Berkeleytrione
Berkeleytrione is a bio-active fungal isolate from the Berkeley Pit.[1]
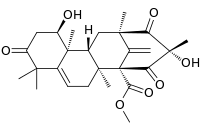 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methyl (1R,6aS,7R,9S,11R,12aR,12bS)-1,9,10-trihydroxy-4,4,6a,9,11,12b-hexamethyl-3,8-dioxo-1,3,4,6,6a,8,9,10,11,12,12a,12b-dodecahydro-7,11-methanocycloocta[a]naphthalene-7(2H)-carboxylate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C26H34O7 | |
| Molar mass | 458.551 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Stierle, DB; Stierle, AA; Hobbs, JD; Stokken, J; Clardy, J (2004). "Berkeleydione and berkeleytrione, new bioactive metabolites from an acid mine organism". Organic Letters. 6 (6): 1049–52. doi:10.1021/ol049852k. PMID 15012097.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.