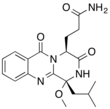
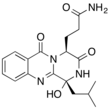
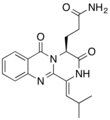
Aurantiomide
Aurantiomides are quinazoline alkaloids isolated from the fungus Penicillium aurantiogriseum.[1] Aurantiomide is contained in the traditional Chinese medicine LeZhe.[2]
| |||
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChEMBL |
| ||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID |
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |||
References
- Xin, Zhi Hong; Fang, Yuchun; Du, Lin; Zhu, Tianjiao; Duan, Lin; Chen, Juan; Gu, Qian-Qun; Zhu, Wei-Ming (2007). "Aurantiomides A−C, Quinazoline Alkaloids from the Sponge-Derived Fungus Penicillium aurantiogriseum SP0-19". Journal of Natural Products. 70 (5): 853–855. doi:10.1021/np060516h. ISSN 0163-3864. PMID 17455978.
- Melrose, James; Smith, Margaret M. (9 October 2022). "Natural and Semi-Synthetic Flavonoid Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Agents for the Treatment of Long COVID-19 Disease and Neurodegenerative Disorders of Cognitive Decline". Frontiers in Bioscience-Elite. 14 (4): 27. doi:10.31083/j.fbe1404027.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.