Bioregionalism
Bioregionalism is a philosophy that suggests that political, cultural, and economic systems are more sustainable and just if they are organized around naturally defined areas called bioregions, similar to ecoregions. Bioregions are defined through physical and environmental features, including watershed boundaries and soil and terrain characteristics. Bioregionalism stresses that the determination of a bioregion is also a cultural phenomenon, and emphasizes local populations, knowledge, and solutions.[1]
Bioregionalism asserts "that a bioregion's environmental components (geography, climate, plant life, animal life, etc.) directly influence ways for human communities to act and interact with each other which are, in turn, optimal for those communities to thrive in their environment. As such, those ways to thrive in their totality—be they economic, cultural, spiritual, or political—will be distinctive in some capacity as being a product of their bioregional environment."[2]
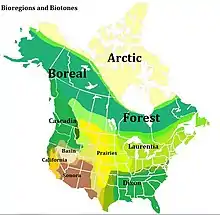
Bioregionalism is a concept that goes beyond national boundaries—an example is the concept of Cascadia, a region that is sometimes considered to consist of most of Oregon and Washington, the Alaska Panhandle, the far north of California and the West Coast of Canada, sometimes also including some or all of Idaho and western Montana.[3] Another example of a bioregion, which does not cross national boundaries, but does overlap state lines, is the Ozarks, a bioregion also referred to as the Ozarks Plateau, which consists of southern Missouri, northwest Arkansas, the northeast corner of Oklahoma, southeast corner of Kansas.[4]
Bioregions are not synonymous with ecoregions as defined by bodies such as the World Wildlife Fund or the Commission for Environmental Cooperation; the latter are scientifically based and focused on wildlife and vegetation. Bioregions, by contrast are human regions, informed by nature but with a social and political element. In this way bioregionalism is simply political localism with an ecological foundation.
Overview
The term was coined by Allen Van Newkirk, founder of the Institute for Bioregional Research, in 1975,[5] given currency by Peter Berg and Raymond F. Dasmann in the early 1970s,[6] and has been advocated by writers such as David Haenke[7] and Kirkpatrick Sale.[8]
The bioregionalist perspective opposes a homogeneous economy and consumer culture with its lack of stewardship towards the environment. This perspective seeks to:
- Ensure that political boundaries match ecological boundaries.[9]
- Highlight the unique ecology of the bioregion.
- Encourage consumption of local foods where possible.
- Encourage the use of local materials where possible.
- Encourage the cultivation of native plants of the region.
- Encourage sustainability in harmony with the bioregion.[10]
Bioregional mapping is a powerful tool to increase understanding, change the story and influence policy. A good bioregional map shows layers of geology, flora, fauna, and inhabitation over time. All the interdisciplinary content that is integrated in this kind of map makes it a great communication tool to illustrate an ecological approach. One of the best examples of a richly communicative bioregional map is David McClosky's new map of Cascadia.
Some thinkers disagree that deep ecology thinking leads to bioregionalism[11] or that bioregionalism is a practicable way of organising human society.[12]
Relationship to environmentalism
Bioregionalism, while akin to environmentalism in certain aspects, such as a desire to live in harmony with nature, differs in certain ways from classical, 20th century environmentalism.[13]
According to Peter Berg, bioregionalism is proactive, and is based on forming a harmony between human culture and the natural environment, rather than being protest-based like the original environmental movement. Also, while classical environmentalists saw human industry as the enemy of nature and nature as a victim needing to be saved; bioregionalists see humanity and its culture as a part of nature, focusing on building a positive, sustainable relationship with both the sociological and ecological environments, rather than a focus on preserving and segregating the wilderness from the world of humanity.[13]
In politics
North American Bioregional Assemblies have been meeting at bi-annual gatherings of bioregionalists throughout North America since 1984 and have given rise to national level Green Parties. The tenets of bioregionalism are often used by green movements, which oppose political organizations whose boundaries conform to existing electoral districts. This problem is perceived to result in elected representatives voting in accordance with their constituents, some of whom may live outside a defined bioregion, and may run counter to the well-being of the bioregion.
At the local level, several bioregions have congresses that meet regularly. For instance, the Ozark Plateau bioregion hosts a yearly Ozark Area Community Congress, better known as OACC, which has been meeting every year since 1980,[14] most often on the first weekend in October. The Kansas Area Watershed, "KAW" was founded in 1982 and has been meeting regularly since that time.[15] KAW holds a yearly meeting, usually in the spring.
The government of the Canadian province of Alberta created the "land-use framework regions" in 2007 roughly corresponding to each major river basin within the province. This is supported by local initiatives such as the Beaver Hills Initiative to preserve an ecoregion which encompasses Elk Island National Park and the surrounding area.[16]
See also
- Cascadia (independence movement) – Bioregion, proposed country in North America
- Distributism – Economic theory promoting local control
- Deep ecology – Ecological and environmental philosophy
- Global Scenario Group – International policy development body
- Ecological footprint – Individual's or a group's human demand on nature
- Élisée Reclus – French geographer, writer and anarchist
- Geo-fence – Virtual perimeter
- Grassroots democracy – Type that favors individual activism
- Green anarchism – Branch of anarchism focused on the environment
- List of ecoregions
- Localism (politics) – Political philosophy
- Permaculture – Approach to agriculture and land management
- Social ecology (Bookchin) – American social theorist (1921–2006)
References
- Alexander, Don (1996). "Bioregionalism: The Need For a Firmer Theoretical Foundation". Trumpeter v13.3. Archived from the original on November 5, 2018.
- M., Ryan (November 15, 2015). "Bioregionalism: Place Shapes Identity". Towards Cascadia. Retrieved March 5, 2017.
- "Cascadia: The New Frontier". Cascadia Prospectus. February 12, 2010. Archived from the original on March 12, 2012. Retrieved November 8, 2012.
- "About OACC Ozark Area Community Congress". OACC Ozark Area Community Congress. Retrieved December 30, 2011.
- McGinnis, Michael Vincent (1999). Bioregionalism. London and New York: Routledge. p. 22. ISBN 041515444-8.
- Berg, Peter; Dasmann, Raymond (1977). "Reinhabiting California". The Ecologist. 7 (10).
- Mongillo, John F.; Booth, Bibi (2001). Environmental Activists. ISBN 9780313308840 – via Google Books.
- Anderson, Walter Truett. There's no going back to nature, Mother Jones (September/October 1996)
- Davidson, S. (2007) "The Troubled Marriage of Deep Ecology and Bioregionalism," Environmental Values, vol. 16(3): 313-332
- Bastedo, Jamie. Shield Country: The Life and Times of the Oldest Piece of the Planet, Red Deer Press, 1994. ISBN 0-88995-191-8
- Davidson, Stewart (2007). "The Troubled Marriage of Deep Ecology and Bioregionalism". Environmental Values. White Horse Press. 16 (3): 313–332. doi:10.3197/096327107X228373. JSTOR 30302156.
- Brennan, Andrew, (1998) Bioregionalism- a Misplaced Project? Worldviews: Global Religions, Culture, and Ecology Volume 2: Issue 3
- "Peter Berg of Planet Drum". Sustainable-city.org. 1998-02-12. Retrieved 2012-11-08.
- "About OACC Ozark Area Community Congress". OACC Ozark Area Community Congress. Retrieved February 1, 2013.
- "Kansas Area Watershed Council History". March 8, 2009. Retrieved February 1, 2013.
- "Home | Beaver Hills Initiative". www.beaverhills.ca. Retrieved 2017-02-21.
Further reading
- Alexander, D. (1990). "Bioregionalism: Science or sensibility?" Environmental Ethics, 12(2), 161-173. DOI:10.5840/enviroethics199012217. Retrieved from: http://hdl.handle.net/10613/2725
- Mike Carr, Bioregionalism and Civil Society: Democratic Challenges to Corporate Globalism, UBC Press, 2004. ISBN 978-0774809443.
- Peter Berg, editor. Reinhabiting A Separate Country: A Bioregional Anthology of Northern California. San Francisco: Planet Drum, 1978. ISBN 0-937102-00-8.
- Peter Berg, Envisioning Sustainability, Subculture Books, 2009. ISBN 978-0-9799194-8-0.
- Michael McGinnis, editor. Bioregionalism, Routledge, 1998. ISBN 0-415-15445-6.
- Ryan Moothart. Towards Cascadia. Minneapolis, MN: Mill City Press. ISBN 978-1-63505-158-2.
- Kirkpatrick Sale, Dwellers in the Land: The Bioregional Vision. Random House, 1985. ISBN 0-8203-2205-9 (University of Georgia Press, 2000).
- Gary Snyder. A Place in Space: Ethics, Aesthetics, and Watersheds. Counterpoint, 1995. ISBN 1-887178-27-9
- Robert Thayer. LifePlace: Bioregional Thought and Practice, University of California Press, 2003. ISBN 0-520-23628-9
- Emanuele Guerrieri Ciaceri. Bioregionalismo. La visione locale di un mondo globale. Argo Edizioni, Italia 2006. ISBN 978-88-88659-19-0
- Doug Aberley, editor. Boundaries of Home: Mapping for Local Empowerment. New Society Publishers, 1998. ISBN 978-0-86571-272-0
External links
- Free Cascadia.org, the website belonging to Alexander Baretich, designer of the Cascadian flag, and advocate of Bioregionalism.
- Encyclopedia of Earth: Ecoregion
- North American Bioregional Congress
- Ozark Area Community Congress
- Planet Drum Foundation website.
- Putah-Cache Bioregion Project Archived 2006-07-12 at the Wayback Machine - interdisciplinary research and educational project at UC Davis
- Bioregionalism at Columbia Encyclopedia, 2020