Battle of Cao Bằng (1949)
The Battle of Cao Bằng was an ongoing campaign in northern Indochina during the First Indochina War, between the French Far East Expeditionary Corps and the Việt Minh, which began in October 1947 and culminated on September 3, 1949. Since the start of the conflict, Việt Minh troops had ambushed French convoys along the Vietnam–China border from the Gulf of Tonkin on a 147-mile route to a French garrison at Cao Bằng, known as Route Colonial 4, or RC4. Repeated ambushes led to repeated French operations of increasing strength to reopen the road, including a costly mission by the Foreign Legion in February 1948. On July 25, 1948, the Cao Bằng encampment was itself attacked and held out for three days with two companies defending against two battalions of Việt Minh. A further 28 ambushes took place in 1948.[1]
| Battle of Cao Bằng | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the First Indochina War | |||||||
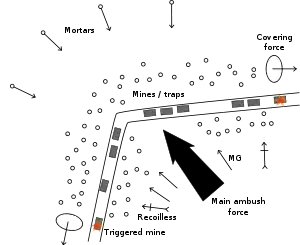 A model of a typical Việt Minh ambush, using information from Bernard Fall’s Street Without Joy, 1961 | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
| |||||||
In February 1949, five Việt Minh battalions and mortar units took a French post at Lào Cai, and resumed ambushes through the monsoon season. On September 3, 1949, 100 vehicles left That Khe in a reinforced convoy which travelled a distance of 16 miles (26 km) through infantry screens. The French, reduced to one soldier per vehicle due to troop numbers, were ambushed by automatic fire. The first twenty trucks were halted, as were the final ten, and the middle of the convoy was cut down by shellfire. The following day, French troops reoccupied the surrounded hilltops, however only four French wounded were found alive.[1]
The campaign at Cao Bằng resulted in a change in convoy practices for the remainder of the war. Vehicles thereafter travelled from post to post in 10-12 vehicle convoys, through security screens of French troops and with aircraft observation. Through 1950, supply convoys to Cao Bằng were discontinued in favour of air supply.[1][2]
References
- Windrow, pp. 103–107.
- 2006 Page 166 ".. se laissaient facilement piéger et essuyaient revers sur revers, en particulier celui de Cao Bằng en septembre 1950 qui eut un effet retentissant en France."
Bibliography
- Fall, Bernard B. (1966). Hell in a Very Small Place. The Siege of Dien Bien Phu. London: Da Capo Press. ISBN 978-0-306-81157-9.
- Fall, Bernard B. (1961). Street Without Joy. The French Debacle in Indochina. New York: Stackpole Military History. ISBN 978-0-8117-3236-9.
- Fall, Bernard B. (1967). The Two Vietnams. A Political and Military Analysis (Second ed.). New York: Frederick A. Praeger, Inc.
- Roy, Jules (1963). The Battle of Dien Bien Phu. New York: Carroll and Graf Publishers. ISBN 978-0-7867-0958-8.
- Windrow, Martin (2004). The Last Valley. Dien Bien Phu and the French Defeat in Vietnam. London: Weidenfeld and Nicolson. ISBN 978-0-304-36692-7.