Boötes Void
The Boötes Void (/boʊˈoʊtiːz/ boh-OH-teez) (colloquially referred to as the Great Nothing)[1] is an approximately spherical region of space found in the vicinity of the constellation Boötes, containing very few galaxies, hence its name. With a radius of 62 megaparsecs (nearly 330 million light-years), it is one of the largest voids in the universe, and is refered to as a supervoid.[2]
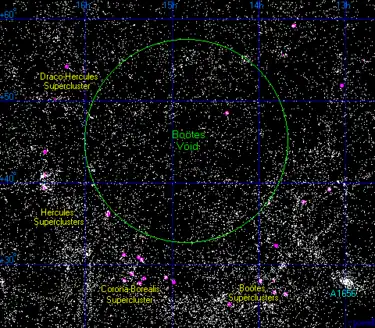
It was discovered in 1981 by Robert Kirshner as part of a survey of galactic redshifts.[3] Its centre is located 700 million light-years from Earth[2], and at approximately right ascension 14h 50m and declination 46°.
The Hercules Supercluster forms part of the near edge of the void.[3]
Origins
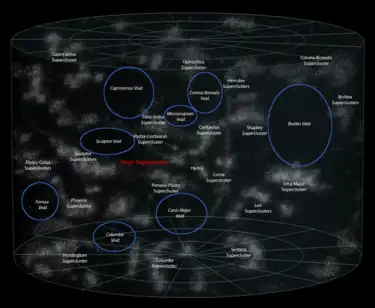
There are no major apparent inconsistencies between the existence of the Boötes Void and the Lambda-CDM model of cosmological evolution.[4] It has been theorized that the Boötes Void was formed from the merging of smaller voids, much like the way in which soap bubbles coalesce to form larger bubbles.[5] This would account for the small number of galaxies that populate a roughly tube-shaped region running through the middle of the void.[6]
Confusion with Barnard 68
The Boötes Void has been often associated with images of Barnard 68, a dark nebula that does not allow light to pass through; however, the images of Barnard 68 are much darker than those observed of the Boötes Void, as the nebula is much closer and there are fewer stars in front of it, as well as its being a physical mass that blocks light passing through.
Footnotes
- Cowen, Ron (2000). "Big, Bigger... Biggest?". Science News. 158 (7): 104–105. doi:10.2307/3981218. JSTOR 3981218.
- "The Boötes void: Why the Universe has a mysterious hole 330 million light-years across". www.sciencefocus.com. Retrieved 26 October 2023.
- Kirshner, Robert P.; Oemler Jr., Augustus; Schechter, Paul L.; Shectman, Stephen A. (1 March 1987). "A survey of the Bootes void". Astrophysical Journal, Part 1. 314: 493–506. Bibcode:1987ApJ...314..493K. doi:10.1086/165080. ISSN 0004-637X. S2CID 118385803.
- "Cosmic_Voids" Retrieved on 10 June 2013
- McCracken, Jason (13 July 2013). "Next Stop: Voids". National Aeronautics and Space Administration. Archived from the original on 4 December 2021. Retrieved 18 December 2021.
- "Filling the void – understanding the formation of the Bootes void in intergalactic space – Brief Article". Discover magazine. August 1995. Archived from the original on 19 November 2007. Retrieved 2 January 2008.
References
- Kirshner, R. P.; Oemler, A. J.; Schechter, P. L.; Shectman, S. A. (1981). "A million cubic megaparsec void in Bootes". The Astrophysical Journal. 248: L57–60. Bibcode:1981ApJ...248L..57K. doi:10.1086/183623.
- Kirshner, R. P.; Oemler, A. J.; Schechter, P. L.; Shectman, S. A. (1987). "A survey of the Bootes void". The Astrophysical Journal. 314: 493. Bibcode:1987ApJ...314..493K. doi:10.1086/165080. S2CID 118385803.