Aurantimycin A
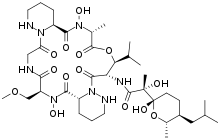
Aurantimycin A is a depsipeptide antibiotic with the molecular formula C38H64N8O14.[2][1] Aurantimycin A is produced by the bacterium Streptomyces aurantiacus.[3][4] Aurantimycin A also show cytotoxic properties.[5]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2R)-N-[(6S,9R,16S,17S,20R,23S)-7,21-dihydroxy-6-(methoxymethyl)-20-methyl-2,5,8,15,19,22-hexaoxo-17-propan-2-yl-18-oxa-1,4,7,13,14,21,27-heptazatricyclo[21.4.0.09,14]heptacosan-16-yl]-2-hydroxy-2-[(2S,5S,6S)-2-hydroxy-6-methyl-5-(2-methylpropyl)oxan-2-yl]propanamide[1] | |
| Other names
Aurantimycin | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C38H64N8O14 | |
| Molar mass | 856.972 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- "Aurantimycin A". Pubchem.ncbi.NLM.nih.gov.
- "Aurantimycin A, Depsipeptide antibiotic (CAS 162478-50-4) (ab144195) | Abcam". www.abcam.com.
- Grigoriev, P.; Schlegel, R.; Dornberger, K.; Gräfe, U. (1 February 1995). "Formation of membrane pores by aurantimycins A and B, new lipopeptide antibiotics from Streptomyces aurantiacus". Bioelectrochemistry and Bioenergetics. 36 (1): 57–59. doi:10.1016/0302-4598(94)01721-C. ISSN 0302-4598.
- Kolar, Patrik; Tišler, Miha (28 October 1999). "Recent Advances in the Chemistry of Pyridazines". Advances in Heterocyclic Chemistry Volume 75. Advances in Heterocyclic Chemistry. Vol. 75. Academic Press. p. 170. doi:10.1016/S0065-2725(08)60985-X. ISBN 978-0-08-057661-9.
- Bycroft, Barrie W.; Payne, David J. (9 August 2013). Dictionary of Antibiotics and Related Substances: with CD-ROM, Second Edition. CRC Press. p. 303. ISBN 978-1-4822-8215-3.
Further reading
- Gräfe, U.; Schlegel, R.; Ritzau, M.; Ihn, W.; Dornberger, K.; Stengel, C.; Fleck, W. F.; Gutsche, W.; Härtl, A.; Paulus, E. F. (1995). "Aurantimycins, New Depsipeptide Antibiotics from Streptomyces aurantiacus IMET 43917 Production, Isolation, Structure Elucidation, and Biological Activity". The Journal of Antibiotics. 48 (2): 119–125. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.48.119. PMID 7706121.
- Hauf, Samuel; Herrmann, Jennifer; Miethke, Marcus; Gibhardt, Johannes; Commichau, Fabian M.; Müller, Rolf; Fuchs, Stephan; Halbedel, Sven (April 2019). "Aurantimycin resistance genes contribute to survival of Listeria monocytogenes during life in the environment". Molecular Microbiology. 111 (4): 1009–1024. doi:10.1111/mmi.14205. PMID 30648305.
- Schlegel, R.; Ritzau, M.; Ihn, W.; Stengel, C.; Gräfe, U. (May 1995). "Aurantimycin D, A Shunt Metabolite of Aurantimycin Biosynthesis by Streptomyces aurantiacus IMET 43917". Natural Product Letters. 6 (3): 171–176. doi:10.1080/10575639508043154.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.