Bisbenzimide
Bisbenzimide (Hoechst 33342) is an organic compound used as a fluorescent stain for DNA in molecular biology applications.[1] Several related chemical compounds are used for similar purposes and are collectively called Hoechst stains.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
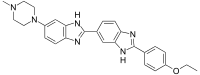
| Preferred IUPAC name
2′-(4-Ethoxyphenyl)-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-1H,3′H-2,5′-bi-1,3-benzimidazole | |
| Other names
Hoechst 33342; Hoe 33342 | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.041.523 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C27H28N6O | |
| Molar mass | 452.562 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Application
Bisbenzimide tends to bind to adenine–thymine-rich regions of DNA and can decrease its density. Bisbenzimide mixed with DNA samples can then be used to separate DNA according to their AT percentage using a cesium chloride (CsCl) gradient centrifugation.
Nuclei of Platynereis dumerilii larvae stained with Hoechst 33342
References
External links
- Fluorescence Spectra: http://www.fluorophores.tugraz.at/substance/463
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.