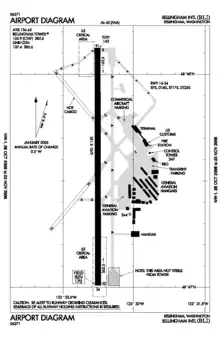
Bellingham International Airport
Bellingham International Airport (IATA: BLI, ICAO: KBLI, FAA LID: BLI) is three miles (5 km) northwest of Bellingham, in Whatcom County, Washington, United States. BLI covers 2,190 acres (886 ha) of land,[2][3] and is the third-largest commercial airport in Washington.
Bellingham International Airport (Bellingham/Tulip Army Airfield) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||
 | |||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||
| Airport type | Public | ||||||||||
| Operator | Port of Bellingham | ||||||||||
| Serves | Bellingham, Washington | ||||||||||
| Location | Whatcom County | ||||||||||
| Hub for | San Juan Airlines | ||||||||||
| Operating base for | Allegiant Air | ||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 170 ft / 52.1 m | ||||||||||
| Coordinates | 48°47′33″N 122°32′15″W | ||||||||||
| Website | www | ||||||||||
| Map | |||||||||||
 BLI Location of airport in Washington  BLI BLI (the United States) | |||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Statistics | |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
Bellingham is a low-fare alternative to Vancouver International Airport, and an estimated 65% of customers come from Canada.[4][5] It is only 54 miles (87 km) from downtown Vancouver, and only 23 miles (37 km) from the Peace Arch Border Crossing, where Greater Vancouver starts.
History
The Works Progress Administration (WPA) began studying a potential airport for Whatcom County in late 1935 as part of a program to build airports in large Washington cities.[6] A plan to build an airport west of Bellingham was endorsed by the Washington's state WPA office by the end of the year and the head office the following July.[7][8] On October 20, 1936, Whatcom County purchased 200 acres (0.81 km2) from Charles F. Larrabee to build an airport using WPA funds.[9]
Construction of the airport began on October 22 under the supervision of the WPA.[10] Three runways were planned, but only the first was built initially; it was 3,600 ft (1,100 m) long by 150 ft (46 m) wide, and it was completed and dedicated on June 1, 1940.[11] Temporary Port of Entry status was secured early, but the slow construction left it in a continually tenuous state – United Airlines would only base there if the field were safe enough for their DC-3s, and it maintained its Port of Entry status.
In 1940, the United States Army Corps of Engineers took over the project and expanded the airport to three full runways, revetments for parking aircraft, and development of personnel quarters on 350 acres (140 ha). The airport opened to the public on December 7, 1941, having employed hundreds of people during its construction. The initial runway, oriented in a northwest-to-southeast direction, was now 5,000 ft (1,500 m) long. The two new runways were another 5,000 ft long (1,500 m) runway oriented northwest-to-southeast, and a north–south runway that had an initial length of 4,400 ft (1,300 m) but would be extended another 600 ft (180 m) to cross Bakerview Road.[12] Following the Attack on Pearl Harbor the same day, Whatcom County offered the use of the airport to the U.S. military, who seized it on December 10.[13][14] During World War II the airport was used by Fourth Air Force for air defense of the Pacific Coast. It was later used by Air Transport Command and Air Technical Service Command as an intermediate ferrying field for Lend-Lease aircraft being flown to Alaska for subsequent transfer to the Soviet Union.
The United States Army Air Forces closed the facility in September 1946, and it was turned over to the War Assets Administration for disposal. A terminal, designed by F. Stanley Piper, was built by United Airlines in anticipation of civilian use.[14] The airport was slowly returned to Whatcom County and redeveloped as a civil airport in the late 1940s. With the rising costs and need for repairs, Whatcom county sold the Airport to the Port of Bellingham for one dollar in 1957. Because of costs, the Port of Bellingham could only resurface the longest of the runways (16/34).[14] Runway 16/34 is still the only runway used as it provides adequate year-round wind coverage for aircraft servicing Bellingham. The airport closed runway 12/30 in 1986, and runway 2/20 was shut down in 1997.[11] The two diagonal runways have fallen into disrepair, their easternmost ends used as taxiways between tarmacs and the sole remaining runway.
Airline service from Bellingham had a modest beginning. During the late 1970s and early 1980s, Harbor Airlines, a commuter air carrier based in Washington, operated nonstop shuttle service to Seattle–Tacoma International Airport with small Britten-Norman Islander twin prop aircraft.[15] By the mid-1980s, Harbor Air had been replaced by San Juan Airlines, a commuter air carrier based in Bellingham which operated shuttle flights to Seattle/Tacoma with Embraer EMB-110 Bandeirante turboprops and Cessna 402 prop aircraft.[16] San Juan Airlines continues to serve the airport at the present time.
In 1985, Pacific Southwest Airlines (PSA) initiated Bellingham's first passenger jet service with McDonnell Douglas MD-80s direct to Los Angeles, San Diego and San Francisco with all PSA flights including a stop at Seattle/Tacoma. PSA was acquired by USAir which continued to serve Bellingham with Boeing 737-300s. Alaska Airlines introduced MD-80 jets in the late 1980s, competing with USAir with both airlines operating nonstop jet service to Seattle/Tacoma and direct one stop service to other destinations. USAir then changed its name to US Airways and eventually merged with American Airlines in 2015; however, by the early 1990s, USAir had ceased serving Bellingham.[17] During the late 1980s, Alaska Airlines was joined by Horizon Air, a wholly owned subsidiary of the Alaska Air Group, with this regional airline flying nonstop service with turboprops to Seattle/Tacoma.[18] Aircraft operated by Horizon Air into the airport over the years included such propjets as the Fairchild Swearingen Metroliner, the de Havilland Canada DHC-8 Dash 8 and the Dornier 328. Horizon Air, which currently operates flights for Alaska Airlines, continues to serve Bellingham at the present time with nonstop service to Seattle/Tacoma flown with the Embraer E175.[19] Commencing in the late 1980s, United Express was serving the airport with nonstop flights to Seattle–Tacoma International Airport on behalf of United Airlines via code sharing agreements with the respective operating air carriers.[20] North Pacific Airlines operated the first United Express flights into Bellingham with British Aerospace BAe Jetstream 31 propjets and were followed by SkyWest Airlines flying as United Express with Embraer EMB-120 Brasilia turboprops. United Express no longer serves Bellingham.
In the 1990s homes were purchased to extend the runway in an effort to attract air carriers. The assumption was that there would not be a third runway at Sea-Tac airport. The airport has seen a high turnover rate.
In September 2010 the airport completed a $26 million resurfacing of the runway to allow aircraft up to the size of Boeing 757s. This project was completed to enable Allegiant Air to operate Boeing 757-200 service nonstop to Hawaii, although this service has since ended.[21] The largest aircraft currently serving Bellingham as of July 2019 are Allegiant Air's Airbus A320 aircraft flying to several destinations on the West Coast.
Terminal
Terminal upgrades were completed in two phases in the 1980s. The first phase was completed in 1980. The second phase, or the expansion phase, was constructed because of increased passenger volumes and the arrival of new air carriers. In 1985, a separate International Terminal was built to the south in order to accommodate the Federal Inspection Services necessary for international travelers to access the United States; it was connected to the main terminal through a covered walkway. The main terminal was approximately 26,000 square feet and included three levels: the basement, the ground floor, and the second floor. The basement housed a small storage facility; the ground floor was where the entire passenger processing area was held; and the second floor contained office space. There was one concession stand: Halibut Henry's store, where light snacks, coffee drinks, gifts, and sundries were offered. The International Terminal was a one-level building consisting of 4,222 square feet (392.2 m2). It served several functions, including the housing of the Federal Inspection Service, FIS offices, Allegiant Airline's mechanic offices, and Bellingham Aviation Service's ground support equipment maintenance.[22]
The airport underwent another $38.5-million terminal expansion in the early 2010s. After the first phase was completed in June 2011, the number of gates increased from 2 to 5, and the overall gate boarding area increased to 20,000 square feet (1,900 m2). With the completion of the second phase in February 2014, the size of the terminal increased from 27,000 to 104,000 sq ft (2,500 to 9,700 m2). In addition, the size of the ticketing lobby area was tripled so that the former 2-station area could now support 20 ticketing stations, the baggage claim area was increased to 8,400 sq ft (780 m2), and the 50 ft bag slide (15 m) was replaced with a 450 ft circumference (140 m) baggage carousel for arriving passengers.[23] The cost of the expansion to the terminal building was covered by surcharges from passengers and parking fees.
Commercial airline service expansion

The early 21st century saw rapid expansion at the Bellingham International Airport from several air carriers operating mainline jet aircraft with these airlines being motivated by the potential passenger loads from lower mainland British Columbia in Canada. Allegiant's commitment to the airport has led to a rapid rise in passenger numbers and the introduction of a number of nonstop destinations served from Bellingham. Other airlines initially recognized the potential of Bellingham International's location and further expanded service into the airport, but all commercial airlines except Alaska, Allegiant, and Southwest had departed as of 2023.
In early 2007 Bellingham International hosted nonstop service to three destinations by the short-lived Western Airlines which was operating Boeing 737-400 jets and was based in Bellingham. Western attempted to establish a small hub at the airport with nonstop service to Ontario, California (ONT), Phoenix, Arizona (via the Phoenix-Mesa Gateway Airport, AZA) and San Diego, California (SAN). Later the same year, Skybus Airlines operated nonstop flights to their Columbus, Ohio (CMH) hub with Airbus A319 jetliners but then shut down quickly like Western Airlines had done earlier. Between June 2006 and April 2008, Delta Air Lines also used to serve Bellingham with flights to Salt Lake City operated by their regional affiliate SkyWest Airlines.
On March 1, 2008, Allegiant Air opened up their sixth base at Bellingham International Airport. The airline currently bases a number of aircraft in Bellingham which serves as a "focus city" for the airline. In 2012 Allegiant announced service to two locations in the Hawaiian islands (Honolulu and Kahului) from Bellingham after receiving ETOPS certification from the FAA for their 757 aircraft. Alaska also entered the market with flights to Honolulu, Kahului and Kona. As of July 2019, both Allegiant and Alaska no longer serve Hawaii from Bellingham. Allegiant has also unsuccessfully tried serving other markets from Bellingham in recent years, such as Denver, Tucson, Reno, and Anchorage.
In September 2010 the airport completed a $26 million resurfacing of the runway to allow aircraft up to the size of Boeing 757s to utilize the airport.[24] This project was completed in order to serve Allegiant 757 service to Honolulu and Maui which began operations in November 2012.[21]
In response to the increased low fare competition offered by Allegiant in their home state, Alaska Airlines expanded service from Bellingham International during the 2010s; adding service to Portland, Las Vegas, Honolulu, Kahului, and Kona, all of which are now discontinued. In early 2012, Frontier Airlines announced the addition of a daily seasonal summer service from Bellingham to its main hub in Denver beginning May 2012. Frontier flew Airbus A319 and Embraer ERJ-190 jets from Bellingham but subsequently ceased serving the airport.
On November 7, 2021, Southwest Airlines began service at Bellingham International Airport. Initial service includes twice daily flights to Oakland, CA (OAK) and once daily service to Las Vegas, NV (LAS).[25]
The runway and taxiway resurfacing and improvement projects were funded with FAA Airport Improvement Program (AIP) grants covering 95% of project costs. In 2010 the FAA contribution towards airport projects was $27,267,000. The 5% local match came from BLI Passenger Facility Charge accounts. FAA AIP grants also have contributed to the acquisition of additional Airport Rescue Fire Fighting (ARFF) equipment, aircraft de-ice equipment and other surface projects. The BLI PFC fee per passenger is currently at the FAA mandated maximum of $4.50 per enplaned passenger. The terminal and ramp expansion projects are not AIP eligible as they are revenue generating facilities for the airport. The Port of Bellingham issued revenue bonds for $31,719,550 to pay for the terminal expansion. The debt service for the bonds also comes from BLI PFC accounts. In this way, the users of the airport facilities are the ones actually paying for the facility.
General aviation
Bellingham International Airport is also a busy general aviation (GA) facility, with numerous flights oriented towards sightseeing in the San Juan Islands, Victoria in British Columbia, or the Canadian Gulf Islands. The majority of GA operations are commercial in nature, including charters, flight training, transient flights, and private business operations, and the airport serves as a port of entry for international travelers. GA facilities occupy about 20 acres (8.1 ha) south of the passenger terminal, and include tie-down spaces, numerous hangars, and a dedicated GA terminal.[22]
Military units
The Washington Air National Guard (WANG) once occupied a 7.5-acre site at Bellingham International Airport. The Washington Air National Guard is home of the 262nd Combat Communications Squadron. The 262nd's mission is to train and equip combat communications personnel, where they field, install, operate, and maintain Ground Mobile Force communications.[26] In other words, the 262nd equips soldiers with their battlefield communication systems and trains them how to use and maintain the equipment. The WANG base consists of vehicle storage, a headquarters building, a maintenance building, and other miscellaneous storage buildings.
The WANG site has now been demolished for a hangar project by a local developer.[27]
Airlines and destinations
Passenger
San Juan Airlines merged with Northwest Sky Ferries in 2009. This merged airline offers scheduled and charter flights from Bellingham to the San Juan Islands in Washington, Seattle, Tacoma, Port Angeles, Olympia, and British Columbia. San Juan Airlines also serves Bellingham; offering scheduled and charter flights to the San Juan Islands and British Columbia.[22] Northwest Sky Ferry and San Juan airlines offer prop aircraft service with Cessna 206, 207 and 182 airplanes.[28]
| Destination map |
|---|
 Bellingham Destinations from Bellingham International Airport Red = Year-round destination Green = Seasonal destination Blue = Future destination |
Cargo
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| Ameriflight | Seattle–Boeing |
| FedEx Express | Seattle/Tacoma |
Statistics
Top destinations
| Rank | City | Passengers | Carriers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Las Vegas, Nevada | 104,551 | Allegiant, Southwest |
| 2 | Seattle/Tacoma, Washington | 85,889 | Alaska |
| 3 | Oakland, California | 73,261 | Allegiant, Southwest |
| 4 | Phoenix/Mesa, Arizona | 18,051 | Allegiant |
| 5 | Los Angeles, California | 16,170 | Allegiant |
| 6 | Palm Springs, California | 14,112 | Allegiant |
| 7 | San Diego, California | 4,659 | Allegiant |
References
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from the Air Force Historical Research Agency.
This article incorporates public domain material from the Air Force Historical Research Agency.
- "WSDOT - Aviation - All State Airports - Bellingham International - Bellingham". wsdot.wa.gov.
- FAA Airport Form 5010 for BLI PDF, effective September 8, 2022
- "BLI airport data at skyvector.com". Retrieved September 18, 2022.
- Nicas, Jack (June 8, 2012). "Canadians Crowd U.S. Airports. Why? Taxes". Wall Street Journal. ISSN 0099-9660. Archived from the original on March 25, 2015. Retrieved May 17, 2019.
- "From Buffalo to Bellingham, U.S. airports court Canadian fliers". usatoday.com. USA Today. Gannett Co., Inc. February 8, 2016.
- "Airport Studied". The Bellingham Herald. September 25, 1935. p. 1. Retrieved October 27, 2022 – via Newspapers.com.
- "Airport Advances". The Bellingham Herald. December 3, 1935. p. 5. Retrieved October 27, 2022 – via Newspapers.com.
- "WPA Engineer Gives Final Approval". The Bellingham Herald. July 25, 1936. p. 1. Retrieved October 27, 2022 – via Newspapers.com.
- "Port History: Bellingham International Airport". Port of Bellingham. Retrieved October 27, 2022.
- "Clearing Underway". The Bellingham Herald. October 22, 1936. p. 1. Retrieved October 27, 2022 – via Newspapers.com.
- Bellingham International Airport Master Plan Update. AECOM (Report). October 2019. pp. 2–2 to 2–3. Retrieved January 23, 2023.
- "Bellingham Airport, Now Nearing Completion, Open to Public Today". The Bellingham Herald. December 7, 1941. p. 1. Retrieved October 27, 2022 – via Newspapers.com.
- "Whatcom Airport Offered Army". The Bellingham Herald. December 8, 1941. p. 6. Retrieved October 27, 2022 – via Newspapers.com.
- "War & the Airport". Port of Bellingham. Retrieved October 27, 2022.
- http://www.departedflights.com, Nov. 15, 1979 & April 1, 1981 editions, Official Airline Guide (OAG), Seattle-Bellingham flight schedules
- http://www.departedflights.com, Feb. 15, 1985 Official Airline Guide (OAG), Seattle-Bellingham flight schedules
- http://www.departedflights.com, Oct. 1, 1991 Official Airline Guide (OAG), Seattle-Bellingham flight schedules
- http://www.departedflights.com, Dec. 15, 1989 Official Airline Guide (OAG), Bellingham flight schedules
- https://www.bellinghamherald.com/news/local/article271166797.html, Jan. 15, 2023, The Bellingham Herald
- http://www.departedflights.com, Dec. 15, 1989 & April 2, 1995 & June 1, 1999 editions, Official Airline Guide (OAG), Seattle-Bellingham flight schedules
- Dave Gallagher (September 8, 2014). "Allegiant drops flights between Hawaii and Bellingham". THE BELLINGHAM HERALD.
- JUB Engineers, Inc. (2004). Bellingham International Airport Master Plan Update.
- Nordstrom, Robert (March–April 2014). "Bellingham Int'l adds gates & triples terminal size to serve Canadian-fueled growth". Airport Improvement. pp. 12–16. Retrieved February 6, 2023.
- "Accommodating Larger Planes". portofbellingham.com. Port of Bellingham.
- https://www.bellinghamherald.com/news/business/article255628411.html
- Salaas, Maj. Kayhy. "Double Chain of Command; WANG". Archived from the original on July 9, 2010. Retrieved November 27, 2012.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on December 7, 2021. Retrieved December 7, 2021.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - Northwest Sky Ferry. "Flight Options". Archived from the original on October 12, 2016. Retrieved November 27, 2012.
- "RITA - BTS - Transtats". transtats.bts.gov. Retrieved March 9, 2023.
- "Bellingham, WA: Bellingham International (BLI)". Bureau of Transportation Statistics. Retrieved March 9, 2023.
External links
- Official website

- WSDOT Pilot's Guide: Bellingham International (PDF 69 kb)
- WSDOT Economic Impacts: Bellingham International
- FAA Airport Diagram (PDF), effective October 5, 2023
- FAA Terminal Procedures for BLI, effective October 5, 2023
- Resources for this airport:
- AirNav airport information for KBLI
- ASN accident history for BLI
- FlightAware airport information and live flight tracker
- NOAA/NWS weather observations: current, past three days
- SkyVector aeronautical chart for KBLI
- FAA current BLI delay information
.svg.png.webp)