Bis(fulvalene)diiron
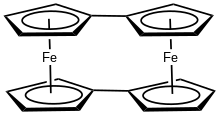
Bis(fulvalene)diiron is the organoiron complex with the formula (C5H4-C5H4)2Fe2. Structurally, the molecule consists of two ferrous centers sandwiched between fulvalene dianions. The compound is an orange solid with lower solubility in benzene than ferrocene. Its structure has been verified by X-ray crystallography.[1] The compound has attracted some interest for its redox properties.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Biferrocenylene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H16Fe2 | |
| Molar mass | 368.038 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | orange solid |
| Density | 1.76 g/cm3 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Preparation
It was first prepared by Ullmann coupling of 1,1'-diiodoferrocene using copper but subsequent work produces the complex is 20-40% yield from dilithiofulvalene and ferrous chloride:[3]
- 2 (C5H4Li)2 + 2 FeCl2 → (C5H4-C5H4)2Fe2 + 4 LiCl
Related compounds
References
- Churchill, Melvyn R.; Wormald, John (1969). "Crystal and molecular structure of bis(fulvalene)diiron". Inorganic Chemistry. 8 (9): 1970–1974. doi:10.1021/ic50079a030.
- Brüggeller, Peter; Jaitner, Peter; Schottenberger, Herwig (1991). "Kristallographische Gegenüberstellung der Monokationen von Bis(fulvalen)dieisien und Bis(fulvalen) Eisen-Cobalt mit Identischem Gegenion (PF6−)". Journal of Organometallic Chemistry. 417 (3): C53–C58. doi:10.1016/0022-328X(91)80206-Y.
- Levanda, Carole; Bechgaard, Klaus; Cowan, Dwaine O.; Mueller-Westerhoff, Ulrich T.; Eilbracht, Peter; Candela, George A.; Collins, R. L. (1976). "Bis(fulvalene)diiron, Its Mono- and Dications. Intramolecular Exchange Interactions in a Rigid System". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 98 (11): 3181–3187. doi:10.1021/ja00427a021.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.