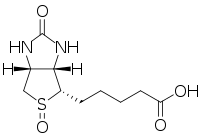
Biotin sulfoxide
Biotin sulfoxide is the substance that is formed when biotin is exposed to certain oxidants,[1] including ultraviolet light in the presence of oxygen.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
5-[(3aS,4S,6aR)-2,5-Dioxooctahydro-5λ4-thieno[3,4-d]imidazol-4-yl]pentanoic acid | |
| Other names
D-Biotin-d-sulfoxide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | D-Biotin-d-sulfoxide |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H16N2O4S | |
| Molar mass | 260.31 g·mol−1 |
| log P | -2.026 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 4.724 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 9.273 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Melville, Donald B. (1954). "Biotin Sulfoxide". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 208 (2): 495–501. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)65575-9. PMID 13174559.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.