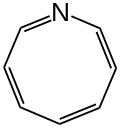
Azocine
Azocine is a heterocyclic organic compound with the molecular formula C7H7N. It consists of an unsaturated eight-membered ring having seven carbon atoms, one nitrogen atom and four double bonds.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(3Z,5Z,7Z)-Azocine | |
| Other names
Azacyclooctatetraene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H7N | |
| Molar mass | 105.140 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Saturated or partially saturated azocine rings form the core structure of a group of opioid compounds sometimes known as azocines. These include cyclazocine, pentazocine, and phenazocine.
The fully saturated analog of azocine is azocane.
Azocine rings are found in many natural products, including the manzamine family of marine alkaloids. One such compound is nakadomarin A, which contains a partially saturated azocine within its hexacyclic fused ring system.
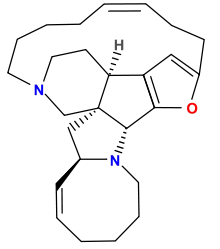
Nakadomarin A
See also
External links
- Azocines at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.