Bình Phước province
Bình Phước (Vietnamese: [ʔɓïŋ˨˩ fɨək̚˧˦] ⓘ) is a province of Vietnam. It is located in the Southeast region of the country, to the north of Hồ Chí Minh City (formerly Saigon). It shares a border with Cambodia.
Bình Phước province
Tỉnh Bình Phước | |
|---|---|
 View from Bà Rá mountain | |
 Seal | |
| Nickname(s): Peace and Happiness | |
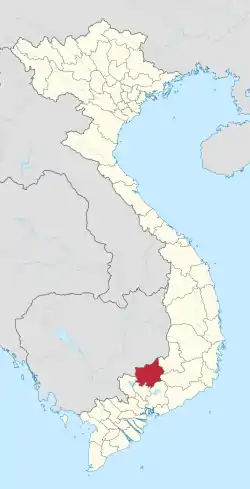 Location of Bình Phước within Vietnam | |
 Bình Phước province Location within Vietnam  Bình Phước province Location within Asia | |
| Coordinates: 11°45′N 106°55′E | |
| Country | |
| Region | Southeast |
| Metropolitan area | Ho Chi Minh City metropolitan area |
| Capital | Đồng Xoài |
| Government | |
| • People's Council Chair | Huỳnh Thị Hằng |
| • People's Committee Chair | Trần Tuệ Hiền |
| • Secretary of Bình Phước Party Committee | Nguyễn Mạnh Cường |
| Area | |
| • Total | 6,880.6 km2 (2,656.6 sq mi) |
| Population (2021)[1] | |
| • Total | 1,121,034 |
| • Density | 160/km2 (420/sq mi) |
| Demographics | |
| • Ethnicities | Vietnamese, Xtiêng, Nùng, Tày, Khmer |
| Time zone | UTC+7 (ICT) |
| Area codes | 651 (until 16 July 2017) 271 (from 17 June 2017) |
| ISO 3166 code | VN-58 |
| Website | www |
History
Bình Phước province is the result of a merger of two former provinces: Phước Long province and Bình Long province, which existed before reunification. Both Phước Long and Bình Long then became part of Sông Bé province in 1976, which also included Bình Dương province. Sông Bé province was dissolved in 1997 and Bình Phước again became a separate province. Several significant battles were fought in what is now Bình Phước province. These include the Battle of Sông Bé in May 1965, the Battle of Đồng Xoài in June 1965, the Battle of Lộc Ninh in April 1972, and the Battle of Phước Long from December 1974 to January 1975.
Geography
Bình Phước province is relatively flat with an elevation of between 50 metres (160 ft) and 200 metres (660 ft) throughout most of the province. The elevation is gradually higher towards the east of the province and reach around 500 metres (1,600 ft) near parts of the border with Đắk Nông province of the Central Highlands. The highest elevation is Bà Rá mountain (736 metres (2,415 ft)) in the centre of the province.[2] There are several hills around the province with heights of up to around 200 metres (660 ft) in the west and 300 metres (980 ft) in the southeast.[3]
Most of the rivers in the province are tributaries of the Bé River, which in turn is a tributary of the Đồng Nai River.[2] Thác Mơ lake is a large artificial lake in the east of the province. Several rivers originating in the Central Highlands flow into it, including Đak G'lun, Đăk Nhau, Đắk R'lấp, and Dak Oa (from north to south).[3] It is the point of origin of the Bé River, which flows through much of central and western Bình Phước.
Forestry land takes up 337,000 hectares (832,750 acres) or 49 percent of the province's total area.[4] Forests are located mostly in the northeast and southeast of the province as well as along the northern border with Cambodia and the western border with Tây Ninh province.[2] Much of the rest of the area is used to grow perennial cash crops. The total agricultural area is 293,700 hectares (725,750 acres). There are 21,900 hectares (54,000 acres) of specially used land and 5,700 hectares (14,000 acres) of residential land.[4]
Demography
Bình Phước's population in 2022 was 1,277,300. This is a significant increase from 684,600 in 2000. In contrast to many other provinces, much of this growth has taken place in rural areas, where the population increased by 118,500 compared to 20,500 in urban areas. Bình Phước is a predominantly rural province, with only 15.4 percent of the population living in towns. The population has grown by 16.5 percent between 2000 and 2005, but has since slowed to 2.23 percent in 2006 and 1 percent in 2007.[4]
Besides the majority Vietnamese, there are minorities of Xtiêng, Nùng, Tày, and Khmer. Ethnic minorities are present throughout the province.[2]
Administrative divisions
Bình Phước is subdivided into 11 district-level sub-divisions:
- 7 districts:
- 3 district-level towns:
- 1 provincial city:
- Đồng Xoài (capital)
They are further subdivided into five commune-level towns (or townlets), 92 communes, and 14 wards.
| District-level sub-divisions | Đồng Xoài city |
Bình Long town |
Chơn Thành town |
Phước Long town |
Bù Đăng district |
Bù Đốp district |
Bù Gia Mập district |
Đồng Phú district |
Hớn Quản district |
Lộc Ninh district |
Phú Riềng district | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (km²) | 167.3 | 126.2 | 390.34 | 118.8 | 1,503 | 377.5 | 1,062 | 935.4 | 663.8 | 854 | 675 | ||
| Population | 162,700 | 105,520 | 121,083 | 81,200 | 135,090 | 52,620 | 150,480 | 90,200 | 100,790 | 120,650 | 95,300 | ||
| Density (people/km²) | 897 | 456 | 310 | 421 | 87 | 120 | 85 | 93 | 144 | 135 | 87 | ||
| Administrative divisions | 6 wards, 2 communes | 4 wards, 2 communes | 5 wards, 4 communes | 5 wards, 2 communes | 1 townlet, 15 communes | 1 townlet, 6 communes | 8 communes | 1 townlet, 10 communes | 1 townlet, 12 communes | 1 townlet, 15 communes | 10 communes | ||
| Year of establishment | 2018 | 2009 | 2022 | 2009 | 1988 | 2003 | 2009 | 1977 | 2009 | 1978 | 2015 | ||
| Source: Website of Bình Phước province | |||||||||||||
Economy
Bình Phước is agriculturally one of the most productive provinces of Vietnam, especially relying on cash crops such as cashew nuts and rubber. As of 2007, its agricultural gross domestic product (GDP) per capita was 7.03 million Vietnamese đồngs, the highest in Vietnam, while industrial GDP per capita was only 1.7 million đồngs, making it one of the least industrialized provinces in the southern half of Vietnam. Bình Phước's GDP in 2007 was 9,534.4 billion đồngs or 11.58 million đồngs per capita, which is 86 percent of the national figure and significantly lower than that of the other provinces in the Southeastern region. Growth in GDP has been between 14% and 15% per year from 2000 to 2007. Bình Phước exported goods with a value of US$325.5 million in 2007, far exceeding its imports of US$57.4 million. Since 2000, exports have increased almost sevenfold while imports increased almost tenfold. The main export products include rubber latex, shelled cashew nuts and pepper.[4]
Ownership structure
The state sector accounted for 41.5 percent of GDP in 2007, an increase from the 29.5 percent in 2000 but somewhat lower than 2006, when its share peaked at 45.9 percent. At the same time, the household sector had seen its share being reduced from 61.1 percent in 2000 to 49.2 percent in 2007, but it was still the largest ownership sector in Bình Phước. The private sector is still very small at only 7.7 percent of GDP. There has been very little foreign investment; this sector contributes only 1.4 percent to the province's GDP.[4]
Agriculture
Agriculture in Bình Phước is dominated by perennial crops, mainly cashew nuts, rubber, coffee and pepper. 4,333 of the 4,458 farms in 2007 were perennial crop farms. The production of cereals is much less significant and accounts only for a small part of agricultural area and output. 34,200 tons of rice and 19.7 tons of maize were harvested in 2007, accounting for only 0.1 and 0.5 percent of the national output. Sweet potatoes and cassava are also grown in Bình Phước. The most important cash crop is cashew nuts. 156,377 tons of cashew nuts were harvested in 2007, accounting for 51.8 percent of the national output. This is a significant increase from 110,000 tons in 2006 and just 19,000 tons in 2000.[4] Cashew nuts are grown mostly in the east and south of the province, roughly along (north and west of) National Route 14.[2] Cashew nuts are an important export product for Bình Phước as well as Vietnam in general. Exports in 2010 are expected to reach US$1 billion, while there are also increasing imports of raw cashew nuts because processing capacity by now significantly exceeds the quantity grown in Vietnam.[5]
Another important crop is rubber, with 147,520 tons produced in 2007. This accounts for 24.5 percent of the national output and has more than doubled since 2000 (67,000 tons).[4] Rubber is mostly produced in the north and west of the province, along the Bé River and National Route 13.[2] Bình Phước's pepper production also accounts for a significant share of national output (24 percent). Production has more than doubled to 21,736 between 2000 and 2007.[4] Pepper is grown in the southwest of the province in the districts of Bình Long and Chơn Thành, between National Route 13 and the Bé River.[2]
Coffee is grown in the northeast of the province, north of Thác Mơ Lake.[2] 56,148 tons of coffee were harvested in 2007, accounting for 5.8 percent of the national output.[4] Other crops include coconuts (877 tons in 2007), sugar cane (28,800 tons), peanuts (800 tons) and cotton (500 tons).
Industry
Industry and construction contribute only 14.7 percent to the province's GDP as of 2007. However, it has contributed significantly to recent economic growth. While the large agricultural sector has been growing by around 10 percent from 2005 to 2007, the growth of industry and construction was 35.8, 25.9, and 21.6 percent in these three years, respectively.[4]
Many of the industries are based on agricultural products or raw materials. Food processing industries include the production of shelled cashew nuts (29,200 tons) and cassava starch (78,100 tons). There is also an industry producing hand farming tools. Other industries include construction materials (stones and bricks) and forest product processing (saw wood and paper).[4]
Transportation
In September 2007, moves were made to consider the construction of a section of the proposed Trans-Asian Railway from Dĩ An on the main north-south line to Lộc Ninh near the Cambodian border.
References
- Statistical Handbook of Vietnam 2014 Archived 2015-07-06 at the Wayback Machine, General Statistics Office Of Vietnam
- Atlat Dia li Viet Nam (Geographical Atlas of Vietnam). NXB Giao Duc, Hanoi: 2010
- Vietnam Administrative Atlas. Cartographic Publishing House, Hanoi 2010
- General Statistics Office (2009): Socio-economic Statistical Data of 63 Provinces and Cities, Vietnam. Statistical Publishing House, Hanoi.
- "Local cashew nut's export-import turnover may reach $1b. Intellasia | VOV. 19 October 2010". Archived from the original on 2011-07-23. Retrieved 2010-11-10.