Blera umbratilis
Blera umbratilis, the Hairy Wood Fly, is an uncommon species of syrphid fly first officially described by Williston in 1887.[2] Hoverflies get their names from the ability to remain nearly motionless while in flight. The adults are also known as flower flies for they are commonly found around and on flowers, from which they get both energy-giving nectar and protein-rich pollen. The larvae are of the rat-tailed type, feeding on exuding sap or in the rot holes of trees.
| Blera umbratilis | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Diptera |
| Family: | Syrphidae |
| Subfamily: | Eristalinae |
| Tribe: | Milesiini |
| Genus: | Blera |
| Species: | B. umbratilis |
| Binomial name | |
| Blera umbratilis | |
| Synonyms | |
Distribution
This is a Nearctic species of the eastern and central areas of the United States. External map
Description
For terms see Morphology of Diptera. External images
- Size
- 10mm.
- Head
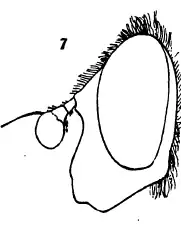
The front is broader above than in the preceding species, mostly shining, with rather long yellowish pile; The face is black, thickly dusted with white on the sides, and with a bare black median stripe vitta and the cheeks shining. The face is considerably excavated below, produced downward and somewhat forwards. The antennae reddish-brown, and the flagellum is orbicular. The frontal prominence is relatively small, The occiput is black, with yellowish pile and gray pollen.
- Thorax
The dorsum of the thorax, scutum and Blera postpronotum are, shining black, with rather abundant, obscurely yellow pile. The pile is black across the middle. The scutellum and pleura are black with yellow pile.
- Abdomen
The abdomen is short, oval; black, shining, with short black pile. The sides of the second segment are broadly orange yellow. The third segment is less broadly orange-yellow and the fourth segment is narrowly orange-yellow. The black ground color is, however, almost wholly obscured by thick woolly orange yellow pile, extending less broadly on the sides of the third segment, and narrowly on the margin of the fourth. The pile of the second segment in the middle is short yellow.
- Wing
The wings are somewhat brownish, a little lighter at the base. There is a darker cloud near the fork of the second (R2+3 ) and third veins (R4+5 ). The vein R4+5 is almost straight and joins the costa just before the tip of the wing. The first posterior cell R4+5 is acute apically and extends almost to the wing margin before the tip.
- Legs
The legs are black, with yellowish white pile. The base of middle femora and basal two-thirds of hind femora are yellow. The basal end of front and middle tibiae and all the tarsi, except the last two joints and hind metatarsi are yellow. [3] [4]
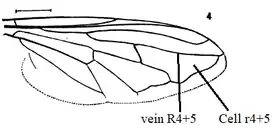 Blera wing veins
Blera wing veins Insect leg
Insect leg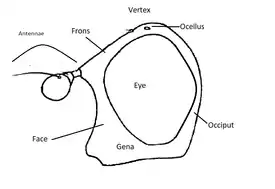 profile syrphid head
profile syrphid head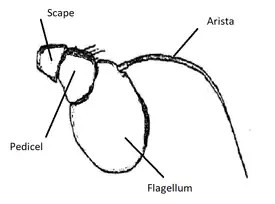 Antenna syrphid
Antenna syrphid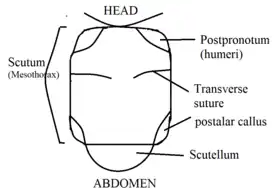 dorsal view of Syrphid thorax
dorsal view of Syrphid thorax Blera umbratilis
Blera umbratilis
References
- Williston, S. W. (1887). "Synopsis of the North American Syrphidae". Bulletin of the United States National Museum. 31: xxx + 335. Retrieved 1 July 2015.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - Skevington, Jeffrey H (2019). Field Guide to the Flower Flies of Northeastern North America. ISBN 9780691189406.
- Curran, Charles Howard (1925). ""Contribution to a monograph of the American Syrphidae north of Mexico"". The Kansas University Science Bulletin. 15: 7–216.
- Williston, Samuel Wendell (1882). "Contribution to a monograph of the North American Syrphidae". Proc. Amer. Philos. Soc. 20 (112): 299–332. Retrieved 23 July 2021.