Auranthine
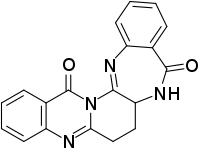
Auranthine is an antimicrobial chemical compound isolated from a nephrotoxic strain[1] of Penicillium fungus, Penicillium aurantiogriseum.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
6,7,7a,8-Tetrahydroquinazolino[3’,2’:1,6]pyrido[2,3-b] [1,4]benzodiazepine-9,16-dione | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H14N4O2 | |
| Molar mass | 330.347 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
A total synthesis of auranthine has been reported.[3]
References
- MacGeorge, K. M; Mantle, P. G (1990). "Nephrotoxicity of Penicillium aurantiogriseum and P. Commune from an endemic nephropathy area of Yugoslavia". Mycopathologia. 112 (3): 139–45. doi:10.1007/bf00436643. PMID 2089255. S2CID 28572592.
- Yeulet, Stephanie E; Mantle, Peter G; Bilton, John N; Rzepa, Henry S; Sheppard, Richard N (1986). "Auranthine, a new benzodiazepinone metabolite of Penicillium aurantiogriseum". Journal of the Chemical Society, Perkin Transactions 1: 1891. doi:10.1039/P19860001891.
- Kshirsagar, Umesh A; Puranik, Vedavati G; Argade, Narshinha P (2010). "Total Synthesis of Proposed Auranthine". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 75 (8): 2702–2705. doi:10.1021/jo100400z. PMID 20302381.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.