Bolshoy Yeravna
Bolshoy Yeravna (Russian: Большо́е Ера́вное озеро; Russian Buryat: Ехэ Ярууна) is a fresh water body in the Yeravninsky District, Buryatia, Russia.[2]
| Bolshoy Yeravna | |
|---|---|
| Большо́е Ера́вное озеро / Ехэ Ярууна | |
 Landscape of Bolshoy Yeravna lake | |
 Bolshoy Yeravna Location in Buryatia, Russian Far East | |
| Location | Vitim Plateau South Siberian System |
| Coordinates | 52°37′00″N 111°29′00″E[1] |
| Primary inflows | Tuldun , Indola , Zhipkesen |
| Catchment area | 972 km2 (375 sq mi) |
| Basin countries | Buryatia, Russia |
| Max. length | 14 km (8.7 mi) |
| Max. width | 13 km (8.1 mi) |
| Surface area | 104 km2 (40 sq mi) |
| Max. depth | 5 m (16 ft) |
| Surface elevation | 949 m (3,114 ft) |
| Frozen | October to May |
| Settlements | Garam |
Common roach, perch, crucian carp, pike, burbot, minnow, are among the native fish species in the lake. Peled, bream and carp have been introduced.[3] Legend says that the origin of the lake and the adjacent ones is in a big hot rock that fell to the earth and broke into big and small pieces that made holes which filled with water.[4]
Geography
The lake is part of the Yeravna-Khorga Lake System (Russian: Еравно-Хоргинской системы озёр), which includes 6 large lakes and a number of smaller ones. Bolshoy Yeravna (Big Yeravna) is the largest of the group.[3]
The 972 square kilometres (375 sq mi) catchment area of the lake is located in a forest steppe zone. The lakeshore is low and gentle, with grassland and bushes. Bolshoy Yeravna has a roughly round shape and is fed by three small rivers, the Tuldun, Indola and Zhipkesen. In the southwestern side it has an outlet, a small sound connecting with neighboring Lake Sosnovo. To the east lies Maly Yeravna lake.[1] When the water levels are high the Yeravna lakes are connected with each other by intermittent channels. The outlet of the lake area is via the Khorga lakes to the northeast through the Kholoy, a small, shallow tributary of the Vitim River flowing from Isinga lake at the northeastern end.[3]
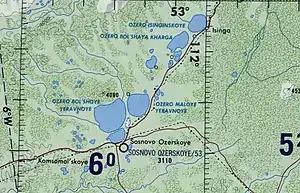 Yeravna-Khorga Lake System |
Flora
There is an abundance of aquatic plants growing in the lake. The semi-aquatic species include sedges, Glyceria and Scolochloa, among others. The floating plants include duckweed, Wolffia, Nuphar and Nymphaea. There is also a dense growth of submerged benthic macrophytes, such as Potamogeton, Myriophyllum, Ceratophyllum, as well as algae (Chara) and water moss. The introduced aquatic plant Elodea canadensis has become an invasive species.[3]
See also
- List of lakes of Russia
- Ivan-Arakhley Lake System, a similar lake formation located about 100 kilometres (62 mi) to the southeast, in Zabaykalsky Krai.
References
External links
 Media related to Yeravna Lakes at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Yeravna Lakes at Wikimedia Commons- Рыбалка на озеро большое Еравное 2013 - Fishing in Bolshoy Yeravna (in Russian)
- Geography of tourism in the Republic of Buryatia