Full-text search
In text retrieval, full-text search refers to techniques for searching a single computer-stored document or a collection in a full-text database. Full-text search is distinguished from searches based on metadata or on parts of the original texts represented in databases (such as titles, abstracts, selected sections, or bibliographical references).
In a full-text search, a search engine examines all of the words in every stored document as it tries to match search criteria (for example, text specified by a user). Full-text-searching techniques appeared in the 1960s, for example IBM STAIRS from 1969, and became common in online bibliographic databases in the 1990s. Many websites and application programs (such as word processing software) provide full-text-search capabilities. Some web search engines, such as the former AltaVista, employ full-text-search techniques, while others index only a portion of the web pages examined by their indexing systems.[1]
Indexing
When dealing with a small number of documents, it is possible for the full-text-search engine to directly scan the contents of the documents with each query, a strategy called "serial scanning". This is what some tools, such as grep, do when searching.
However, when the number of documents to search is potentially large, or the quantity of search queries to perform is substantial, the problem of full-text search is often divided into two tasks: indexing and searching. The indexing stage will scan the text of all the documents and build a list of search terms (often called an index, but more correctly named a concordance). In the search stage, when performing a specific query, only the index is referenced, rather than the text of the original documents.[2]
The indexer will make an entry in the index for each term or word found in a document, and possibly note its relative position within the document. Usually the indexer will ignore stop words (such as "the" and "and") that are both common and insufficiently meaningful to be useful in searching. Some indexers also employ language-specific stemming on the words being indexed. For example, the words "drives", "drove", and "driven" will be recorded in the index under the single concept word "drive".
The precision vs. recall tradeoff
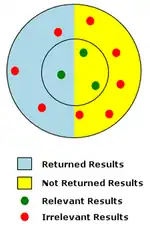
Recall measures the quantity of relevant results returned by a search, while precision is the measure of the quality of the results returned. Recall is the ratio of relevant results returned to all relevant results. Precision is the ratio of the number of relevant results returned to the total number of results returned.
The diagram at right represents a low-precision, low-recall search. In the diagram the red and green dots represent the total population of potential search results for a given search. Red dots represent irrelevant results, and green dots represent relevant results. Relevancy is indicated by the proximity of search results to the center of the inner circle. Of all possible results shown, those that were actually returned by the search are shown on a light-blue background. In the example only 1 relevant result of 3 possible relevant results was returned, so the recall is a very low ratio of 1/3, or 33%. The precision for the example is a very low 1/4, or 25%, since only 1 of the 4 results returned was relevant.[3]
Due to the ambiguities of natural language, full-text-search systems typically includes options like stop words to increase precision and stemming to increase recall. Controlled-vocabulary searching also helps alleviate low-precision issues by tagging documents in such a way that ambiguities are eliminated. The trade-off between precision and recall is simple: an increase in precision can lower overall recall, while an increase in recall lowers precision.[4]
False-positive problem
Full-text searching is likely to retrieve many documents that are not relevant to the intended search question. Such documents are called false positives (see Type I error). The retrieval of irrelevant documents is often caused by the inherent ambiguity of natural language. In the sample diagram to the right, false positives are represented by the irrelevant results (red dots) that were returned by the search (on a light-blue background).
Clustering techniques based on Bayesian algorithms can help reduce false positives. For a search term of "bank", clustering can be used to categorize the document/data universe into "financial institution", "place to sit", "place to store" etc. Depending on the occurrences of words relevant to the categories, search terms or a search result can be placed in one or more of the categories. This technique is being extensively deployed in the e-discovery domain.
Performance improvements
The deficiencies of full text searching have been addressed in two ways: By providing users with tools that enable them to express their search questions more precisely, and by developing new search algorithms that improve retrieval precision.
Improved querying tools
- Keywords. Document creators (or trained indexers) are asked to supply a list of words that describe the subject of the text, including synonyms of words that describe this subject. Keywords improve recall, particularly if the keyword list includes a search word that is not in the document text.
- Field-restricted search. Some search engines enable users to limit full text searches to a particular field within a stored data record, such as "Title" or "Author."
- Boolean queries. Searches that use Boolean operators (for example, "encyclopedia" AND "online" NOT "Encarta") can dramatically increase the precision of a full text search. The AND operator says, in effect, "Do not retrieve any document unless it contains both of these terms." The NOT operator says, in effect, "Do not retrieve any document that contains this word." If the retrieval list retrieves too few documents, the OR operator can be used to increase recall; consider, for example, "encyclopedia" AND "online" OR "Internet" NOT "Encarta". This search will retrieve documents about online encyclopedias that use the term "Internet" instead of "online." This increase in precision is very commonly counter-productive since it usually comes with a dramatic loss of recall.[5]
- Phrase search. A phrase search matches only those documents that contain a specified phrase, such as "Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia."
- Concept search. A search that is based on multi-word concepts, for example Compound term processing. This type of search is becoming popular in many e-discovery solutions.
- Concordance search. A concordance search produces an alphabetical list of all principal words that occur in a text with their immediate context.
- Proximity search. A phrase search matches only those documents that contain two or more words that are separated by a specified number of words; a search for "Wikipedia" WITHIN2 "free" would retrieve only those documents in which the words "Wikipedia" and "free" occur within two words of each other.
- Regular expression. A regular expression employs a complex but powerful querying syntax that can be used to specify retrieval conditions with precision.
- Fuzzy search will search for document that match the given terms and some variation around them (using for instance edit distance to threshold the multiple variation)
- Wildcard search. A search that substitutes one or more characters in a search query for a wildcard character such as an asterisk. For example, using the asterisk in a search query "s*n" will find "sin", "son", "sun", etc. in a text.
Improved search algorithms
The PageRank algorithm developed by Google gives more prominence to documents to which other Web pages have linked.[6] See Search engine for additional examples.
Software
The following is a partial list of available software products whose predominant purpose is to perform full-text indexing and searching. Some of these are accompanied with detailed descriptions of their theory of operation or internal algorithms, which can provide additional insight into how full-text search may be accomplished.
Free and open source software
Proprietary software
- Algolia
- Autonomy Corporation
- Azure Search
- Bar Ilan Responsa Project
- Basis database
- Brainware
- BRS/Search
- Concept Searching Limited
- Dieselpoint
- dtSearch
- Elasticsearch
- Endeca
- Exalead
- Fast Search & Transfer
- Inktomi
- Lucid Imagination
- MarkLogic
- SAP HANA[7]
- Swiftype
- Thunderstone Software LLC.
- Vespa
- Vivísimo
References
- In practice, it may be difficult to determine how a given search engine works. The search algorithms actually employed by web-search services are seldom fully disclosed out of fear that web entrepreneurs will use search engine optimization techniques to improve their prominence in retrieval lists.
- "Capabilities of Full Text Search System". Archived from the original on December 23, 2010.
- Coles, Michael (2008). Pro Full-Text Search in SQL Server 2008 (Version 1 ed.). Apress Publishing Company. ISBN 978-1-4302-1594-3.
- B., Yuwono; Lee, D. L. (1996). Search and ranking algorithms for locating resources on the World Wide Web. 12th International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE'96). p. 164.
- Studies have repeatedly shown that most users do not understand the negative impacts of boolean queries.
- US 6285999, Page, Lawrence, "Method for node ranking in a linked database", published 1998-01-09, issued 2001-09-04. "A method assigns importance ranks to nodes in a linked database, such as any database of documents containing citations, the world wide web or any other hypermedia database. The rank assigned to a document is calculated from the ranks of documents citing it. In addition, the rank of a document is..."
- "SAP Adds HANA-Based Software Packages to IoT Portfolio | MarTech Advisor". www.martechadvisor.com.
See also
- Pattern matching and string matching
- Compound term processing
- Enterprise search
- Information extraction
- Information retrieval
- Faceted search
- WebCrawler, first FTS engine
- Search engine indexing - how search engines generate indices to support full-text searching