BAAT
Bile acid-CoA:amino acid N-acyltransferase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the BAAT gene.[5]
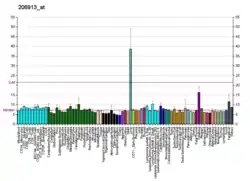
The protein encoded by this gene is a liver enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of the bile acid moiety from the acyl-CoA thioester to either glycine or taurine, the second step in the formation of bile acid-amino acid conjugates which serve as detergents in the gastrointestinal tract.[5]
References
- ENSG00000276559 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000136881, ENSG00000276559 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000039653 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Entrez Gene: BAAT bile acid Coenzyme A: amino acid N-acyltransferase (glycine N-choloyltransferase)".
External links
- Human BAAT genome location and BAAT gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
Further reading
- Johnson MR, Barnes S, Kwakye JB, Diasio RB (1991). "Purification and characterization of bile acid-CoA:amino acid N-acyltransferase from human liver". J. Biol. Chem. 266 (16): 10227–33. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)99213-6. PMID 2037576.
- Falany CN, Johnson MR, Barnes S, Diasio RB (1994). "Glycine and taurine conjugation of bile acids by a single enzyme. Molecular cloning and expression of human liver bile acid CoA:amino acid N-acyltransferase". J. Biol. Chem. 269 (30): 19375–9. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(17)32178-6. PMID 8034703.
- Lench NJ, Telford EA, Andersen SE, et al. (1997). "An EST and STS-based YAC contig map of human chromosome 9q22.3". Genomics. 38 (2): 199–205. doi:10.1006/geno.1996.0616. PMID 8954802.
- Solaas K, Ulvestad A, Söreide O, Kase BF (2000). "Subcellular organization of bile acid amidation in human liver: a key issue in regulating the biosynthesis of bile salts". J. Lipid Res. 41 (7): 1154–62. doi:10.1016/S0022-2275(20)32022-8. PMID 10884298.
- Sfakianos MK, Wilson L, Sakalian M, et al. (2003). "Conserved residues in the putative catalytic triad of human bile acid Coenzyme A:amino acid N-acyltransferase". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (49): 47270–5. doi:10.1074/jbc.M207463200. PMID 12239217.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Carlton VE, Harris BZ, Puffenberger EG, et al. (2003). "Complex inheritance of familial hypercholanemia with associated mutations in TJP2 and BAAT". Nat. Genet. 34 (1): 91–6. doi:10.1038/ng1147. PMID 12704386. S2CID 21900697.
- Wang H, Tamba M, Kimata M, et al. (2003). "Expression of the activity of cystine/glutamate exchange transporter, system x(c)(-), by xCT and rBAT". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 305 (3): 611–8. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(03)00808-8. PMID 12763038.
- O'Byrne J, Hunt MC, Rai DK, et al. (2003). "The human bile acid-CoA:amino acid N-acyltransferase functions in the conjugation of fatty acids to glycine". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (36): 34237–44. doi:10.1074/jbc.M300987200. PMID 12810727.
- Humphray SJ, Oliver K, Hunt AR, et al. (2004). "DNA sequence and analysis of human chromosome 9". Nature. 429 (6990): 369–74. Bibcode:2004Natur.429..369H. doi:10.1038/nature02465. PMC 2734081. PMID 15164053.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. Bibcode:2005Natur.437.1173R. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514. S2CID 4427026.
- Pellicoro A, van den Heuvel FA, Geuken M, et al. (2007). "Human and rat bile acid-CoA:amino acid N-acyltransferase are liver-specific peroxisomal enzymes: implications for intracellular bile salt transport". Hepatology. 45 (2): 340–8. doi:10.1002/hep.21528. PMID 17256745. S2CID 6163420.
- Tougou K, Fukuda T, Ito T, et al. (2007). "Genetic polymorphism of bile acid CoA: amino acid N-acyltransferase in Japanese individuals". Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 22 (2): 125–8. doi:10.2133/dmpk.22.125. PMID 17495420.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.