Binary octahedral group
In mathematics, the binary octahedral group, name as 2O or ⟨2,3,4⟩[1] is a certain nonabelian group of order 48. It is an extension of the chiral octahedral group O or (2,3,4) of order 24 by a cyclic group of order 2, and is the preimage of the octahedral group under the 2:1 covering homomorphism of the special orthogonal group by the spin group. It follows that the binary octahedral group is a discrete subgroup of Spin(3) of order 48.
The binary octahedral group is most easily described concretely as a discrete subgroup of the unit quaternions, under the isomorphism where Sp(1) is the multiplicative group of unit quaternions. (For a description of this homomorphism see the article on quaternions and spatial rotations.)
Elements
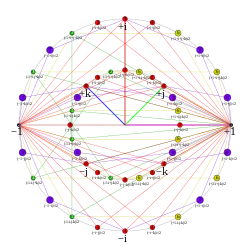
• 1 order-1: 1
• 1 order-2: -1
• 6 order-4: ±i, ±j, ±k
• 12 order-8: (±1±i)/√2, (±1±j)/√2, (±1±k)/√2
• 12 order-4: (±i±j)/√2, (±i±k)/√2, (±j±k)/√2
• 8 order-6, (+1±i±j±k)/2
• 8 order-3, (-1±i±j±k)/2.
Explicitly, the binary octahedral group is given as the union of the 24 Hurwitz units
with all 24 quaternions obtained from
by a permutation of coordinates and all possible sign combinations. All 48 elements have absolute value 1 and therefore lie in the unit quaternion group Sp(1).
Properties
The binary octahedral group, denoted by 2O, fits into the short exact sequence
This sequence does not split, meaning that 2O is not a semidirect product of {±1} by O. In fact, there is no subgroup of 2O isomorphic to O.
The center of 2O is the subgroup {±1}, so that the inner automorphism group is isomorphic to O. The full automorphism group is isomorphic to O × Z2.
Presentation
The group 2O has a presentation given by
or equivalently,
Quaternion generators with these relations are given by
with
Subgroups
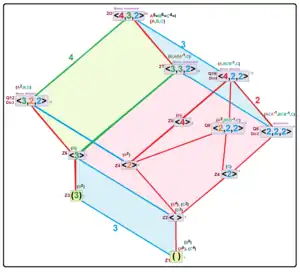
• 2T=⟨2,3,3⟩, index 2,
• Q16=⟨2,2,4⟩ index 3, and
• Q12=⟨2,2,3⟩ index 4.
• ⟨l,m,n⟩=binary polyhedral group
• ⟨p⟩≃Z2p, (p)≃Zp (cyclic groups)
The binary tetrahedral group, 2T, consisting of the 24 Hurwitz units, forms a normal subgroup of index 2. The quaternion group, Q8, consisting of the 8 Lipschitz units forms a normal subgroup of 2O of index 6. The quotient group is isomorphic to S3 (the symmetric group on 3 letters). These two groups, together with the center {±1}, are the only nontrivial normal subgroups of 2O.
The generalized quaternion group, Q16, also forms a subgroup of 2O, index 3. This subgroup is self-normalizing so its conjugacy class has 3 members. There are also isomorphic copies of the binary dihedral groups Q8 and Q12 in 2O.
All other subgroups are cyclic groups generated by the various elements (with orders 3, 4, 6, and 8).[2]
Higher dimensions
The binary octahedral group generalizes to higher dimensions: just as the octahedron generalizes to the orthoplex, the octahedral group in SO(3) generalizes to the hyperoctahedral group in SO(n), which has a binary cover under the map
See also
- Binary polyhedral group
- binary cyclic group, ⟨n⟩, index 2n
- binary dihedral group, ⟨2,2,n⟩, index 4n
- binary tetrahedral group, 2T=⟨2,3,3⟩, index 24
- binary icosahedral group, 2I=⟨2,3,5⟩, index 120
References
- Coxeter, H. S. M. & Moser, W. O. J. (1980). Generators and Relations for Discrete Groups, 4th edition. New York: Springer-Verlag. ISBN 0-387-09212-9.
- Conway, John H.; Smith, Derek A. (2003). On Quaternions and Octonions. Natick, Massachusetts: AK Peters, Ltd. ISBN 1-56881-134-9.
Notes
- Coxeter&Moser: Generators and Relations for discrete groups: <l,m,n>: Rl = Sm = Tn = RST
- Binary octahedral group = on GroupNames