Black Mountains (Rhön)
The Black Mountains (German: Schwarze Berge) are part of the High Rhön in Germany, in particular of the Southern High Rhön, which lies south of the Kreuzberg Group and is thus the southernmost part of the High Rhön. Since 1993, most of the region has been protected by the Black Mountain Nature Reserve (Naturschutzgebiet Schwarze Berge), the second largest in Bavaria outside of the Alps, in order to counteract its afforestation by coniferous forest.[1]
| Black Mountains (Schwarze Berge) | |
|---|---|
 View of the Totnasberg from the Kissinger Hut | |
| Highest point | |
| Peak | Totnansberg |
| Elevation | 839 m (2,753 ft) |
| Geography | |
| State | Counties of Bad Kissingen and Rhön-Grabfeld, Bavaria |
| Range coordinates | 50°19′15″N 9°55′47″E |
| Parent range | Southern High Rhön, High Rhön, Rhön |
Natural region grouping
The name Schwarze Berge was defined as a natural region in 1968 as part of the natural regional classification of Germany in the 1960s at a scale of 1:200,000 (Sheet 140 Schweinfurt) and grouped as follows:[2]
- (part of 35 East Hesse Highlands)
- (part of 354 High Rhön)
- (part of 354.0 Southern High Rhön)
- 354.01 Black Mountains (Schwarze Berge)
- (part of 354.0 Southern High Rhön)
- (part of 354 High Rhön)
Boundaries
In the north is the municipality of Wildflecken. From there the natural region's boundary with the Kreuzberg Group runs east-southeast along the valley between the Feuerberg and Kreuzberg in order finally to follow the Kellersbach after the Guckas Pass. North of Langenleiten the boundary runs southwards in order to leave the valleys of the tributaries of the Kleiner Steinach. Continuing westwards, the boundary of the natural region runs through the villages of Platz and Geroda.
Between the Kellersbach and Geroda the Black Mountains border on the Adelsberg Forest, part of the Schondra-Thulba-South Rhön, which in turn is part of the Hammelburg South Rhön. The latter is part of the South Rhön which in turn belongs to the major natural region unit of Odenwald, Spessart and South Rhön, which is part of the South German Scarplands and not the Central Uplands.
The natural regional boundary with the Brückenau Kuppenrhön, which is part of the Kuppenrhön, follow the Milzbach as it flows north past Schildeck. After its confluence with the Sinn the boundary follows the river downstream heading northwards. North of Oberbach the region is bounded by the Dammersfeld Ridge to the west as far as Wildflecken.[2]
Geology
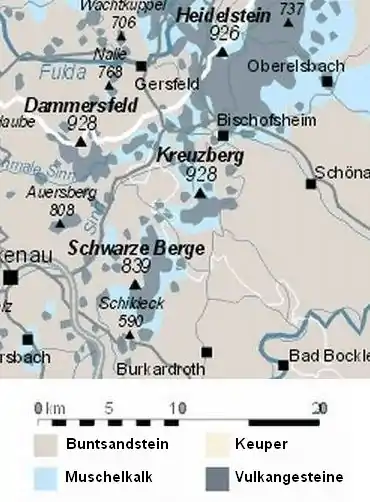
As well as the Black Mountains, the Southern High Rhön also includes the Kreuzberg Group and the Dammersfeld Ridge. All three mountain ridges consist of a basalt shield, which is occasionally intruded, and thus are different from Long Rhön and, to a lesser extent, the Wasserkuppenrhön, even if they clearly differ from the individual summits of the Kuppenrhön (see adjacent map).
In terms of its rock composition, the region compares to the Kreuzberg Group. The Black Mountains consist of two mountain ridges, which are formed of individual domed summits or kuppen. The basement is formed of red clays and marls overlaid by rocks of the Lower Muschelkalk. The summits are mostly composed of basalt. In most places the rock s covered by a layer of loam soil.[2]
Mountains
- Totnansberg (839 m; central location; with youth campsite; was named in 1968)
- Schwarzenberg (832 m; north of the Totnansberg; with its spur, the Feuerberg, Kissinger Hut and Feuerberglifte ski area)
- Erlenberg (826 m; south of the Totnansberg)
- Farnsberg (786 m; west of the Totnansberg; Würzburger Haus, Farnsberg recreation area and ski lifts on the Farnsberg)
- Löserhag (765 m; in the north; geotope)
- Platzer Kuppe (737 m; in the south)
- Schindküppel (659 m; in the west)
- Knörzchen (643 m; in the southwest)
Natural region
The natural region is drained to the east by the Thulba and Aschach into the Franconian Saale. No noteworthy streams flow into the Sinn. In 1968, at the time of the publication of Sheet 140 "Schweinfurt", the annual precipitation was 1000–1100 mm, on 90–110 days of the year there was a continuous layer of snow. In addition, extensive pastures characterised the area and there were deciduous woods on the mountainsides.[2] Since then, over half the area has become colonised by coniferous forest.[1]
References
- Information about nature conservation, retrieved 12 October 2013
- Brigitte Schwenzer: Geographische Landesaufnahme: The Natural Region Units on Sheet 140, Schweinfurt - Bundesanstalt für Landeskunde, Bad Godesberg, 1968 → online map (pdf, 4 MB)