Azobenzene dioxide
Azobenzene dioxide is the organic compound with the formula (C6H5N(O))2. Both cis and trans isomers are known. The cis isomer has been crystallized. It is colorless.[1]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H10N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 214.224 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless solid |
| Density | 1.31 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 68 °C (154 °F; 341 K) with decomposition to the monomer |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Reactions
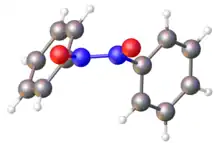
Structure of (PhNO)2 viewed down an approximate C2 axis. The N-O and N-N distances are 1.26 (average of two) and 1.33 Å, respectively.[1] Color code: blue=N, red = O, gray = C.
When dissolved, azobenzene dioxide converts to deeply blue nitrosobenzene:
- (C6H5N(O))2 → 2 C6H5NO
Azobenzene dioxide is a weak base, forming coordination complexes such as [Co[(C6H5N(O))2]4]2+.[2]
References
- Dieterich, David A.; Paul, Iain C.; Curtin, David Y. (1974). "Structural studies on nitrosobenzene and 2-nitrosobenzoic acid. Crystal and molecular structures of cis-azobenzene dioxide and trans-2,2'-dicarboxyazobenzene dioxide". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 96 (20): 6372–6380. doi:10.1021/ja00827a021.
- Emhoff, Kylin A.; Balaraman, Lakshmi; Simpson, Sydney R.; Stromyer, Michael L.; Kalil, Haitham F.; Beemiller, James R.; Sikatzki, Philipp; Eshelman, Teya S.; Salem, Ahmed M. H.; Debord, Michael A.; Panzner, Matthew J.; Youngs, Wiley J.; Boyd, W. Christopher (2018). "Synthesis and Characterization of Cobalt(II) N , N ′-Diphenylazodioxide Complexes". ACS Omega. 3 (11): 16021–16027. doi:10.1021/acsomega.8b01200. PMC 6643636. PMID 31458240.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.