and coping strategies among college students". Current Psychology. 28 (2): 85–97. doi:10.1007/s12144-009-9047-0. S2CID 18784775.
- Welle PD, Graf HM (2011). "Effective lifestyle habits and coping strategies for stress tolerance among college students". American Journal of Health Education. 42 (2): 96–105. doi:10.1080/19325037.2011.10599177. S2CID 17099952.
- "Managing Stress". Campus Mind Works. Regents of the University of Michigan. 2018.
- Carver CS. The Handbook of Stress Science: Biology, Psychology and Health. New York, NY: Springer Publishing Company.
- Cheng ST, Tsui PK, Lam JH (February 2015). "Improving mental health in health care practitioners: randomized controlled trial of a gratitude intervention". Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 83 (1): 177–186. doi:10.1037/a0037895. PMID 25222798.
- Waterson L (16 October 2018). "Stress and Alcohol Use Among College Students: What Are the Real Dangers". Alta Mira Recovery Programs.
- "The College Student's Guide to Stress Management". Purdue University Global. March 2019.
- Shoss MK, Hunter EM, Penney LM (2016-03-14). "Avoiding the issue: Disengagement coping style and the personality–CWB link". Human Performance. 29 (2): 106–122. doi:10.1080/08959285.2016.1148036. ISSN 0895-9285. S2CID 147082374.
- Hall NC, Chipperfield JG, Perry RP, Ruthig JC, Goetz T (2006). "Primary and secondary control in academic development: gender-specific implications for stress and health in college students". Anxiety, Stress, & Coping. 19 (2): 189–210. doi:10.1080/10615800600581168. S2CID 13667123.