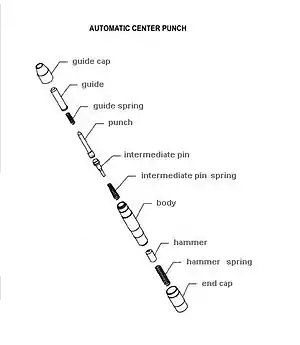
Automatic center punch
An automatic center punch is a hand tool used to produce a dimple in a workpiece (for example, a piece of metal). It performs the same function as an ordinary center punch but without the need for a hammer. When pressed against the workpiece, it stores energy in a spring, eventually releasing it as an impulse that drives the punch, producing the dimple. The impulse provided to the point of the punch is quite repeatable, allowing for uniform impressions to be made.
History
The patent history of automatic punches indicates two principal goals for the development of the tool: repeatability of impact, and convenience of operation. Other desirable properties include low recoil when triggered, ease of adjustment, and reliability.
A number of designs for automatic center punches have been developed since the late 19th century as improvements over punches requiring the use of a striking tool. The earliest types were not fully automatic, using a captive weight lifted by the user or a spring and weight drawn by the user to provide the striking impulse. A number of patents have been issued for these designs, and they continue to be referenced in patents into the 21st century.[1][2][3][4][5] There are also a number of examples of hammer and punch combinations intended for one-handed use, but being modeled upon a conventional hammer striking a separate punch tool.[6]
The earliest US patents for the modern automatic center punch were filed during 1904 by Hartley and Stryhal for designs using a leaf spring catch to release the hammer,[7][8] both assigned to Brown and Sharpe. In 1905, Seitz patented a manually triggered punch that has many of the internal structural elements of some later fully automatic models,[9] and Spalding was granted a patent in 1908 on an application filed in 1904 for a different design of leaf spring controlled fully automatic punch that included easy adjustment of blow as well as interchangeable, threaded on points.[10]
Adell and Baltzer, of L. S Starrett Co., patented a design with concentric shells and pins in cam slots as the triggering mechanism,[11] and Adell and Starrett received a 1907 patent for a design using a sliding block actuated by a tapered bore in the body to hold back the hammer.[12]
Some of the modifications introduced in the Seiler patent of 1923[13] saw substantial manufacture in the United States, and this patent has been referenced by other patents into the 21st century. This design uses a sliding block similar in concept to the Adell and Starrett patent, but with a coil spring to return the sliding block rather than a leaf spring, but a more involved scheme to slide the block to release the hammer.
The Sweet patent of 1942[14] is the first description of the most manufactured trigger type in the later 20th century, using a tilted intermediate pin to hold back the hammer until the main spring is compressed. This design is referenced by a large number of other patents, and was the basis for the Frey patent of 1965,[15] which was intended to improve the reliability of the device resetting. This design has also seen substantial manufacture.
There are a variety of other mechanisms used, of varying complexity and reliability, some of which have been patented or had patent applied for into the 21st century.[16]
Better quality modern designs tend to follow on Sweet's patent[17][18] or Frey's patent,[19] though some are based on the Adell and Starrett design.[20]
A variety of other mechanisms also exist and have been used, including cam based, ball bearings trapped in a sliding collar, and bidirectional mechanisms that take pulling attachments.
Applications
The automatic center punch mechanism has been used for a wide variety of other applications. These include
- Marking and starting a hole for drilling without the bit "walking" out of alignment
- Letter stamp sets
- Glass-breaking tools used in rescue work and a common tool for a car thief.
- Impact tool for hardness testing[21]
- Pin presses for electronic assembly[22][23]
In many applications, such as hardness testing, the mechanism does not have an adjustment for impulse strength, and may require periodic calibration checks.
Common elements
All designs have several elements in common:
- A spring to store energy
- A mass to provide the impulse (a hammer)
- A release mechanism that releases the stored energy at a consistent point in the travel of the body
- A provision to reset the device after actuation
Typical Mechanism and Operation
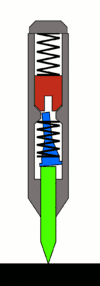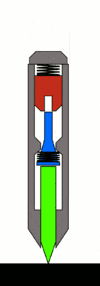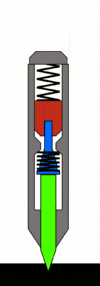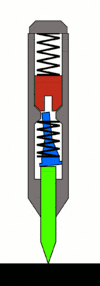

The most common mechanism is based upon the Sweet patent. Within the body of the punch, there are three principal moving parts arranged in line:
- The punch
- The intermediate rod (tumbler)
- The hammer (hammer mass)
The hammer mass is spring-loaded from the back of the punch by a large spring. (The spring's preload compression can usually be adjusted by loosening or tightening the end cap at the back-most portion of the punch, to decrease or increase the force of the punch.) A stopped hole drilled in the front center portion of the hammer mass facing the tumbler acts as a receiver for the rod, and as an anvil for the punch action.
The tumbler provides the automation. When reset, a provision is made such that the tumbler rod is cocked slightly, so that its resting position is skewed and the tip contacts the hammer mass on the face of the hammer slightly offset to the hole. This is commonly done by using a special bent end on the tumbler spring[17] or using an out-of-flat face on the bottom end of the pin or top of the punch.[18] It bears on the hammer mass and pushes it back against its spring as the punch is pressed, storing energy in the hammer spring.
As the punch is further pressed against the workpiece, the tumbler travels back until the point where its tapered midsection begins contacting the surface of the guide hole in the body of the punch. As it continues back, it is pushed into alignment with the center axis of the tool. When the tip of the tumbler is nearly centered, it slips into the receiving hole in the hammer mass, and releases the hammer. The hammer mass is then allowed to move forward, propelled by the rear spring. Because the hole in the hammer mass does not go through the mass and is less deep than the end section of the tumbler, the tip of the tumbler bottoms out in the hole in the hammer, and the impulse of the hammer mass is transmitted through the tumbler, through the punch, and to the workpiece.
Other common mechanisms
Adell & Starrett
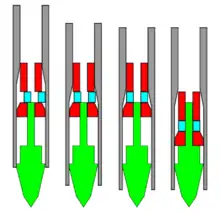
The Adell and Starrett mechanism uses a sliding block crosswise through the hammer rather than an intermediate pin. The hammer has a hole through its center that the top of the punch sits in, and holds the top of the punch centered. The sliding block has a hole through it that, when reset, is misaligned with the hole through the hammer. When the body is pressed to the trip point, a taper in the body forces the block sideways until the hole in the block is aligned with the hole through the hammer, and the hammer is released to strike the punch.
This mechanism is used in heavy duty punches as it is less likely to bind on reset than the Sweet mechanism, it doesn't tend to wear the inside of the body as much as the Sweet mechanism and, because the end of the hammer can be used to provide impact on a larger area of the punch tip, reduces the stress on the material. The primary disadvantages are that there are more parts than in the Sweet design, and that both the hammer and the block require manufacturing other than on a lathe.
Frey (1963)
The Frey mechanism uses a steel ball and an out-of-flat end for the intermediate pin to force the intermediate pin to cock at reset. This means the intermediate spring doesn't need a special end, but the high stresses at the contact with the steel ball can lead to brinelling of the intermediate pin end or the top of the punch by the ball.
References
- Geisenhoner US833712
- Ainsworth US913677
- Williams US1458961
- Berninger US2602360
- Hager US2455577
- Komatar US1341373
- Hartley US783749
- Hartley US781947
- Seitz US797824
- Spalding US889409
- Adell and Baltzer US789520
- Adell and Starrett US843655
- Seiler US1572046
- Sweet US2384707
- Frey US3172204
- Utz US2004/0154171
- General 70079 Center Punch manual retrieved 2013aug8 Archived April 6, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- General 87 Center Punch manual retrieved 2013aug8 Archived April 6, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- General 77 Center Punch manual retrieved 2013aug8 Archived April 6, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- General 78 Center Punch manual retrieved 2013aug8 Archived April 6, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- PTC316 hardness tester retrieved 2013aug8
- West US3177952
- Morgan US4577400